AI Chatbots In Healthcare: Examples, Use Cases, Best Practices

Chatbots, or conversational agents, have emerged as significant tools in health care in the early 1960s, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence and digital technology.
From ELIZA’s therapeutic breakthrough to Watson’s knowledge powerhouse capabilities, AI chatbots in healthcare have evolved from simple conversational programs to sophisticated digital physicians capable of reducing wait times by 50% and increasing healthcare accessibility by 38%.
Whether you’re a healthcare administrator or AI developer, check our guide to find out:
- How healthcare AI assistants like Ada Health, Suki, Buoy Health, Wysa, and “Amina” by Black Doctor 24/7 help to achieve up to $201M funding success, 72% documentation time and 35% depression reduction.
- Common use cases of AI chatbots in healthcare that help reduce scheduling time by 65%, drop administrative workload by 50%, and improve patient satisfaction by 75%.
- Top risks and limitations of AI agents like false medical content generation, inadvertent information disclosure, and cybersecurity exposure and how expert AI chatbot development companies like Riseapps can mitigate them.
What is the History of AI Chatbots in Healthcare?
Healthcare chatbots didn’t emerge overnight. Their story begins in 1950 when British mathematician Alan Turing asked a revolutionary question: “Can machines think?” This simple inquiry would eventually transform how patients communicate with healthcare systems worldwide. And during the 1960s pioneering years, computers first became healers.
ELIZA: The Therapeutic Breakthrough (1964)
At MIT, researcher Joseph Weizenbaum created something unprecedented. It was a computer program that could hold conversations like a therapist. Named ELIZA, this chatbot could detect emotional cues in text and respond with appropriate questions. When patients typed “I feel sad,” ELIZA might respond, “Tell me more about feeling sad.”
INTERNIST-1: The Digital Diagnostician (1971)
Seven years later, the first AI medical consultant was born. INTERNIST-1 could analyze patient symptoms and suggest possible diagnoses. Imagine describing your headache, fever, and stiff neck to a computer, and having it correctly identify potential meningitis..
MYCIN: The Prescription Assistant (1970s)
MYCIN took AI further by helping doctors choose the right antibiotics for infections. It asked logical questions: What’s the patient’s age? What symptoms do they have? What bacteria might be causing the infection? Then it recommended specific medications and dosages.
In the 2000s AI chatbots in healthcare got even smarter.
Watson: The Knowledge Powerhouse
IBM’s Watson changed everything. Unlike earlier systems that followed rigid rules, Watson could understand natural language and process massive amounts of medical literature instantly. It could read thousands of medical journals in seconds and apply that knowledge to patient cases.
Today’s chatbots like Pharmbot AI can explain complex medication instructions in simple terms, remind patients about dosages, and answer questions like “What happens if I miss a dose?” These chatbots have become digital health assistants available 24/7.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, healthcare chatbots became frontline workers. They screened millions of patients, provided symptom checking, and reduced the burden on overwhelmed healthcare systems. One chatbot could handle the initial screening that would have required dozens of human staff members.
Why Do AI Chatbots Matter Today?
AI-powered chatbots in healthcare solve three major problems:
- Time barriers: they never sleep, never take breaks, and respond instantly to urgent health questions. In addition, implementation of AI-powered platforms like chatbots may result in a significant 50% reduction in wait times and no-show rates.
- Location barriers: rural patients can access expert medical knowledge without traveling hundreds of miles. With an AI-powered app, Black Doctor 24/7, 30,000+ African American men have been screened for diabetes and hypertension across 800 black-owned barbershops in more than 50 cities.
- Language barriers: advanced chatbots can communicate in multiple languages and adjust their explanations based on the patient’s health literacy level. It can lead to increased accessibility of health care by 38%.
How Do AI-Powered Chatbots in Healthcare Actually Work?
Healthcare AI chatbots function as digital physicians, combining multiple technologies to deliver intelligent medical assistance through specialized components that work in harmony. They include:
- Conversational interface: multi-modal patient interaction through text, voice, video, or gesture recognition. Advanced systems detect emotional cues through voice tone analysis and typing patterns.
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU): interprets medical terminology, slang, and emotional context. Distinguishes between “I feel terrible” as physical pain versus mental distress, and adapts to regional healthcare language variations.
