AI Benefits in Healthcare: 10 Use Cases to Tap Into the $1 Trillion Market

If we take the hype, buzzwords, and tones of unnecessary info away, what are the benefits of using AI in healthcare that can help your healthcare business achieve better results in operations, finances, and diagnostics? Here’s the short answer:
- AI-powered medical diagnostics enhance diagnostic accuracy by up to 40% (The Lancet) in identifying patterns in imaging and lab results faster than humans.
- Faster data processing reduces the time doctors spend reviewing medical data, including test results, patient histories, and clinical notes.
- Robotic aid in surgeries improves surgical precision and reduces complications.
- Personalized healthcare based on a patient’s genetics, lifestyle, and medical history, improves outcomes and minimizes side effects.
- Continuous patient monitoring driven by wearable devices and AI-powered monitoring systems helps reduce emergency hospitalizations by up to 35% (American Heart Association).
- Healthcare documentation automation to minimize manual data entry for doctors and nurses, saving hours of administrative work per week and reducing human errors in records.
- AI-driven incident management helps hospitals detect critical incidents, like equipment malfunctions or patient deterioration, in real-time and improve patient safety.
- Drug discovery, development, and prescription with AI accelerate drug research, reducing development timelines by up to 50% and cutting costs significantly (McKinsey).
- Advancing personal genetics predicts disease risks, allowing for preventive interventions before symptoms even appear.
- AI in administrative efficiency reduces healthcare administrative costs by 30% (Accenture) and operational burden by streamlining billing, scheduling, and claims processing.
In this article, we’ll break everything down in detail — real-world use cases, benefits of AI in healthcare, key AI applications, and the best forms for businesses to integrate AI into their operations.
AI in healthcare statistics: 5 facts for AI growth in 2025 and further
AI in healthcare is a response to real financial, operational, and technological shifts that are reshaping the industry. The numbers tell the story: global healthcare spending is expected to hit $12 trillion by 2040, while labor shortages, rising operational costs, and increasing patient demand are forcing hospitals to rethink their approach. Analysts from McKinsey, Deloitte, and Gartner highlight key reasons why AI in healthcare is booming.
1. AI adoption is being driven by economic pressures, not just innovation
Healthcare isn’t just expensive — it’s inefficient. 25% of hospital spending goes toward administrative costs (Deloitte), and operational inefficiencies are eating into profit margins. At the same time, insurers and governments are tightening reimbursement policies, putting financial pressure on hospitals. AI-powered automation is becoming less of an optional upgrade and more of a financial necessity. McKinsey estimates that AI could generate up to $1 trillion in annual savings across healthcare by improving workflows, reducing errors, and streamlining operations.
2. Workforce shortages leading to automation
The World Health Organization (WHO) warns of a global shortage of 10 million healthcare workers by 2030, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. AI is stepping in to bridge the gap by automating routine administrative tasks, assisting in diagnostics, and supporting remote patient monitoring.
3. AI’s proven impact in real-world applications
AI-powered diagnostic tools are already showing impressive results. For example, AI models for breast cancer detection have outperformed human radiologists, reducing false positives by 5.7% and false negatives by 9.4%. Additionally, AI-assisted stroke detection has cut the time to treatment by 60 minutes, improving survival rates.
4. Patient demand for AI-driven services
According to a 2024 survey by Statista, 69% of U.S. adults were comfortable with the use of AI in healthcare for scheduling appointments, while only 15% felt comfortable with AI diagnosing them. The rise of telehealth services surged 38x from pre-pandemic levels, increasing the need for AI-driven virtual care solutions.
5. Policy changes encouraging AI integration
Governments and insurers are updating policies to support AI adoption. In the U.S., Medicare and Medicaid have expanded reimbursements for AI-driven diagnostics and virtual consultations, making AI-powered care financially viable for providers. Meanwhile, the European Union’s Artificial Intelligence Act is expected to set global standards for safe AI deployment in healthcare.
10 use cases showing how AI in healthcare benefits your business
How exactly does AI translate into measurable business benefits? We’re going to break down 10 use cases where AI is already making a tangible impact in healthcare — enhancing efficiency, optimizing workflows, and ultimately driving better financial and operational outcomes.
1. More efficient medical diagnostics
AI has delivered significant improvements in medical diagnostics by augmenting clinicians’ abilities to detect diseases early and accurately. Across the globe, artificial intelligence algorithms now analyze patient data, medical images, lab results, and clinical data to catch patterns often imperceptible to humans. For example, AI tools for radiology and pathology can screen thousands of images in minutes, helping flag subtle abnormalities like early tumors or microscopic disease markers.
