IT Infrastructure in Healthcare: Implementation, Examples, and Best Practices

The U.S. healthcare industry continues to face escalating cybersecurity threats. According to IBM’s 2025 Cost of a Data Breach Report, healthcare data breaches remain the costliest industry impact over the past 14 years, averaging $7.42 million per incident.
Despite a year-over-year decline of $2.35 million, healthcare breaches still significantly outpace other sectors, overall reaching a record $10.22 million, a 9.2% increase from 2024.
Robust healthcare IT infrastructure with advanced security capabilities and scalable architecture can significantly lower breach costs and ensure security measures evolve seamlessly as organizations grow.
In our guide, you’ll find about:
- Key components of an efficient healthcare IT infrastructure
- Implementation steps for a medical platform infrastructure
- How Riseapps helped PIPRA, CareHalo, The Wound Pros implement cloud-based and HIPPA-compliant solutions
- How to calculate the total cost of ownership and ROI for healthcare IT infrastructure
What is IT Infrastructure in Healthcare?
Healthcare IT infrastructure demands seamless integration of third-party systems, devices, and data sources while maintaining stringent security protocols.
Healthcare data flows through multiple touchpoints:
- Patient touchpoints: mobile apps, web portals, and wearables (smartwatches, IoT devices)
- Clinical systems: EHRs, EMRs, laboratory platforms, and external provider networks
The critical challenge for healthcare digitization is managing data security, integration reliability, and system resilience during provider failures.
To ensure Protected Health Information (PHI) compliance, organizations must choose the right deployment model.
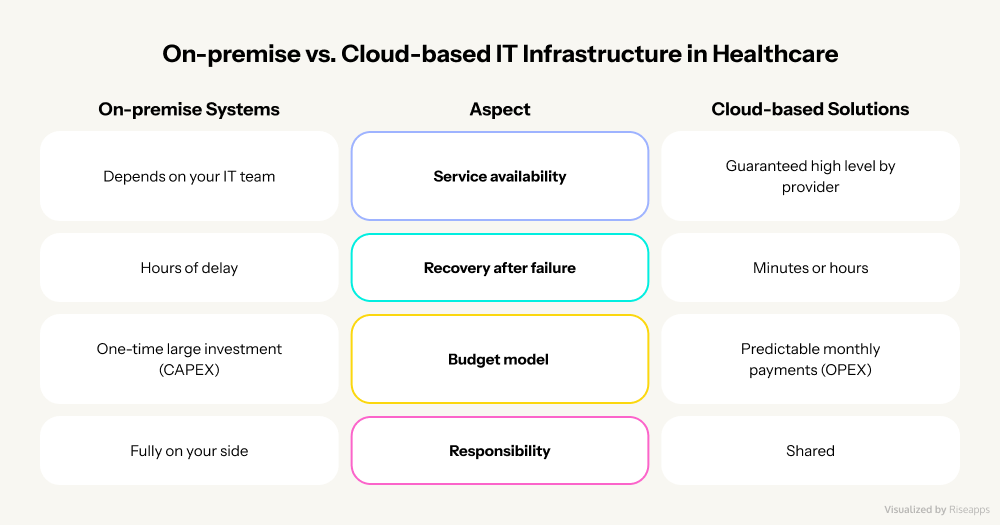
Here are two types of these models:
- On-premise systems require local servers and dedicated IT specialists for security and maintenance.
- Cloud solutions eliminate this overhead, offering secure, scalable infrastructure with simplified access, enabling rapid growth without additional costs. According to the research, cloud technology can lower costs by up to 30% compared to traditional systems. In addition, cloud computing is projected to reach $89 billion by 2027, and 81% of healthcare leaders implement cloud-based solutions across their enterprise operations.
What are Core Components of Healthcare IT Infrastructure?
Understanding your cloud architecture’s building blocks is essential.