- Clinical decision engine: contains medical ontologies, treatment protocols, drug interaction databases, risk assessment algorithms, and triage decision trees for accurate healthcare guidance.
- Integration hub: seamlessly connects to EHRs, laboratory systems, medical imaging (PACS), pharmacy networks, insurance platforms, telehealth services, and IoT medical devices.
- Predictive analytics enables forecasting health risks, medication non-adherence, and potential emergencies before they occur.
- Contextual memory enables learning individual patient preferences, communication styles, and health patterns while maintaining conversation history.
- Emotional intelligence allows recognizing distress signals, adapts communication tone, and identifies crisis situations requiring immediate intervention.
On top of that, healthcare chatbots must comply with strict regulations like HIPAA through:
- End-to-end data encryption
- Multi-level access controls
- Regular security audits
- Secure data storage protocols.
12 Most Common Use Cases of AI-Powered Healthcare Chatbots
AI-powered healthcare chatbots improve medical practice through two distinct application categories. Patient-facing chatbots handle 8 core functions including symptom triage, appointment scheduling, and medication management. Provider-focused systems automate 4 essential clinical workflows from insurance processing to medical report analysis..
8 Use Cases of AI Chatbots for Patients
1. AI Chatbots for Symptom Assessment & Triage
AI chatbots in healthcare help patients assess symptoms, determine urgency levels, and guide them to appropriate care settings. They can handle initial screening questions and direct patients to emergency care, urgent care, or schedule routine appointments based on symptom severity.
Key features: Natural language processing, smart follow-up questioning, symptom severity assessment, red flag detection for emergency symptoms
Real-life examples: Some chatbots, like Ada Health and Intermedica, can ask a series of questions to assess a user’s symptoms and recommend the appropriate next step, whether it’s self-care or seeing a doctor. For instance, implementation of the Infermedica virtual triage tool resulted in modified care-seeking behavior in 83.9% of interactions and a 35.7% reduction in emergency care intent.
Another example is the virtual assistant “Amina” and Black Doctor 24/7 app developed by Riseapps, which reduced patient service time by 65% and screened over 30,000 individuals through its AI-powered screening tool, enabling faster access to medical advice.

2. AI Assistants for Appointment Management
Healthcare chatbots automate comprehensive administrative tasks including appointment scheduling, provider availability checks, automated reminders, scheduling conflict resolution, billing inquiries, and paperwork processing, eliminating the need for human intervention.
Key features: Smart appointment matching, multi-appointment coordination, wait-list management, cancellation management
Real-life example: Bitontree AI chatbot for healthcare helped reduce scheduling time by 65%, drop administrative workload by 50%, and improved patient satisfaction by 75%.
3. AI-Powered Chatbots for Medication & Vaccination Reminders
AI assistants support medication management by providing reminders, dosage guidance, and basic drug interaction checks. They help track patient adherence and deliver educational content about prescribed medications.
Key features: Vaccination calendar management, personalized reminder schedules, dosage guidance and verification, drug interaction screening
Real-life example: With MEDIC (Medication Extraction and Drug Interaction Chatbot) users can submit images of medication bags, check for drug-drug interactions / contraindications, integrate into their AI medical knowledge platform and set up reminders..
4. AI Chatbots for Fast Information Search
AI chatbots in healthcare offer immediate answers to common health questions, covering symptoms, medical advice, and general health information.
Key features: Natural language query processing, contextual search, multi-language support, real-time answer generation
Real-life example: CataractBot, a multilingual and multimodal chatbot for cataract patients, answers surgery-related questions using an LLM and curated knowledge base. Expert verification confirmed 91.7% of responses, with 84.52% of medical answers rated as accurate.
5. AI Agents for Appointments Preparation
Healthcare chatbots provide automated pre-appointment messages, videos, and advice to prepare patients for diagnostic tests and appointments.
Key features: Automated preparation timelines, language and literacy adaptation, recovery and post-procedure guidance, anxiety reduction support
Real-life example: A perioperative chatbot deployed at SGH’s Preoperative Assessment Clinic assists with pre-surgery preparation by assessing patient health history, providing pre-operative recommendations, and delivering patient instructions for fasting times and medication protocols.

6. AI-Powered Chatbots for Health Monitoring
Chatbots enable early intervention by monitoring chronic condition health metrics and alerting healthcare professionals when needed.