A notable global case is in Japan, where doctors developed an AI for endoscopy that analyzes live video of the stomach and colon to predict cancer risk. This system was trained on over 200,000 high-resolution endoscopic videos and can review an image in 0.02 seconds, versus ~4 seconds for an expert doctor. In trials it reached 94% accuracy in detecting early gastric cancers.
Beyond imaging, AI diagnostic decision-support is used in areas like cardiology (e.g. ECG analysis algorithms that detect arrhythmias) and dermatology (AI screening apps for skin lesions). For example, at Johns Hopkins Hospital, an AI-based early warning system scours patient vitals and lab results continuously to detect sepsis hours earlier than traditional methods. In a two-year study on over half a million patients, this AI reduced sepsis mortality by ~20% by prompting earlier intervention.
2. Accurate, accelerated, and high-quality data processing
Modern healthcare generates massive volumes of data – from electronic health records (EHRs) and lab results to medical images, genomic sequences, and research databases. AI has become indispensable in processing this data deluge faster and more efficiently than traditional methods. Globally, healthcare data is estimated to be doubling every few years far outpacing human clinicians’ ability to review or analyze it unaided. AI algorithms (particularly those in the big-data and analytics domain) can parse through millions of records or images in a fraction of the time it would take experts.
The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) – which has health records for millions of veterans – collaborated with industry to use AI for analyzing this trove. In one project, AI algorithms reviewed over 700,000 echocardiogram reports to flag patients with heart failure who might benefit from intervention, a review that would have been prohibitively slow manually. The AI sifted text reports in seconds per record using natural language processing (NLP) to extract key indicators (ejection fraction, etc.), enabling VA clinicians to reach out to at-risk patients sooner.
The U.S. tech sector, including giants like Microsoft and IBM, as well as many startups, have created healthcare-specific AI data platforms which many provider organizations have adopted to handle everything from population health analytics to quality reporting much faster and with more granularity than before.
3. Robotic aid in surgeries
One of the most visible and exciting applications of AI in healthcare is in robotic-assisted surgery. Surgical robots – once exclusively manually controlled tools – are increasingly augmented with AI to improve precision, safety, and outcomes. From operating rooms in the U.S. to surgical centers in Europe and Asia, AI-driven robotics are transforming how surgeons perform complex procedures. These systems offer steadier hands, finer motion scaling, and even autonomous actions in certain tasks, leading to minimally invasive surgeries with smaller incisions, less blood loss, and faster recovery for patients.
Robotic surgery has seen worldwide growth. By early 2023, over 11 million surgical procedures had been performed using the leading robotic platform (Intuitive Surgical’s da Vinci system) across the globe. AI’s role in these robots ranges from enabling advanced imaging guidance (e.g., real-time 3D vision and AI image recognition to identify tissue types) to motion stabilization (filtering surgeon hand tremor) and even partial automation of certain surgical steps.
A milestone was reported in 2022 by a Johns Hopkins University team: the Smart Tissue Autonomous Robot (STAR) performed a delicate laparoscopic surgery (intestinal anastomosis) on the soft tissue of a pig without human guidance, achieving better precision than human surgeons.
4. Personalized healthcare based on individual characteristics
Traditional medicine often used a one-size-fits-all approach, but from 2022 to 2025 we have seen AI enable a more nuanced strategy – considering a person’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, environment, and health history to provide precision medicine. This benefit spans developing individualized treatment plans, predicting risks at an individual level, and customizing interventions for maximum efficacy and minimum side effects.
Around the world, healthcare providers are harnessing AI to analyze diverse personal health data and deliver “the right treatment to the right person at the right time.” For instance, AI models can integrate data on a patient’s genes, blood biomarkers, and even social determinants of health to recommend targeted prevention or therapy.
5. Continuous patient monitoring for preventive healthcare
By analyzing streaming data from wearable sensors, implanted devices, and monitoring equipment, AI can detect early signs of trouble and facilitate timely interventions. From ICU units where every heartbeat is tracked, to patients’ homes where smartwatches now perform medical surveillance, AI-driven monitoring is improving safety and enabling proactive care 24/7.
Worldwide, the adoption of remote and continuous monitoring exploded during the COVID-19 pandemic and continues to grow. By the end of 2023, there were an estimated 76.7 million connected home medical monitoring devices in use globally, ranging from blood pressure cuffs and glucometers that sync to phones, to wearable ECG patches.