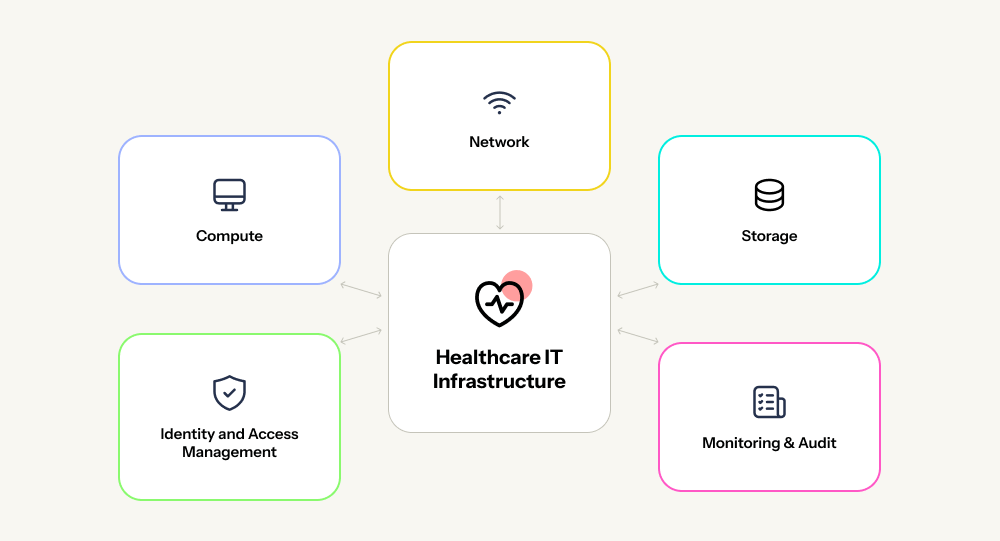
Here are the key elements:
- Network: secure data “corridors” with isolated access, encrypted transmission, and complete audit logging for data tracking and recovery.
- Computing: virtual machines and remote servers enabling diverse technologies like FAX integration, IP telephony, video/audio calls, and specialized healthcare systems.
- Storage: encrypted, backed-up “patient care archives” with multiple replicas across servers. If one fails, data remains accessible. Without encryption keys, breached data is unusable.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): digital access control defining user permissions and data visibility. Prevents unauthorized actions like nurses altering diagnoses or patients modifying prescriptions.
- Monitoring and auditing: system oversight tracking all data interactions, revealing vulnerabilities, ensuring accountability, and optimizing cloud costs through performance metrics.
This modular architecture enables rapid scaling and project launches. Unlike monolithic systems, cloud infrastructure operates on pay-per-use pricing.
Our team has proven expertise in building scalable medical solutions that fully comply with HIPAA and GDPR requirements. We help healthcare businesses move from uncertainty to reliable, secure, and cost-effective IT infrastructure. Partner with Riseapps to design and implement the right infrastructure for your clinic.
Key Component #1: Security and Compliance for Healthcare IT
Healthcare IT infrastructure requires rigorous security standards before launch.
Use this framework to evaluate readiness or conduct a professional audit to ensure compliance:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): adds verification layers through authenticator apps (Google Auth, Microsoft Authenticator) or SMS codes, blocking unauthorized access attempts.
- Zero Trust architecture: verifies every user and device at each login. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) ensures users access only data relevant to their role, preventing lateral breaches.
- End-to-end encryption: protects data at rest (databases, servers) and in transit (TLS/HTTPS), rendering intercepted information unusable.
- Comprehensive logging: records all system activities, creating audit trails that detect suspicious behavior and ensure accountability.
- Tested recovery protocols: establish validated backup systems and incident response procedures for breaches or data loss.
However, robust IT infrastructure cannot eliminate human vulnerabilities. Research shows that 71% of healthcare IT leaders moved their cloud applications back to on-premises systems due to security concerns.
Moreover, with credential phishing attacks exceeding 16% of all data breaches, it’s mandatory to train staff on phishing recognition and social engineering tactics is non-negotiable.
Beyond technical safeguards, IT systems must satisfy stringent data protection regulations. The following sections detail HIPAA and GDPR compliance requirements essential for legal operation.