Key features: Multi-source data integration, automated vital sign tracking, symptom progression monitoring, multi-level alert system
Real-life example: DigiBete Chatbot facilitates Type 1 diabetes care transitions for young adults by delivering information, reassurance, and self-management guidance while supporting clinic engagement. The AI platform excels in patient support and early issue detection but does not feature automated metric monitoring or clinical alert systems.
7. Chatbots for Mental Health Support
Mental health chatbots provide therapeutic support through cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) exercises. They offer accessible and non-judgmental resources for depression support, substance abuse assistance, and general mental health care.
Key features: Daily mood check-ins, behavioral pattern analysis, empathetic conversation design, crisis intervention protocols
Real-life example: ChatThero, an LLM-powered addiction recovery chatbot, integrates CBT with motivational interviewing and adaptive persuasive strategies. Clinical results show 41.5% improved patient motivation, 26% faster resolution of resistance cases versus GPT-4o, and higher ratings for empathy and behavioral realism.
8. AI Chatbots for Patient Education
AI chatbots offer 24/7 personalized patient education with interactive learning, medication guidance, and chronic disease support in multiple languages. They deliver consistent, easily understood health information that can be repeated as needed and tailored to individual patient requirements.
Key features: Progress tracking and learning milestones, interactive multimedia content, gamification elements, integration with care plans
Real-life example: NeuroBot represents an advanced LLM-powered chatbot for Hong Kong neurosurgery patients, offering bilingual perioperative education through retrieval-augmented generation technology. The system achieved high validation scores (5.28/6) across 306 bilingual responses and demonstrated measurable benefits: reduced healthcare provider workload and improved patient understanding of neuroendovascular procedures.
4 AI Chatbot Use Cases for Healthcare Professionals
1. AI Chatbots for Patient Follow-up
AI chatbots automate time-consuming tasks like appointment scheduling, patient check-ins, and insurance processing. They handle routine communications, prescription refills, and data entry without human intervention. This frees up healthcare staff to focus on patient care rather than paperwork.\
Key features: Intelligent appointment scheduling, queue management and wait time optimization, prior authorization management, automated data entry
Real-life example: The Arsturn pharmaceutical chatbot handles prescription refills, medication information, and health advice, potentially reducing manual tasks for pharmacy and clinical staff. While the system claims to improve response times and provide reliable information, these benefits require peer-reviewed validation.
2. AI Assistants for Data Collection
AI assistants automatically gather patient histories, symptoms, and health assessments before appointments. They continuously monitor patients between visits, tracking medication adherence and treatment responses. This provides clinicians with comprehensive, real-time data while reducing manual documentation work.
Key features: Automated history taking, real-time health metric collection, medication adherence tracking, smart data validation
Real-life example: AiCure employs AI-powered assistant and computer vision technology to provide real-time medication adherence monitoring through video verification of proper medication administration. The system analyzes patient behaviors to identify adherence risks and supplies clinicians with comprehensive data on adherence patterns and treatment compliance barriers.
3. AI-Powered Chatbots for Insurance Support
AI chatbots automate complex insurance processes including prior authorizations, eligibility checks, and claims submissions. They manage appeals, monitor reimbursements, and ensure regulatory compliance automatically. This streamlines insurance workflows and accelerates payment cycles for healthcare providers.
Key features: Real-time insurance eligibility verification, coverage decision monitoring, automated claims submission, claims status tracking and follow-up
Real-life example: Healthcare AI startup Mandolin automates insurance verification processes for specialty medications. Their AI agents reduce verification timeframes from approximately 30 days to 3 days.
4. AI Assistants for Medical Report Interpretation
Chatbots analyze medical reports to highlight key findings, abnormal values, and concerning patterns. They provide clinical decision support by suggesting diagnoses and treatment recommendations based on report data. This accelerates report interpretation while helping clinicians avoid missing critical information.
Key features: Treatment recommendation algorithms, multi-report correlation analysis, temporal trend identification, executive summary generation
Real-life example: Paige (Paige.ai) develops AI-powered pathology tools including slide analysis and case summarization capabilities. Their flagship product, Paige Alba, functions as a pathologist co-pilot by highlighting key findings and providing workflow suggestions.