6. Healthcare documentation automation
Globally, the market for AI in medical documentation is growing rapidly – projected to exceed $6 billion by 2025 with adoption in North America, Europe, and Asia leading the way.
The burden of documentation in healthcare – from writing clinical notes to managing electronic health records (EHRs) – is enormous. Physicians often spend hours entering data, which contributes to burnout and pulls time away from patients. AI-driven automation is now tackling this challenge by transcribing, organizing, and even generating documentation, allowing clinicians to focus more on care and less on paperwork.
From voice recognition that types up a doctor’s encounter, to intelligent software that codes and summarizes visits, AI is making healthcare documentation faster, more accurate, and less onerous across the globe.
We worked on the case that required streamlining medical documentation for healthcare providers. PareIT, a healthcare company approached us looking for a solution to reduce the time doctors spent on patient documentation. The goal was to develop an AI-driven medical summarization tool that could automatically extract key details from doctor-patient conversations and structure them into concise, EHR-ready summaries.

After assessing the workflow, we identified that the best approach was to integrate a natural language processing (NLP) model capable of analyzing medical conversations in real time. The tool needed to recognize medical terminology, extract essential details, and ensure summaries were accurate, structured, and compliant with industry standards.

How we optimized the system for different roles:
For physicians:
- Developed an AI-powered speech-to-text system to transcribe and summarize consultations.
- Created structured medical notes that could be reviewed and edited before being stored in EHRs.
- Ensured that AI-assisted summaries met HIPAA compliance standards for patient data security.
For healthcare admins & IT teams:
- Integrated the summarization tool with existing EHR systems, reducing manual data entry.
- Designed customizable templates to fit different specialties and documentation styles.
- Implemented data encryption and access controls to ensure security and compliance.
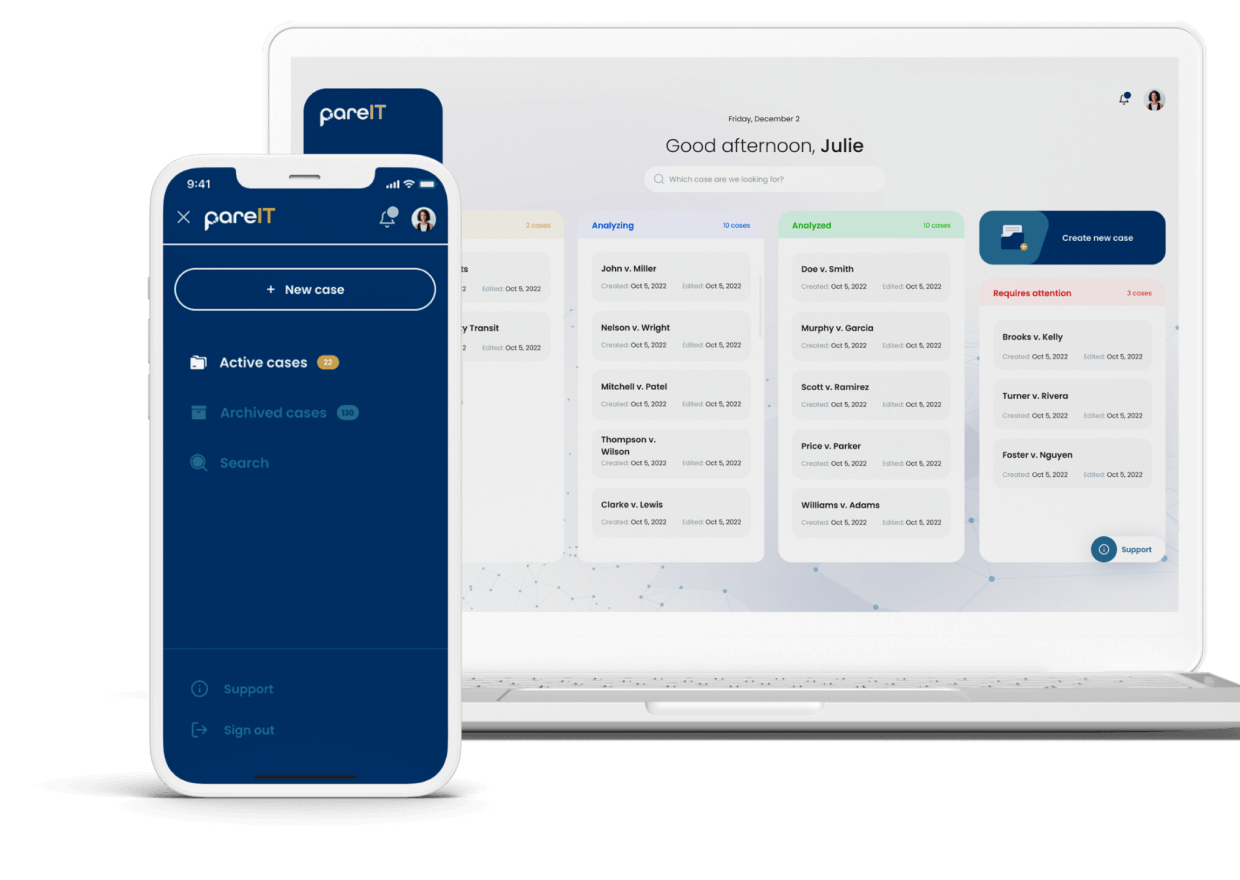
Business impact: Faster documentation, more patient focus
The AI-powered tool significantly cut down the time spent on paperwork, enabling doctors to spend more time with patients while ensuring accurate documentation. Key results included:
- 40% reduction in documentation time, allowing doctors to see more patients.