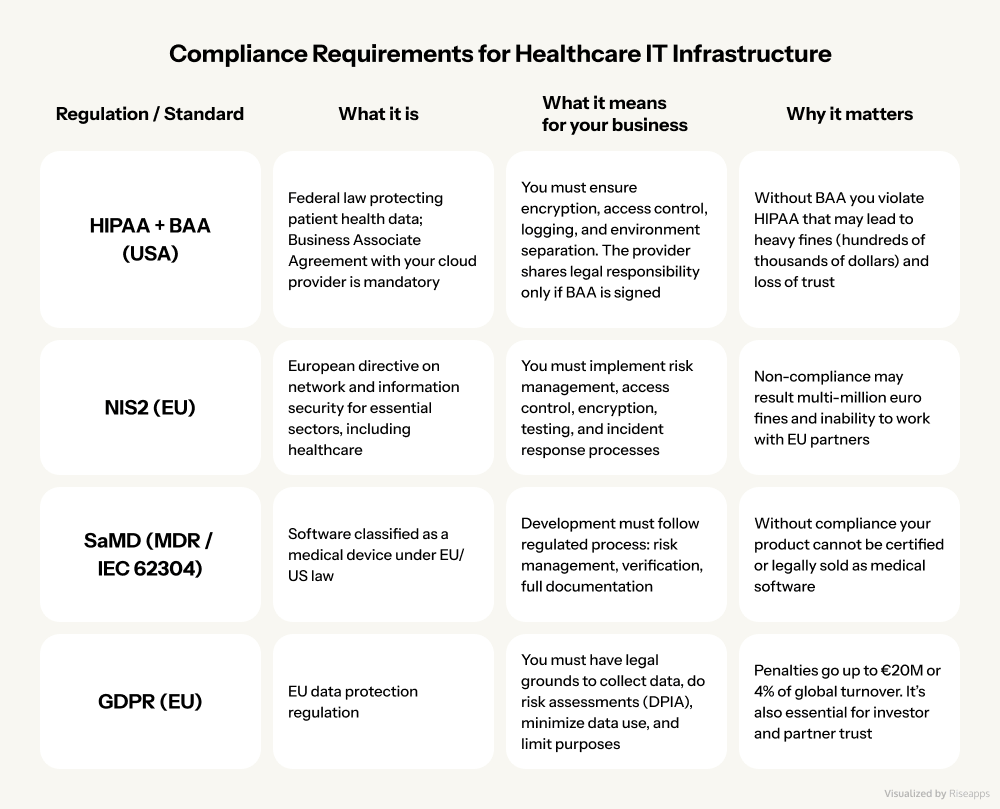
Key Component #2: Interoperability and Integration for EHR Ecosystem Compatibility
Healthcare systems communicate through standardized protocols (HL7 and FHIR) that enable seamless data exchange between different providers. They harmonize terminology and formats across EHRs, laboratory systems, and mobile applications.
For example, The American Medical Association found that 85% of physicians believe EHR systems integrated with secure cloud infrastructure help them better share patient information.
FHIR (the modern HL7 evolution) accelerates integration timelines, reduces support costs, and enables easier scaling. These standards eliminate custom-built integrations and streamline operations, replacing expensive manual healthcare processes with automated, standardized exchange.
Integration Challenges and Solutions
However, there are three critical integration challenges that you need to consider are financial barriers, technical fragmentation, and organizational readiness. To get around these issues, there are a few tried-and-true solutions for healthcare services that we use:
- Middleware adapters that normalize disparate data formats into unified structures.
- Reusable API connectors that provide pre-built integration modules that scale across multiple projects, reducing per-integration costs.
- Phased rollouts that introduce changes incrementally with hands-on training, maintaining operational continuity while building user competency.
Essential Components for Robust Integration Architecture
Architectural solutions for integrations make data exchange convenient, reliable, and secure.
Enterprise-grade architecture should deploy:
- API gateway: for centralized authentication and access control protecting all external connections. Internal services remain isolated behind this security perimeter, accessible only through authenticated gateway requests.
- Message queuing systems (AWS SQS/SNS, Apache Kafka): for asynchronous data delivery that will guarantee zero message loss during system outages, essential for clinical environments where data integrity is non-negotiable.
- Transformation engine: for bidirectional conversion between HL7/FHIR standards and proprietary formats, handling custom field mapping without core system modifications.
- Isolated sandbox testing: for validated integration protocols in replicated environments eliminate production risks and protect sensitive patient information.
Mini-checklist: How to Get Ready for EHR Integration
Our integration readiness checklist provides systematic verification to ensure on-time, on-budget Electronic Health Records (EHR) connectivity.
Step #1: Map data fields
- Clearly define what data is being transferred (e.g., name, date of birth, diagnosis, test results).
- Agree on formats: date in MM/DD/YYYY or DD/MM/YYYY format, units of measurement, etc.
Expert comment: Without this, the system cannot process data, and integration will turn into manual data transfer between systems.
Step #2: Set a consent model
- Decide on what grounds and in what cases data can be transferred.
- Set up the process: how a patient gives and withdraws consent.
Expert comment: This is a requirement of HIPAA and GDPR. Without a consent model, integration is legally unsafe.
Step #3: Define an error & retry strategy
- What should you do if one system is temporarily down?
- How can you ensure that data is redelivered without loss or duplication?
Expert comment: This step reduces the risk of data loss and lawsuits in the event of incidents.
Step #4: Launch a load testing
- Check whether the system can handle the actual flow of requests (for example, hundreds of requests per minute).