The PanCancer Detect system has received FDA Breakthrough designation and regulatory clearances, with peer-reviewed clinical evaluations demonstrating improved diagnostic speed and reduced missed findings in pathology interpretation.
5 Best and Widely Used Examples of AI for Chatbots in Healthcare
Five AI healthcare platforms like Wysa, Suki, Ada Health, Buoy Health, and “Amina” by Black Doctor 24/7 represent the industry’s most successful implementations, collectively serving over 5 million users worldwide. From Wysa’s 35% depression reduction rates and Suki’s $500 million valuation to Ada Health’s $201 million funding success, these solutions demonstrate proven clinical outcomes and commercial viability across mental health support, clinical documentation, diagnostic triage, and healthcare equity initiatives.
Wysa: Leading AI Mental Health Platform
Wysa leverages evidence-based CBT principles to deliver therapeutic support through AI conversations, reaching 5 million users across 65 countries with 500 million interactions completed.
Clinical studies demonstrate significant mental health improvements: 35% reduction in depression and 32% decrease in anxiety among its active users. The platform’s breakthrough crisis detection technology identifies 82% of mental health emergencies among users and has a 91% user satisfaction rate.
Suki: Enterprise AI Documentation Solution
Suki revolutionizes clinical workflows through AI-powered voice assistance and automated documentation, partnering with 300+ health systems and integrating seamlessly with major EHR platforms including Epic, Cerner, and MEDITECH.
The platform achieves remarkable efficiency gains: 72% reduction in documentation time and 70% decrease in medical note completion time during pilot studies. With a 93.2 KLAS performance score, $165 million in funding, and $500 million valuation, Suki represents the gold standard for commercially successful healthcare AI chatbot platform.
Ada Health: AI Diagnostic and Triage Platform
Ada Health delivers AI-powered symptom assessment and patient triage from Berlin, serving healthcare systems globally with $201 million in funding and 284 employees. The platform demonstrates measurable clinical impact through intelligent care routing and diagnostic support.
Real-world evidence validates Ada’s effectiveness: 42% of patients change their intended care setting after AI assessment, with 62% of uncertain patients appropriately redirected away from emergency departments. Healthcare providers report substantial workflow improvements: 77% of physicians experience enhanced efficiency when treating Ada-assisted patients.
Buoy Health: AI Symptom Assessment and Care Navigation
Buoy Health provides intelligent symptom evaluation through AI-powered conversations, delivering free, privacy-focused guidance on potential diagnoses and appropriate care settings.

Clinical evidence from 150,000+ patient interactions shows significant value: uncertainty about care level selection dropped from 34% to 21% after using Buoy. The platform effectively de-escalates care settings in over 25% of cases while appropriately increasing urgency in 5%, optimizing healthcare resource utilization.
“Amina” by Black Doctor 24/7: AI-Driven Healthcare Equity Solution
Founded by renowned podiatric surgeon Dr. Bill Releford, Black Doctor 24/7 eliminates healthcare disparities through AI-powered telemedicine connecting African-American patients with culturally competent physicians.

The platform reduces care delivery costs by 40% while featuring “Amina,” an intelligent assistant that accelerates diagnosis by 65% through automated symptom triage and patient screening. Built in 6 months with complete HIPAA compliance, the comprehensive solution integrates real-time video consultations, secure messaging, and automated clinical workflows through a unified physician portal.
➡️ See BlackDoctor 24/7 app in action in the video demo
What are Key Benefits of AI Chatbots in Healthcare?
AI chatbots in healthcare deliver transformative advantages across two critical stakeholder groups. For patients, these systems provide 24/7 accessibility with 4.58/5 satisfaction ratings, stigma-free care environments, and 9.6% improved self-management capabilities.
