Aspiring edtech entrepreneurs envision achieving unicorn status akin to Amazon, Uber, and Instagram. However, success in e learning app development is fraught with challenges, including competition, market saturation, evolving trends, technological advancements, time constraints, and limited funding.
A significant proportion of online learning startups (90%) fail, amplifying the pressure to avoid being out-competed. To increase the likelihood of success, initiate with a minimum viable product (MVP) to validate market demand before committing extensive resources.
Though seemingly straightforward, MVP development poses complexities, prompting questions such as: How do I build my elearning app? Should I use custom or low-code/no-code development? What are the must-have features of my edtech product? How much effort do I need to put into my product?, and how much time would I invest in development?
This article delves into various elearning app examples, offering a thorough process for online learning solution development while examining the pros and cons of low-code and custom methods.
6 Types of eLearning Apps: From MOOCs to Accelerators
Remote learning apps can be broadly classified into three types according to their purpose and the target audience served. Let’s discuss them and give some examples.
Massive Open Online Courses (MOOC)
The success of MOOCs, however, depends on aligning their offerings with sound pedagogical principles, as per Hancock. He believes the sector must do more to be sustainable, with Moocs focusing on engagement retention and lifetime learning to become the preferred platform.
Such an app represents a modern and innovative approach to democratizing education, providing learners with access to comprehensive and high-quality academic resources on a global scale. These digital education platforms offer diverse courses, from basic subjects to advanced, specialized topics.
FutureLearn’s new CEO, Andy Hancock, sees potential for online course providers to attract students seeking business education beyond traditional MBAs.
Typically, MOOCs are created by esteemed educational institutions, industry experts, and renowned organizations to ensure the highest standards of content quality. The market is projected to experience remarkable growth, surpassing a valuation of $48.4 billion by 2033. With an impressive compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.2%, the MOOC sector demonstrates substantial potential for expansion, reflecting the increasing demand for accessible, high-quality educational apps in the online education industry.
Coursera is an example of a MOOC.
Coursera, a hybrid platform, embodies the original MOOCs’ spirit while building a significant business. With over $300 million in venture funding, it provides access to 4,000+ online courses created by university professors and companies like Google and IBM.
Coursera’s CEO, Jeff Maggioncalda, compares the virtual learning site to a “managed marketplace” similar to Apple’s app store. Coursera decides which institutions can publish courses and sets format and pricing guidelines. Degree courses have a 60-40 revenue split favoring universities, while certificate courses in technology and business maintain a 50-50 split.
Learning Management System (LMS)
An online LMS is a sophisticated digital space designed to streamline the delivery, administration, tracking, and reporting of educational content, courses, and training programs. As a comprehensive solution, LMSs are commonly utilized in various sectors, including education, corporate education, and professional development.
TJ Hoffman, COO at Sibme, a professional learning software for educators, highlighted the benefits of integrating such platforms like Canvas and Schoology.
He noted that after integrating Sibme with Canvas for a major university in Texas, user engagement surged by 70%, demonstrating the remarkable impact of LMS integration on learning experiences.
The LMS market, as per MarketsandMarkets, is anticipated to reach $25.7 billion by 2025, with an impressive CAGR of 28.2%. This growth stems from the increasing need for cost-effective, engaging, and scalable learning solutions across educational institutions and enterprises.
TalentLMS is an example of an LMS.
TalentLMS is an online learning platform valued at $12 million, that effortlessly facilitates the delivery of exceptional learning courses to employees, partners, customers, or students. Ideal for offline learning, micro-learning, and micro-certifications, the learning app focuses on providing rich, mobile-optimized courses without replicating the entire web-based experience.
Cohort-based Learning Platforms
Cohort-based online learning platforms are a novel approach to online education, enabling users to engage in groups or “cohorts” under the guidance of expert instructors. The idea is to simulate a traditional learning experience with added flexibility.
According to Wes Kao, one of Maveen’s co-founders, content is no longer king in online ed —cohorts are.