- Identify bottlenecks before launch, rather than after user complaints.
Expert comment: This demonstrates to investors and partners that you are prepared for scaling.
Key Component #3: Cloud Scalability and Reliability for 10× Healthcare Growth
When healthcare organizations scale tenfold, traditional IT infrastructure fails. In healthcare, system failures don’t just inconvenience users, they erode patient trust, trigger HIPAA/GDPR violations, and cause direct financial losses.
To ensure healthcare IT infrastructure scalability, our experts design systems based on modern architecture foundations:
- Containerization packages applications with all dependencies, ensuring consistent performance across any environment. This enables rapid feature deployment without environment-specific failures.
- Serverless architecture executes functions on-demand without permanent servers. You pay only for active processing time. This reduces costs while enabling automatic scaling based on real-time demand.
- Horizontal scaling adds servers as load increases rather than over-provisioning upfront capacity. If one server fails, others continue processing. It’s critical when service interruptions can halt clinical operations.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) deploys servers, networks, and databases through code, eliminating manual configuration errors. New clinics or laboratories launch in hours instead of weeks, with consistent, reproducible environments.
Advanced Approaches to System Monitoring and Recovery
In addition, for high-quality system monitoring, it is important to keep track of:
- Observability that provides comprehensive system insights: service performance bottlenecks, integration delays, and EHR behavior. Automated alerts notify teams of issues before they impact users, ensuring service quality during rapid growth.
- RTO (Recovery Time Objective) that defines system restoration time after failures. An RTO of 15 minutes versus 24 hours means the difference between unnoticed downtime and clinic paralysis.
- RPO (Recovery Point Objective) that determines acceptable data loss. Hourly backups minimize loss compared to daily backups. It’s critical when a single lost patient record can exceed infrastructure costs. Multi-zone, multi-region backup strategies ensure compliance and data integrity.
Tips for Healthcare IT Infrastructure Cost Optimization
To optimize cloud-based IT infrastructure cost in healthcare without compromise, use the following best practices:
- Scheduled serverless functions for daily tasks to eliminate 24/7 server costs and pay only for execution time.
- Test environment automation to disable development systems during off-hours and weekends when unused.
- Tiered storage to move archived data accessed monthly to cost-effective storage versus high-speed databases.
- Auto-scaling to connect resources during peak demand, disconnecting during low-traffic periods.
But savings should not compromise safety and regulatory compliance. Because a mistake and savings of $1,000 can lead to a fine of $50,000. We recommend not saving on:
- data backup and replication,
- security systems and encryption,
- monitoring and alerts,
- access auditing.
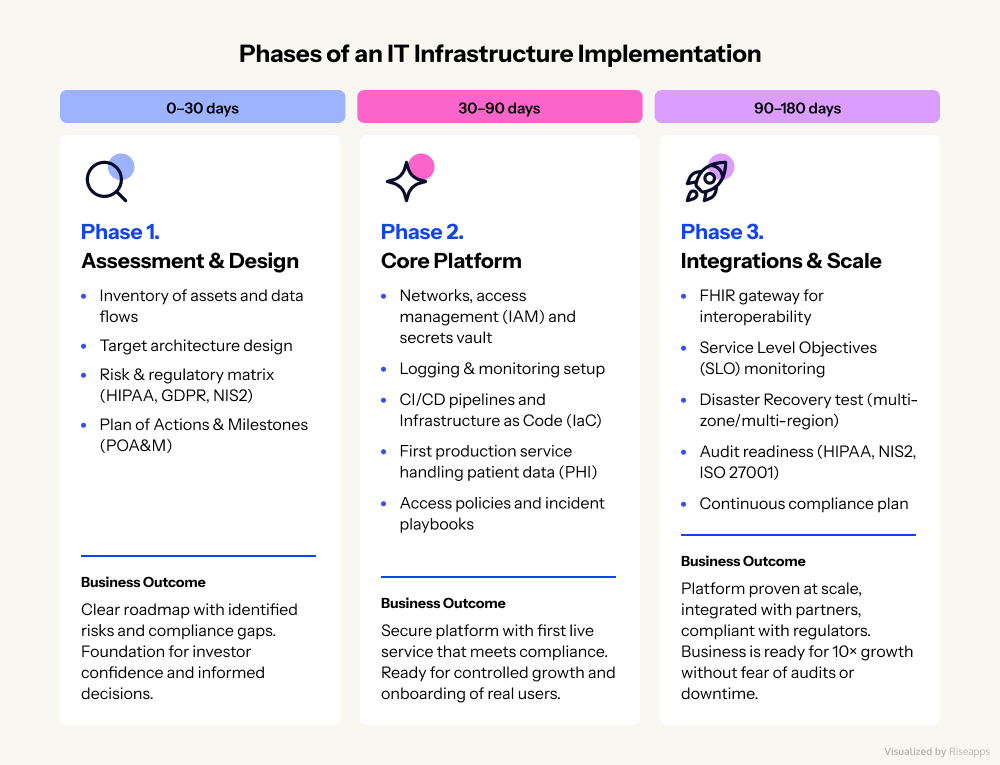
3 Implementation Phases for an IT Infrastructure in Healthcare
The growth of the healthcare business requires not only new patients and services, but also a reliable IT foundation.