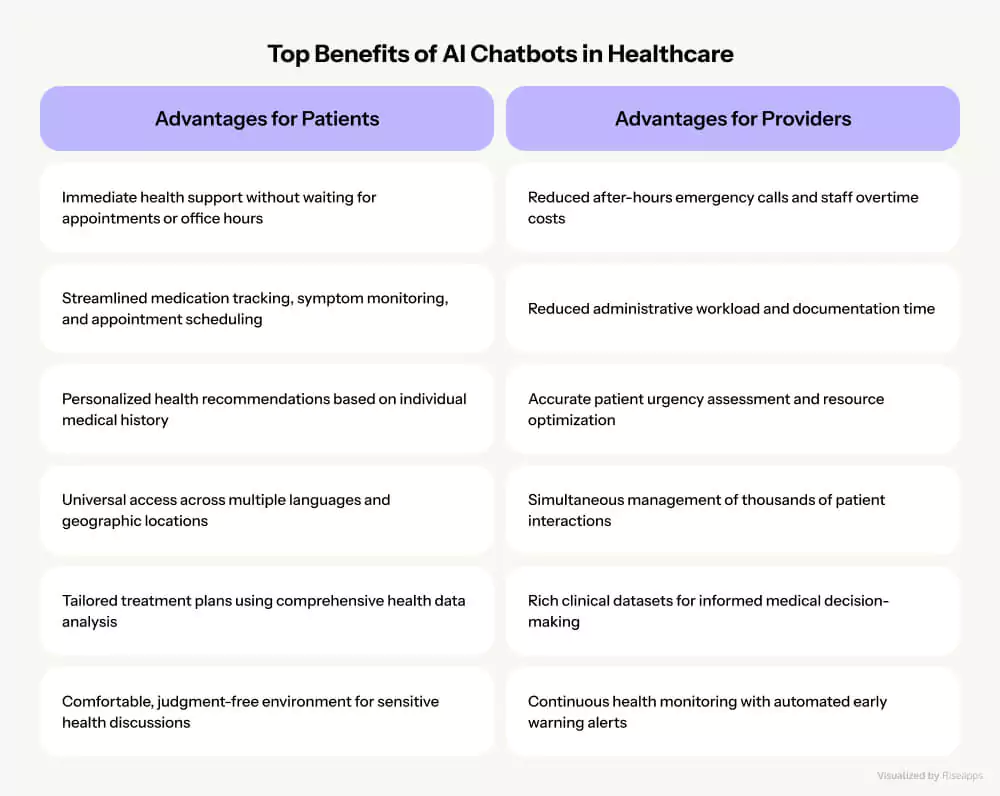
Healthcare providers benefit from up to 65% administrative workload reduction, intelligent patient triage systems, and scalable care delivery that manages thousands of simultaneous interactions while maintaining quality standards
Top 6 Benefits of AI Chatbots for Patients
Continuous Accessibility
AI chatbots deliver immediate healthcare support around the clock, eliminating traditional barriers of office hours and appointment wait times. Patients receive instant responses to health questions and concerns without delays.
Users reported significantly higher overall satisfaction (4.58 vs 4.42 out of 5) when using the AI-assisted conversations versus standard care.
Enhanced Patient Engagement
According to the research, automated health reminders, personalized educational content, and interactive communication tools significantly increase patient participation in their care. This sustained engagement leads to measurably improved satisfaction scores and treatment adherence.
Tailored, Stigma-free Care
Advanced algorithms provide personalized health recommendations based on individual patient profiles and medical history. The non-human interface creates a judgment-free environment where patients feel comfortable discussing sensitive topics like mental health or substance abuse.
Streamlined Self-management
Integrated medication tracking, symptom monitoring, and chronic disease support tools within AI chatbots empower patients to actively manage their health conditions and enhance self-management by 9.6%. These features result in improved clinical outcomes and reduced emergency interventions.
Universal Healthcare Access
Multi-language support and 24/7 availability extend quality healthcare information to underserved populations and remote communities. This democratization of health resources reduces geographical and socioeconomic barriers to care.
Population Health Education
AI chatbots serve as accessible educational platforms, delivering evidence-based health information and promoting preventive care practices. This widespread health literacy improvement contributes to better community health outcomes and reduced disease burden.
Top 5 Benefits of AI-Powered Chatbots for Healthcare Providers
Operational Efficiency
Automation of administrative tasks including scheduling, prescription processing, and data documentation reduces staff workload by up to 65%. These efficiency gains translate directly into cost savings and improved resource allocation.
Intelligent Patient Prioritization
AI-powered symptom assessment and triage systems accurately categorize patient urgency levels. This capability ensures critical cases receive immediate attention while routine matters are handled appropriately.
Comprehensive Data Intelligence
Systematic patient data collection creates rich datasets for clinical decision-making and population health analysis. Real-time data integration with EHR systems enhances diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning.