Her recent tweet highlights top company execs developing courses on Maven.
In contrast to conventional online learning, which often lacks social interaction and structure, cohort-based learning apps boast completion rates exceeding 90%, compared to a meager 3% for self-paced courses. These elearning solutions foster community and accountability by synchronizing course timelines irrespective of how many students are within a cohort.
Maven is an example of a cohort learning platform.
Maven is a new online learning platform for cohort-based courses started by Udemy, altMBA, and Socratic founders.
In November 2020, Maven raised $4.3M in a round led by First Round Capital. Maven, an innovative cohort-based course platform established by Udemy, altMBA, and Socratic founders, secured $4.3 million in funding led by First Round Capital in November 2020.
Corporate Training Apps
In alignment with the Elearning Industry report, 39% of small businesses implement classroom-led training, 25% utilize blended learning techniques, and 17% employ virtual classrooms. Corporate training apps epitomize a state-of-the-art solution for professional development and skill augmentation within organizations, incorporating advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and adaptive learning algorithms to provide employees with personal learning and efficient training experiences.
Bronson Ledbetter, VP of Financial Services at the University of Phoenix, emphasizes the importance of utilizing various tools and practices to assess training impact, establish multiple feedback loops, and modify programs accordingly.
GOLearn is an example of a corporate training app.
GOLearn is one of several quick and affordable mobile learning apps for organizations to train, test, and track employees, students, customers, or vendors. This mobile learning app is a part of the Courseplay Cloud Learning Platform and requires an active login ID.
Bootcamps
Bootcamp platforms offer concentrated, short-term programs, primarily in technology and programming domains, providing practical, hands-on learning with collaborative projects and expert guidance. As an alternative to traditional education, boot camps attract individuals aiming to pivot careers or enhance new skills.
Course Report states that while university computer science programs span four years and cost around $163,140, yielding an average income of $59,124, coding bootcamps last approximately 14 weeks with an average tuition of $11,874, making them a time-efficient and cost-effective option.
Coders Lab is an example of a Bootcamp.
Grzegorz Morawski, Global Development Manager at Coders Lab IT Academy, highlights the growth of programming schools in Poland since their inception six years ago.
According to Marcin Tchórzewski, founder of Coders Lab, approximately 5,000 Poles enroll in programming courses yearly.
With at least a dozen such institutions, thousands of graduates are being produced annually. Coders Lab expects to train around 2,000 juniors in 2019, a 40% increase compared to the previous year.
Community-Based Learning Apps
In a 2021 study by McKinsey & Company, the efficacy of online learning technology in fostering interactivity during the pandemic was assessed. The market research indicated a 19% average uptick in the utilization of learning technologies since the onset of COVID-19, with the most significant growth observed in group work, connectivity, and community building.
Community-based learning apps epitomize a dynamic educational approach, catalyzing collaboration and engagement within an elearning application.
Tom Ross, CEO of Design Cuts says communities mature like relationships. The initial phase may be exciting, but the deep connections and sustainable cadence that sets in later are so satisfying.
Acquiring knowledge on these online learning platforms through social learning empowers users, deliberate on ideas, and collaboratively problem-solve. Key features such as discussion forums, chat groups, and peer feedback systems foster interaction and mutual support, amplifying collective intelligence and optimizing educational outcomes.
Mighty Networks is an example of a learning community app.
Mighty Pro, an exclusive online learning community for select Mighty Pro Hosts, concentrates on fostering business expansion on Mighty Networks. The mobile app grants members access to mastermind groups, community engagement masterclasses, and specialized resources, facilitating rapid learning and prompt adaptation in response to new data and insights. As reported by TechCrunch, Mighty Networks secured $50 million in Series B funding in 2021.
Acceleration Programs
Accelerator programs, characterized by their highly structured and time-bound nature, cater to early-stage startups, expediting growth and development. With durations spanning three to six months, these programs supply resources, mentorship, and capital to accelerate progress and market readiness.