That’s why we offer a 90-180 day roadmap that takes you step by step from assessment and design to a ready-to-go platform that’s integrated with partners and audit-ready. This lets you safely scale up 10× and build your business on a solid foundation.
Healthcare IT Infrastructure Solutions: Riseapps Client Success Stories
Case Study: 1. PIPRA
PIPRA AG is a Swiss AI healthcare company focused on predicting postoperative delirium risk in elderly surgical patients. Their mission is to help hospitals reduce preventable complications, improve patient outcomes, and optimize perioperative workflows through predictive intelligence.
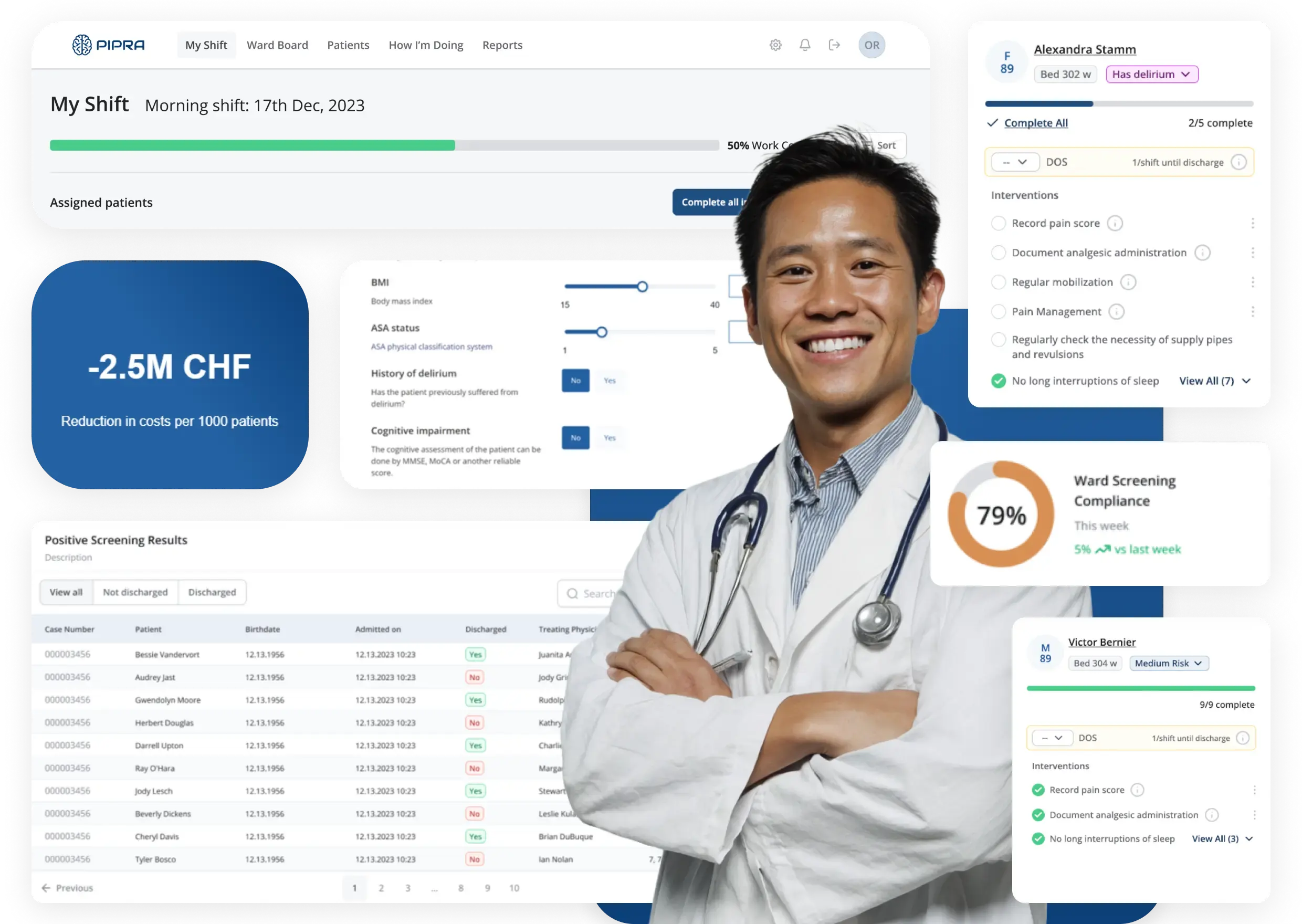
Implemented Solutions by Riseapps:
- MDR-ready AI SaaS platform: Transformed research prototype into commercial, hospital-ready web platform with authentication, comprehensive logging, and audit trails required for EU MDR compliance and regulatory deployments.