Scalable Care Delivery
Single chatbot platforms can simultaneously manage thousands of patient interactions without requiring proportional staffing increases. This scalability enables healthcare systems to expand services while controlling operational costs.
Preventive Health Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of vital signs and health metrics enables early detection of concerning trends. Automated alerts to healthcare providers facilitate timely interventions before minor issues escalate into serious medical emergencies.
What are Top Risks and Limitations of AI Chatbots in Healthcare?
Healthcare AI chatbots present 10 critical risk categories requiring immediate attention: technical failures (medical hallucinations, compromised training data), operational risks (critical thinking erosion, emergency response gaps), privacy threats (inadvertent disclosure, re-identification attacks), security vulnerabilities, ethical concerns (bias amplification), and regulatory uncertainties around legal accountability and oversight frameworks.
Risk #1: False Medical Content Generation
AI systems like chatbots may produce confident but entirely incorrect medical information, creating non-existent conditions and inappropriate treatment recommendations. These “hallucinations” can lead to misdiagnoses and patient harm when users cannot distinguish fabricated content from legitimate medical advice. A study examining ChatGPT’s responses to glaucoma patient questions illustrates this risk clearly.
Nearly 30% of the 72 evaluated responses received suboptimal accuracy ratings from ophthalmology experts, with the AI achieving a mean accuracy score of only 3.29 out of 4 points. This demonstrates how even well-trained AI systems can generate unreliable medical guidance that patients might mistake for authoritative advice.
Healthcare software development specialists like Riseapps deploy retrieval-augmented generation systems anchored to verified medical databases with multi-tiered expert validation processes that eliminate fabricated content before reaching patients.
Risk #2: Compromised Data Sources
Training algorithms on indiscriminate internet content treats peer-reviewed medical journals and unvetted forum discussions as equivalent sources. This approach generates unreliable medical guidance that lacks clinical validation and creates verification challenges for users. A comprehensive analysis of healthcare education research reveals the scope of this problem.
Studies found that over 16% of healthcare professionals reported problems with citation inaccuracies and inadequate referencing practices. These findings reveal how AI systems trained on mixed-quality data sources systematically compromise medical accuracy, leaving healthcare professionals and patients unable to distinguish between evidence-based guidance and unreliable information.
Expert telemedicine app developers like Riseapps implement rigorous source verification pipelines that curate medical datasets exclusively from peer-reviewed journals, clinical trials, and validated treatment protocols.
Risk #3: Critical Thinking Erosion
Based on the research, over-dependence on AI for chatbots in healthcare is one of the leading risks that diminishes both patient and clinician analytical skills. It may result in reduced human medical consultation as patients may inappropriately substitute chatbot advice for professional medical care, potentially worsening existing health conditions.
Riseapps can design AI co-pilot architectures that enhance clinical decision-making while maintaining clear system limitations and seamless handoff protocols to human specialists.
Risk #4: Emergency Response Inadequacy
AI chatbots demonstrate significant limitations in recognizing complex medical situations and emotional nuances, particularly during mental health crises. These systems may fail to appropriately identify and respond to suicidal ideation and other emergency scenarios.
AI healthcare development specialists like Riseapps will implement advanced crisis detection frameworks combining natural language processing with emotional sentiment analysis and direct emergency service integration protocols.
Risk #5: Inadvertent Information Disclosure
Medical professionals often unknowingly transfer sensitive patient data to third-party companies when using chatbot platforms. This transmitted information becomes part of AI training datasets, constituting unauthorized disclosure with permanent privacy implications.
High-profile data breaches illustrate the catastrophic potential of these vulnerabilities. WotNot’s misconfigured cloud storage exposed over 346,000 files containing medical records and sensitive healthcare documents. Brazil’s Unimed system suffered an even more severe breach when their “Sara” chatbot’s unsecured database leaked millions of confidential patient-doctor conversations. These incidents demonstrate how chatbot platforms create cascading security risks for healthcare providers.
Riseapps ensures data protection through zero-data-retention policies and HIPAA-compliant infrastructure that legally protect healthcare organizations.
Risk #6: Advanced Re-identification Risks
Evolving AI capabilities can potentially identify individuals from seemingly anonymous datasets using minimal data points. This technological advancement undermines traditional de-identification privacy protection methods.