Emphasizing the significance of mentorship, DigitalOcean’s co-founder, Mitch Wainer, suggests startup founders should seek guidance instead of merely bootstrapping their businesses.
As per the 2020 Global Accelerator Report, 11,722 startups participated in accelerator programs worldwide, amassing over $1.3 billion in total investment.
Y Combinator and Kickstarter are examples of accelerators
As of July 2021, Y Combinator, a Californian seed money startup accelerator, emerged as the most active in the United States, boasting 3,777 investments by mid-2021. On the other hand, Kickstarter is a creative project funding platform facilitating connections between creators and the public via its website and mobile platforms.
Statista reports that, as of February 2023, most successfully funded Kickstarter projects raised between $1,000 and $10,000, totaling nearly 30,000 projects in this category. Additionally, 696 projects successfully raised over $1 million on the platform.
Basic & Advanced (Post-MVP) Features of eLearning Solutions
In the context of e-learning app development, basic and advanced features can be delineated based on the complexity, functionality, and level of user engagement they offer. Basic features on an elearning mobile app typically encompass essential functionalities that lay the foundation for an e-learning app. These fundamental components establish the groundwork for a functional and straightforward learning experience. Complex features, on the other hand, involve more intricate capabilities that enhance user interaction, personalization, and overall learning outcomes.
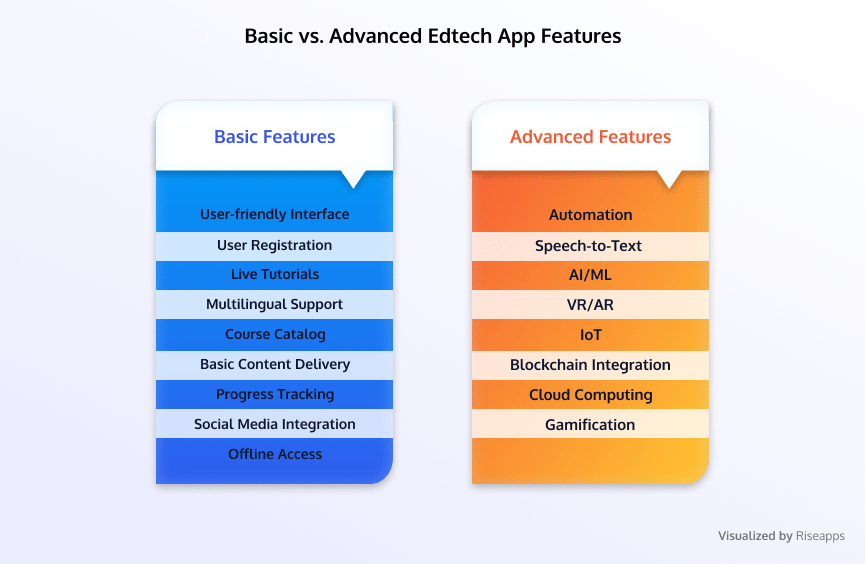
Basic Features to Integrate on Mobile Apps
User-Friendly Interface
A user-friendly UI/UX in e-learning apps ensures intuitive navigation, appealing design, and strong aesthetics to maintain user engagement. Simplifying the interface and including only relevant features prevents users from becoming overwhelmed and enhances the overall learning experience.
User Registration
A vital aspect of e-learning apps, user registration facilitates secure and personalized access, often employing mechanisms such as Single Sign-On (SSO) and role-based access control for streamlined user management.
Live Tutorials
Incorporating live tutorials and sessions into e-learning apps addresses student grievances in real time, fostering a virtual learning environment where students practice and teachers interact and discuss different learning materials or topics and promoting a complete communication cycle.
Multilingual Support
For an online learning platform to cater to its global target audience, e-learning apps should provide multilingual support for major world languages, enhancing the app’s accessibility and usability for international users.
Course Catalog
The course catalog is a well-organized and searchable directory of each learning material available, enabling efficient navigation and discovery of courses, modules, and resources based on subject matter or expertise level.