- Improved accuracy and consistency in medical records.
- Seamless integration with EHRs, reducing administrative workload.
7. Effective incident management
In healthcare, “incidents” refer to unexpected events that can harm patients or disrupt operations – from medical errors and adverse drug reactions to falls, infections, or emergency situations. AI is increasingly being used to improve incident management by predicting, preventing, and streamlining the response to such events. Whether it’s identifying patients at risk of an in-hospital fall, analyzing incident reports to prevent future errors, or coordinating swift action during a crisis, AI tools are making healthcare environments safer and more resilient.
Worldwide, hospitals are starting to use AI-driven early warning systems that act like smoke detectors for clinical deterioration or errors. For example, across several countries, AI programs are monitoring medication errors: they scan prescription orders in real-time and flag anomalies – such as a dose that is 10x higher than usual for a pediatric patient – potentially preventing a harmful overdose.
In Asia, large hospitals in Japan and Singapore use AI to detect patterns in vital signs that precede a cardiac arrest (like subtle changes in heart rhythm instability) and alert rapid response teams (this overlaps with continuous monitoring but specifically helps incident response to crashes).
8. Drug discovery, development, and prescription
Between 2022 and 2025, the integration of AI in drug R&D has yielded promising drug candidates in record time and helped tailor treatments to individual patients. The technology’s ability to analyze vast chemical and biological datasets, predict molecular behavior, and design novel compounds is transforming how we find and use medications.
Historically, finding a lead drug molecule took years of trial-and-error; now AI systems can screen and optimize compounds in months. A headline achievement was in 2023, when a startup in Hong Kong (Insilico Medicine) announced an AI-discovered drug for pulmonary fibrosis entering Phase II trials just 30 months after project start – significantly faster than the 4-5 years typical for preclinical to Phase I.
A Deloitte report noted that AI could potentially improve drug R&D productivity by 20% and significantly lower costs by 2030. Patients around the world might see new, effective treatments for diseases that were previously untreatable or get medications chosen just for them with far less trial-and-error.
9. Advancing personal genetics
The field of personal genetics – analyzing individual DNA to guide healthcare – has been turbocharged by AI. From interpreting complex genomic data to unlocking insights about disease risk and treatment from a person’s genetic code, AI is enabling truly genome-informed healthcare. Between 2022 and 2025, AI has helped sift through massive genomic datasets, predicted functions of genetic variants, and paved the way for personalized gene-based therapies and preventive strategies.
For example, the global GUARDIAN project used AI to analyze neonatal genomes and could diagnose genetic conditions in sick newborns in under 24 hours – something that used to take weeks, crucial for starting life-saving treatments early.
10. Administrative efficiency and costs reduction
Hospitals and health systems are complex organizations with scheduling, billing, supply chain, and management tasks that traditionally consume significant resources. Between 2022 and 2025, AI has been increasingly deployed to streamline these operations – automating routine tasks, optimizing resource allocation, and reducing administrative burdens. The result is improved productivity, lower overhead costs, and ultimately, more resources available for personalized patient care.
A notable global trend is AI chatbots for administrative queries: Many healthcare organizations now use the services of AI chatbot development companies and benefits of generative AI in healthcare on their websites or phone lines to answer common questions (“What are the visiting hours?”, “Is Dr. X available?”, “How do I refill my prescription?”), which reduces call center loads. In China, for instance, large hospitals use WeChat-based AI assistants for patients to schedule appointments and get lab results, tasks that used to require human clerks.