To mitigate this risk, healthcare AI developers deploy cutting-edge privacy-preserving technologies including differential privacy algorithms and sophisticated anonymization techniques that resist modern re-identification attacks.
However, Riseapps offers flexible pricing models for MVP development and provides cost-effective quotes through our AI estimation tool. Get instant rough estimates in 60 seconds to plan budgets accurately while avoiding weeks to final calculations.
Risk #7: Cybersecurity Exposure
AI chatbot platforms present vulnerable targets for data breaches and cyberattacks, potentially exposing large volumes of confidential patient information. These security risks increase proportionally with healthcare system AI adoption.
Security researchers identified over 1.2 million internet-connected medical devices (MRI machines, X-ray systems, and laboratory equipment) actively leaking patient data through weak passwords and misconfigurations.
This widespread exposure reveals how healthcare organizations’ fundamental security weaknesses create cascading risks across all digital health infrastructure, with AI chatbots particularly vulnerable since they often integrate with these same compromised medical systems and inherit identical architectural security flaws.
Riseapps implements its clients military-grade security protocols including zero-trust architectures, continuous threat monitoring, and SOC 2 compliance.
Risk #8: Systemic Inequality Amplification
AI training on biased historical healthcare data perpetuates and amplifies existing disparities based on race, gender, and socioeconomic factors. Studies demonstrate chatbots providing different care recommendations for identical clinical presentations based solely on patient demographics.
Healthcare-focused developers actively combat algorithmic bias through diverse dataset curation, bias detection algorithms, and continuous demographic parity monitoring across all patient populations.
Risk #9: Legal Responsibility Ambiguity
AI-related medical errors create unclear accountability chains among healthcare providers, institutions, and technology developers. This liability uncertainty complicates malpractice proceedings and may leave patients without adequate legal recourse.
Professional healthcare AI companies like Riseapps establish clear liability frameworks through comprehensive audit trails, professional liability insurance for healthcare AI applications, and legally defensible accountability structures.
Risk #10: Inconsistent Regulatory Development
Rapid AI advancement significantly outpaces regulatory framework creation, resulting in fragmented oversight across jurisdictions. State-level regulations vary considerably while comprehensive federal guidelines remain incomplete.
To avoid this risk, forward-thinking healthcare software companies like Riseapps implement adaptable compliance frameworks that exceed current requirements while maintaining partnerships with healthcare law firms and FDA guidance development processes.
10 Best Practices of Implementing Healthcare Chatbots
Drawing from expert consensus and regulatory guidance, the best practices below ensure AI systems address bias, accessibility, and ethical concerns throughout the implementation lifecycle.
1. Conduct Comprehensive Equity-Centered Needs Assessment
Perform systematic health disparities analysis to identify specific populations disproportionately affected by healthcare access barriers. Conduct intersectionality mapping considering:
- age,
- ethnicity,
- religion,
- gender identity,
- sexual orientation,
- socioeconomic status,
- disability status.
Establish measurable behavioral and health outcomes with specific targets (e.g., 20% increase in screening attendance among underserved populations) aligned with evidence-based health equity frameworks.
2. Establish Multidisciplinary Expert Consensus Development
Form diverse expert panels comprising:
- AI specialists,
- clinical medicine practitioners,
- bioethics experts,
- patient advocates,
- community representatives from target populations.
Implement modified Delphi consensus methodology across multiple review rounds to ensure comprehensive coverage of clinical, technical, and ethical considerations. Mandate transparent AI identity disclosure and accountability frameworks from conception phase.
3. Implement Rigorous Co-Production and Community Engagement
Establish formal Patient and Public Involvement and Engagement (PPIE) groups with meaningful decision-making authority throughout the development lifecycle. Conduct preliminary psychosocial and behavioral research to assess AI hesitancy and cultural barriers. Engage native speakers and cultural competency experts for linguistically diverse populations, ensuring accurate translation and culturally appropriate content development.
4. Deploy HIPAA-Compliant Infrastructure with Zero Data Retention
Implement open-source large language models within HIPAA Health Information Trust Alliance (HITRUST) compliant environments, whether on-premises or cloud-based. Establish business associate agreements with zero data retention protocols and real-time data processing with immediate deletion. Incorporate advanced encryption, intrusion detection systems, and regular penetration testing for cybersecurity validation.