- Multi-EHR integration layer: Built flexible FHIR/HL7/CSV integration layer supporting varied hospital IT ecosystems, enabling seamless connection with multiple EHR formats across European healthcare providers.
- GDPR-compliant cloud infrastructure: Deployed secure, scalable cloud environment with data isolation for each hospital instance, ensuring regulatory safety for sensitive patient data handling.
- Clinical-grade UX/UI: Redesigned interface, featuring risk visualizations and streamlined one-screen patient summaries optimized for hospital workflows.
Project Results:
- Rapid platform delivery: Transformed prototype to deployable MDR-ready SaaS platform in under 6 months
- Multi-hospital deployment: Successfully integrated 4 EU hospitals under Horizon grant pilot program
- Onboarding efficiency: Reduced hospital onboarding time by 70% through modular integration architecture
- Grant compliance: Met tight delivery deadlines, securing $1.2M+ EU Horizon funding for clinical deployment
- Clinical validation: Facilitated pilot testing with 10-15 clinicians across multiple hospital sites
- Regulatory achievement: Delivered CE-ready platform meeting EU MDR and GDPR compliance requirements
Case Study: 2. CareHalo
CareHalo is a U.S.-based healthcare technology company specializing in chronic disease management through remote patient monitoring (RPM) solutions. Their platform enables continuous care delivery outside traditional clinical settings, reducing preventable hospital visits and improving patient outcomes.

Implemented Solutions by Riseapps:
- HIPAA-compliant RPM platform: Riseapps developed a specialized web application with role-based access control (medical assistant and provider roles) built on HIPAA-compliant infrastructure with full e-PHI protection, access control, and end-to-end data encryption.
- Scalable IT infrastructure: Riseapps built a secure, scalable backend capable of handling large volumes of sensitive health data in real-time while maintaining regulatory compliance and system performance.
- Case management system: We engineered a case-based workflow architecture featuring “case cards” that organize patient data chronologically with timestamps, vital signs, symptoms, and clinical notes for efficient high-volume data management.
- User-centric clinical interface: We designed an intuitive, adaptable UX/UI optimized for healthcare practitioners to streamline data entry, status updates, and clinical alerts.
Project Results:
- Improved patient engagement: The client achieved 77% increase in patient adherence through continuous remote monitoring capabilities
- Regulatory compliance: Delivered 100% HIPAA compliance across all infrastructure layers, data handling processes, and user access controls
- Rapid deployment: Successfully delivered enterprise-grade RPM infrastructure with a dedicated 7-person expert team
- Healthcare impact: Contributed to potential $300B annual savings for U.S. healthcare system through effective RPM implementation
Case Study: 3. Advanced Dementia Care Platform
The client is a U.S.-based at-home healthcare practice specializing in chronic condition management with a focus on dementia care, empowering healthcare providers and caregivers with tools that enhance care quality and reduce operational inefficiencies.

Implemented Solutions by Riseapps:
- Cost-effective HIPAA infrastructure: Deployed self-hosted LiveKit (telemedicine) and OpenSign (eSignatures), while maintaining secure, compliant data handling
- Scalable architecture: Modernized monolithic system into scalable infrastructure supporting growing patient volumes and complex care coordination.
- AI-powered care planning: Implemented LLM-based algorithms with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for personalized care recommendations.
- Real-time AI documentation: Integrated Deepgram voice transcription to auto-generate medical notes from calls, telemedicine, and visits with human-in-the-loop validation for HIPAA compliance.
- Automated eligibility & resources: Integrated Approved Admissions for eligibility verification and Find Help.org APIs for community resource access.