Riseapps has experience building such platforms. Black Doctor, a healthcare platform focused on improving access to medical resources for Black communities, approached us with a challenge. They needed a virtual assistant that could streamline patient interactions, provide accurate medical guidance, and reduce the workload on healthcare professionals. The goal was to enhance engagement, improve efficiency, and ensure patients receive reliable information without delays.

Following a detailed discovery phase, we identified key areas where AI could bridge the gap between patients and healthcare providers. The strategy focused on developing an AI-powered chatbot that could:
- handle patient inquiries
- assist with symptom checking
- provide resources tailored to users’ needs
Our healthcare app development company ensured seamless integration with EHR systems and telemedicine platforms to support doctors and administrative staff.

We optimized the system for different roles
For patients:
- Implemented an AI-driven virtual assistant to provide instant answers to common medical questions.
- Designed a symptom checker to guide users on whether they should seek in-person care.
- Developed a personalized recommendation system to connect patients with relevant healthcare resources.
For healthcare providers:
- Integrated the AI assistant with EHR systems to help doctors quickly access patient history.
- Automated appointment scheduling to reduce administrative workload.
- Enabled smart patient triaging, ensuring that urgent cases were prioritized efficiently.
For admin & support teams:
- Introduced automated FAQ handling, significantly reducing the need for human intervention in repetitive queries.
- Developed a streamlined ticketing system, directing complex cases to human agents only when necessary.
- Ensured HIPAA-compliant security for all AI-driven interactions.

As an experienced generative AI development company, we created a powerful AI virtual assistant that transformed the way Black Doctor interacted with patients. Key outcomes included:
- 35% reduction in administrative workload due to automated patient inquiries and scheduling.
- 50% faster response times for patient queries, improving satisfaction and engagement.
- Increased provider efficiency, allowing doctors to focus on critical cases instead of routine administrative tasks.
- Enhanced security and compliance, ensuring patient data remained protected while integrating AI functionalities.
As of 2025, we see substantial progress in all these areas, with numerous case studies and data demonstrating AI’s positive impact. Experts across disciplines echo that sentiment. As Dr. Eric Topol – Cardiologist and Digital Medicine Researcher famously said,
Cons of AI in healthcare: What’s the catch?
AI in healthcare offers impressive benefits, but it’s not without its challenges. High implementation costs, data security risks, and ethical concerns make AI adoption a complex process. While AI can enhance efficiency and accuracy, it also raises questions about bias, regulatory compliance, and reliance on automation. Before fully embracing AI-driven solutions, healthcare businesses need to weigh these drawbacks carefully.
Reliability and risks
AI has the potential to improve accuracy, efficiency, and patient outcomes, but it’s not without its challenges. Reliability in AI-driven healthcare depends on the quality of data, algorithm transparency, and regulatory compliance. A misdiagnosis due to biased or incomplete training data can have serious consequences, making rigorous validation and continuous monitoring essential.
On the risk side, data privacy concerns, ethical dilemmas, and regulatory hurdles remain major challenges. AI systems must comply with strict standards like HIPAA, GDPR, and FDA regulations to ensure patient safety and trust. Additionally, AI should be used as a decision-support tool, not a replacement for human expertise, as over-reliance on automation can introduce blind spots in clinical decision-making.
The perpetuation of healthcare biases
Another stressor is ChatGPT just carrying on with the same old healthcare biases. If a model’s trained on data-heavy on a particular group, it could start leaning against others.
AI doesn’t have the green light to diagnose, treat, or prescribe without a human in the driver’s seat. But we’ve seen AI take a shot at areas like experimental CT, MRI, and X-ray reading with mixed grades. The model’s first run caught heat for pushing out biased and sexist answers, which got patched up afterward.
Ethnicity data gaps and minority underrepresentation
Building AI models is data-hungry work, using everything from healthcare websites to scientific research. The rub is that a lot of healthcare research plays hooky when including ethnicity data. This leaves ethnic minorities out in the cold in medical research trials.
Mohammad Ali, a Ph.D. in Epidemiology at the University of Leicester, gives a red flag about the fallout: we might end up with dud drug treatments or skewed treatment guidelines due to this under-representation. Ali warns:
Absence of health equity among AI Tools
Even with all their potential, AI tools often get tangled with biases that threaten health equity.
The AI blueprint drives it home: algorithms and systems shouldn’t keep discrimination on life support and need to be designed and used fairly.