5. Integrate Evidence-Based Clinical Decision Support Frameworks
Develop knowledge bases exclusively from peer-reviewed, reputable sources with GRADE (Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation) evidence strength indicators. Implement confidence thresholds with explicit uncertainty communication when insufficient data exists. Establish clear delineation between clinical decision support versus diagnostic decision-making, with mandatory human professional oversight for all clinical determinations.
6. Establish Comprehensive Emergency Protocols and Crisis Intervention
Deploy natural language processing algorithms trained to recognize linguistic patterns associated with suicidal ideation, self-harm, and acute psychological distress. Implement tiered risk assessment systems with immediate escalation pathways to human professionals for high-risk situations. Maintain detailed crisis event documentation for quality improvement and legal compliance, with culturally competent emergency response protocols.
7. Conduct Systematic Bias Detection and Algorithmic Fairness Testing
Implement continuous algorithmic auditing using standardized equity metrics across demographic subgroups. Conduct cultural and language sensitivity testing with diverse user cohorts to identify potential discrimination patterns. Establish algorithmic transparency protocols allowing users access to information sources and decision-making rationale used by AI systems.
8. Deploy Human-in-the-Loop Supervision Architecture
Maintain qualified healthcare professional oversight for all AI-assisted clinical interactions and decisions. Implement real-time monitoring capabilities with predetermined intervention triggers for complex cases, clinical uncertainty, or user distress. Establish comprehensive documentation protocols for AI system usage, including rationale for AI-assisted decisions and human professional overrides.
9. Implement Longitudinal Performance Analytics with Health Equity Metrics
Establish comprehensive monitoring systems tracking user engagement stratified by demographic characteristics, clinical accuracy scores, and patient satisfaction indices across diverse populations. Implement pre- and post-implementation comparative effectiveness research using anonymous user identifiers to assess impact on health inequalities. Monitor conversation features most utilized by different patient groups to guide targeted improvements.
10. Establish Systematic Knowledge Base Maintenance and Regulatory Compliance
Implement scheduled update cycles aligned with evolving medical standards and clinical practice guidelines. Establish interoperability testing protocols to ensure seamless integration with electronic health records and existing healthcare technology infrastructure. Maintain compliance with FDA Software as Medical Device requirements, including clinical validation, postmarket surveillance, and regulatory audit capabilities for medical device classification scenarios.
Why Choose Riseapps for Custom AI Assistants Development?
Choosing the right partner to develop your custom LLM-powered assistants and copilots is key. Riseapps combines in-depth technical knowledge and expertise in healthcare to ensure your AI project’s success from strategy to implementation.
Here’s why healthcare providers trust Riseapps as their AI consulting partner:
- We are trusted by 80+ Fortune-500 healthcare organizations and innovative digital health startups worldwide.
- Riseappps’ expertise is verified by 58 client reviews on Clutch, for high quality results and exceptional service.
- Our custom solutions are trusted by over 100,000 physicians and 1 million patients worldwide.
- 8+ years in healthtech and 70+ senior healthcare experts.
We offer full scope of AI consulting and development for healthcare providers including:
- AI strategy consulting aligned with your healthcare delivery models.
- Generative AI development for individualized patient education content, automation and personalized patient communications.
- Integration of advanced AI assistants and chatbots into existing EHR, telehealth platforms, and custom patient portals.
Ready to drive lasting change in your healthcare outcomes?
FAQ
Are AI chatbots used in healthcare?
Yes, AI chatbots are widely used in healthcare for symptom assessment, appointment scheduling, medication reminders, mental health support, and patient education. Examples include Wysa serving over 5 million users and Suki deployed across 300+ health systems.
Which AI chatbot is best for medical?
There's no single "best" medical AI chatbot as effectiveness depends on specific use cases. Leading examples include Wysa for mental health (5 million users), Ada Health for symptom assessment, and Suki for clinical documentation (300+ health systems).
How is AI being used in healthcare?
AI is used in healthcare for medical imaging analysis, drug discovery, clinical decision support, chatbots for patient engagement, predictive analytics for risk assessment, electronic health records management, and robotic surgery assistance to improve patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Contact Us