Project Results:
- Rapid deployment: Delivered complete AI-integrated ecosystem in 5 months with 6-person expert team
- Efficiency breakthrough: Reduced treatment plan generation time by 84% (4 hours to 30 minutes)
- Market-ready solution: Delivered HIPAA-compliant platform with CPT code documentation and clearinghouse integrations
- Documentation savings: Cut medical documentation time by 50% through AI automation
- Cost reduction: Achieved 40-60% operational cost savings via self-hosted infrastructure
- Workflow optimization: Improved caregiver efficiency by 35% and clinical response times by 25%
Case Study: 4. The Wound Pros
The Wound Pros is a U.S.-based, AI-powered wound care management company and Medicare Part B biller. As a DMEPOS-accredited provider, they offer full-cycle wound care from treatment to supply management, merging high-touch clinical care with high-tech solutions to revolutionize chronic wound management.
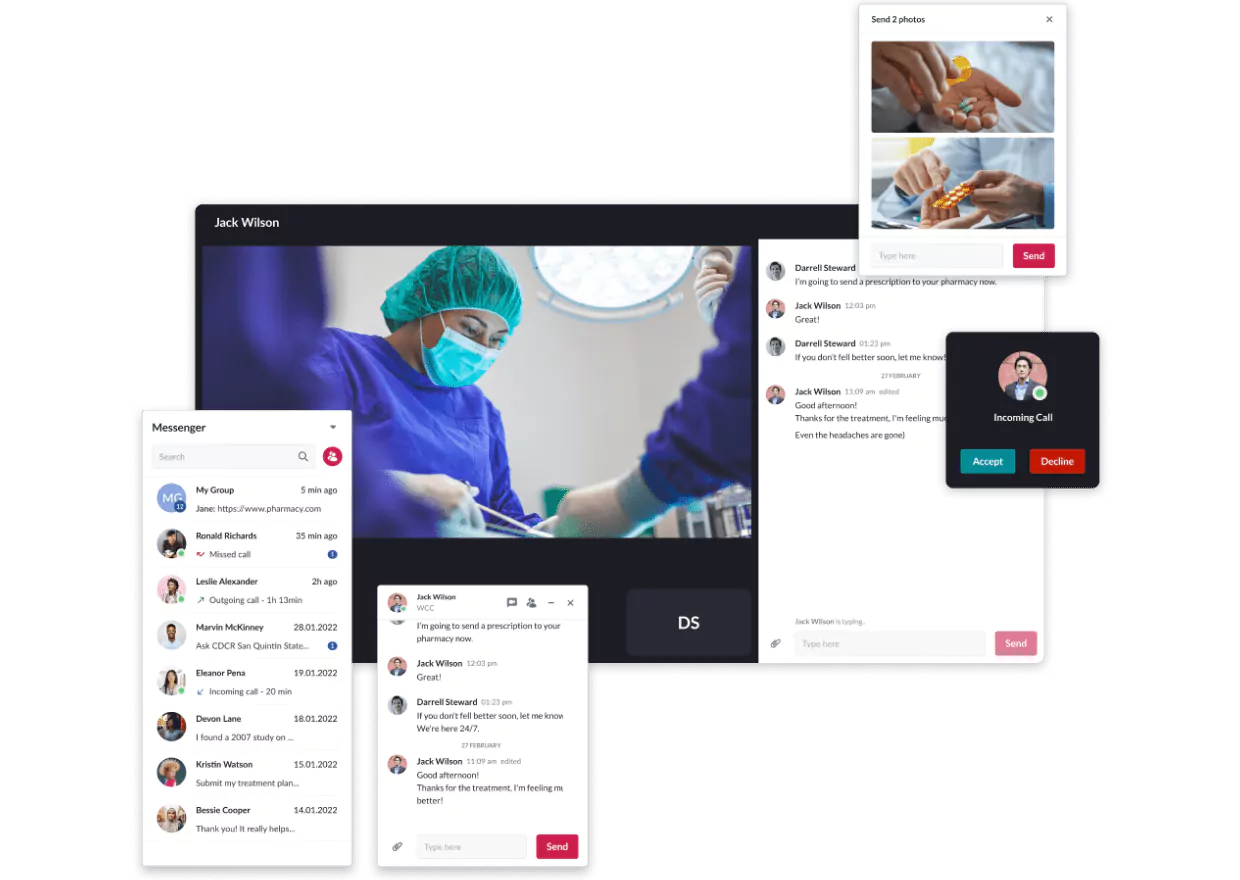
Implemented Solutions by Riseapps:
- Cloud-based platform migration: Transitioned from manual SmartSheet operations to an automated, scalable web-based platform streamlining documentation, PHI tracking, and clinical workflows with multi-device compatibility.