But, let’s not forget, biases could be more on the minds of the individuals coding the algorithms than the algorithms themselves.
An algorithm on its own doesn’t discriminate. The people coding it could knowingly or unknowingly let discriminatory attitudes creep in, which could get baked into the algorithm.
The digital bill of rights pushes algorithm designers and software coders to have the backs of communities against algorithmic discrimination. It calls for fairness in ensuring access for people with disabilities, running disparity tests, and putting the test results out there for everyone to see.
7 applications of AI in healthcare
AI in healthcare manifests in various forms, each addressing specific challenges in patient care, diagnostics, and operations. Here’s how AI is shaping modern healthcare:
1. AI-powered diagnostics
AI algorithms analyze medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to detect conditions like cancer and neurological disorders. For instance, AI-assisted CT imaging has reduced the reading time for detecting lung nodules and pleural effusions by over 44%, enhancing diagnostic efficiency.
2. Predictive analytics for risk assessment
AI processes vast datasets to predict disease progression and patient outcomes. Hospitals utilize predictive modeling to identify patients at high risk of complications or readmissions. Implementing AI-driven predictive analytics has led to a 20–30% reduction in hospital readmissions, resulting in better patient outcomes and reducing costs.
3. Virtual assistants & AI chatbots
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants manage routine patient inquiries, appointment scheduling, and symptom assessments, enhancing patient engagement and reducing administrative burdens. For instance, Cleveland Clinic has announced the rollout of Ambience Healthcare’s AI platform to assist with clinical documentation, aiming to reduce the administrative workload for caregivers and allow more time for personal interaction during visits.
4. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for administrative tasks
AI automates repetitive administrative tasks such as medical coding, claims processing, and appointment scheduling. A McKinsey survey found that 56% of hospitals using AI reported improved operational efficiency, while 45% noted a decrease in patient readmission rates.
5. Personalized treatment & AI-driven drug development
AI tailors treatments based on a patient’s genetics, medical history, and real-time health data. In drug development, machine learning models help identify promising compounds and expedite clinical trials. AI-based personalized treatments have been associated with up to a 30% reduction in hospital readmissions and improved overall patient outcomes.
6. AI in surgery & robotics
AI-powered surgical robots assist in minimally invasive procedures, enhancing precision and reducing recovery times. Systems like the da Vinci Surgical System enable surgeons to perform complex operations with greater accuracy, leading to fewer complications and faster patient recovery.
7. Remote patient monitoring & AI wearables
AI-powered wearables monitor real-time vitals such as heart rate and oxygen levels, offering continuous health monitoring. This is particularly beneficial for managing chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension. The integration of AI into health analytics could save the global healthcare system over $150 billion annually by 2026.
Is AI in healthcare worth the hype?
AI’s role in healthcare is transformative, improving patient outcomes and streamlining operations. For instance, Google’s DeepMind used AI to predict acute kidney injury 48 hours before it happened, potentially saving lives.
However, AI has its pitfalls, especially regarding data security and mental care. In one distressing instance, a man from Belgium took his own life following prolonged interaction with an AI chatbot, discussing the climate crisis.
This chatbot was built using EleutherAI’s GPT-J, a model akin to the widely-known ChatGPT from OpenAI. Thus, while integrating AI can offer great benefits, understanding its limitations and risks is crucial.
FAQ
What are the advantages and benefits of using AI in healthcare?
The biggest advantage of AI is its ability to process large volumes of data quickly, leading to faster and more accurate diagnoses. AI also personalizes treatment plans, predicts disease progression, and enhances operational efficiency by automating scheduling, billing, and patient monitoring. By improving efficiency and decision-making, AI helps healthcare providers deliver better care with fewer resources.
How has artificial intelligence helped healthcare?
AI has changed healthcare for good by reducing diagnostic errors, improving workflow efficiency, and expanding access to care. AI-driven imaging tools detect diseases like cancer years earlier than traditional methods, virtual hospitals provide 24/7 remote monitoring, and AI chatbots assist with triage, appointment booking, and medication adherence.
How does AI reduce costs in healthcare?
AI minimizes unnecessary hospital visits, cuts administrative costs, and optimizes treatment pathways. Predictive analytics help prevent avoidable hospital readmissions, while AI-driven automation reduces labor-intensive tasks like medical coding and claims processing. According to McKinsey, AI could help the healthcare industry save up to $360 billion annually by increasing efficiency and reducing waste.
Contact Us