- Mobile clinical application: Developed robust iOS/Android app enabling nurses to schedule appointments, communicate in real-time, manage patients, and visualize routes for remote care coordination.
- Supply chain & facility management system: Built centralized modules for ordering, warehouse logistics tracking, facility profile management, and permissions-based access control.
- Analytics & reporting infrastructure: Implemented dashboards for appointment tracking, patient healing rates, location-based analytics, and consultant performance monitoring.
Project Results:
- Comprehensive system delivery: Designed and delivered 120+ workflows for wound care management professionals with 8-person expert team
- Digital transformation: Successfully migrated from manual SmartSheet to modern cloud-based automation system
- Enhanced accessibility: Achieved seamless multi-device compatibility improving usability for clinical staff
- Clinical productivity: Boosted consultant efficiency through real-time mobile coordination and communication tools
- Scalable infrastructure: Built future-ready platform supporting rapid company growth and expansion
How to Calculate the Total Cost of Ownership and ROI for Healthcare IT Infrastructure?
Healthcare IT investments extend beyond infrastructure. They encompass regulatory compliance, patient trust, and market velocity. Therefore, Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and Return on Investment (ROI) calculations must account for technology, licensing, audits, security, and their impact on Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), Lifetime Customer Value (LTV), and feature delivery speed.
Let’s compare common TCO models. Traditional on-premise requires large upfront capital expenditures (CapEx) for equipment that rapidly becomes obsolete and non-scalable. Cloud infrastructure has predictable monthly operational expenses (OpEx) that scale with business growth, including:
- EHR integration licenses
- Compliance audits (HIPAA, GDPR, NIS2)
- 24/7 security monitoring (SOC, alerting)
Also, a well-built infrastructure directly impacts key business metrics like:
- Lower CAC: standardized FHIR connectors and API gateways accelerate clinic/hospital integrations, reducing acquisition friction.
- Higher LTV: reliable, secure systems increase patient retention and partner confidence, eliminating data breach concerns.
- Faster time-to-market: automated scaling and Infrastructure as Code (IaC) deliver new features in weeks versus months, maintaining competitive advantage.
In addition, your security investment may vary by stage:
Early stage (Seed/Series A) should have an essential baseline: MFA, data encryption, audit logging, regular backups, and employee security policies. It demonstrates investor responsibility while mitigating critical risks.
Growth Stage (Series B+) should have more advanced requirements as patient/partner volume scales:
- Security Operations Center (SOC)
- Automated incident detection
- Multi-region backups
- External audit certification (HIPAA, NIS2, ISO 27001, HITRUST)
Properly architected healthcare IT infrastructure transforms from cost center to growth accelerator. Transparent TCO modeling, quantified ROI, and stage-appropriate security prioritization signal to investors that your organization scales responsibly.
Why Riseapps for Healthcare App Development
Riseapps delivers ISO 27001/9001 and HIPAA-certified healthcare software development services to medical providers, clinics, and tech startups. We build custom AI-powered solutions from scratch, customize existing products, and engineer secure, interoperable electronic health/medical record platforms that centralize every clinical note, lab result, and care plan.
Besides that Riseapps offers:
- Express IT infrastructure audit in just 2 weeks with a personalized remediation plan and NIS2/GDPR/HIPAA risk map.
- Basic HIPAA/GDPR-compliant platform development in 6-8 weeks (with IaC, logs, IAM, backups, DR plan).
- FHIR/EHR integration package with SLA agreement.
Want to build a secure healthcare solution with scalable architecture?
FAQ
What is infrastructure in healthcare?
Healthcare infrastructure encompasses the physical facilities, technology systems, networks, data centers, and IT platforms that support clinical operations, patient care delivery, electronic health records management, and seamless communication between healthcare providers, patients, and administrative systems.
What are the 7 components of IT infrastructure?
The 7 components of IT infrastructure are: hardware (servers, computers), software (applications, operating systems), networking (routers, firewalls), data storage and management, cloud services, security systems, and IT support services.
What are the three main IT infrastructures?
The three main IT infrastructures are: On-Premises Infrastructure (owned and managed locally), Cloud Infrastructure (third-party hosted services), and Hybrid Infrastructure (combination of on-premises and cloud resources), each offering different levels of control, scalability, and cost efficiency.
Contact Us