Basic Content Delivery
Central to e-learning apps, this feature ensures the efficient presentation of learning materials in various formats (text, images, video lessons, audio) while adhering to instructional design best practices and catering to diverse learning preferences.
Progress Tracking
Progress tracking on an online education app offers learners a glimpse into their advancement through courses and modules, allowing them to monitor progress, identify improvement areas, and stay motivated. Concurrently, it enables instructors or administrators to evaluate learner performance and engagement, informing data-driven decisions and particular course adjustments. Skillshare and Canvas have progress-tracking features.
Social Media Integration
Social media integration is a crucial e-learning app feature, enabling users to create accounts and log in through platforms like Google, Facebook, Twitter, and Pinterest. Admins can also leverage social media to reach a larger target audience by establishing a presence on platforms with a high user base.
Offline Access
This feature ensures continuous learning experiences in e-learning apps, allowing users to download educational materials and resources for offline use. By enabling offline access, learners can engage with content regardless of internet connection, thus promoting flexibility and accommodating various learning situations.
Advanced Features to Consider
Automation
Streamlining administrative tasks and content personalization, automation enhances the efficiency and efficacy of e-learning platforms by adapting to individual learners’ needs and minimizing manual intervention. Docebo, TalentLMS, and Absorb LMS are some elearning apps that leverage automation.
Speech-to-Text
By converting spoken language into written text, this feature supports accessibility and diverse learning preferences, enabling users to engage with content in multiple formats. Examples of educational platforms with speech-to-text are Gboard (Google’s keyboard app with speech-to-text functionality) and Voice Dream Reader.
AI/ML
Artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities enhance e-learning platforms by powering personalized learning experiences, predictive analytics, and adaptive course recommendations based on learners’ behavior and performance. Examples of AI/ML-engineered software include Quillionz (AI-powered question generator) and Knewton (adaptive learning platform).
VR/AR
Virtual and augmented reality technologies enrich the learning experience by enabling immersive, interactive, and experiential learning, simulating real-world scenarios, and fostering a deeper understanding of complex subjects. You can find VR/AR capabilities on Unimersiv (VR learning platform) and Mondly (AR language learning app).
IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) enables the integration of interconnected devices, sensors, and data sources, enhancing the learning experience by providing contextual, real-time feedback and promoting a seamless, multi-device learning environment. McGraw-Hill Education Connect (integrates with IoT devices for data collection) and ClassDojo (integrates with smartboards and other classroom devices) are two ed techs using IoT.
Blockchain Integration
Leveraging distributed ledger technology, blockchain offers secure, transparent, and verifiable credentials management, streamlining the validation and sharing of learners’ achievements and skills. Blockcerts (open standard for creating, issuing, viewing, and verifying blockchain-based certificates) and Woolf University (blockchain-powered online university) are blockchain-inspired online classes.
Cloud
The cloud-based architecture allows e-learning platforms to scale, remain accessible, and securely store data, enabling seamless content delivery, cross-platform compatibility, and flexible infrastructure management. Google Classroom and Blackboard Learn currently host their elearning premise using the cloud infrastructure.
Gamification
Incorporating game design elements into the learning experience, gamification promotes learner engagement at their own pace, motivation, and retention by transforming educational content into an interactive and enjoyable experience. Duolingo (language learning platform) and Kahoot! (game-based learning platform) standout because of their gamification features.
eLearning Mobile App Development: Custom Vs. No-Code/Low-Code
Low-code development platforms empower you to make elearning applications through a user-friendly, drag-and-drop visual interface, utilizing pre-made modules that seamlessly interact with one another. These low-code/no-code platforms, as the first generation of rapid tools for mobile app development, enable individuals without programming experience to create business elearning applications efficiently.
On the other hand, custom app development involves creating software applications tailored to specific business needs and user groups. These personalized applications address the unique requirements of users, differentiating them from conventional, off-the-shelf software applications. Custom software is often developed to bridge the gap between existing solutions and the desired features, providing a more comprehensive and targeted solution for users.
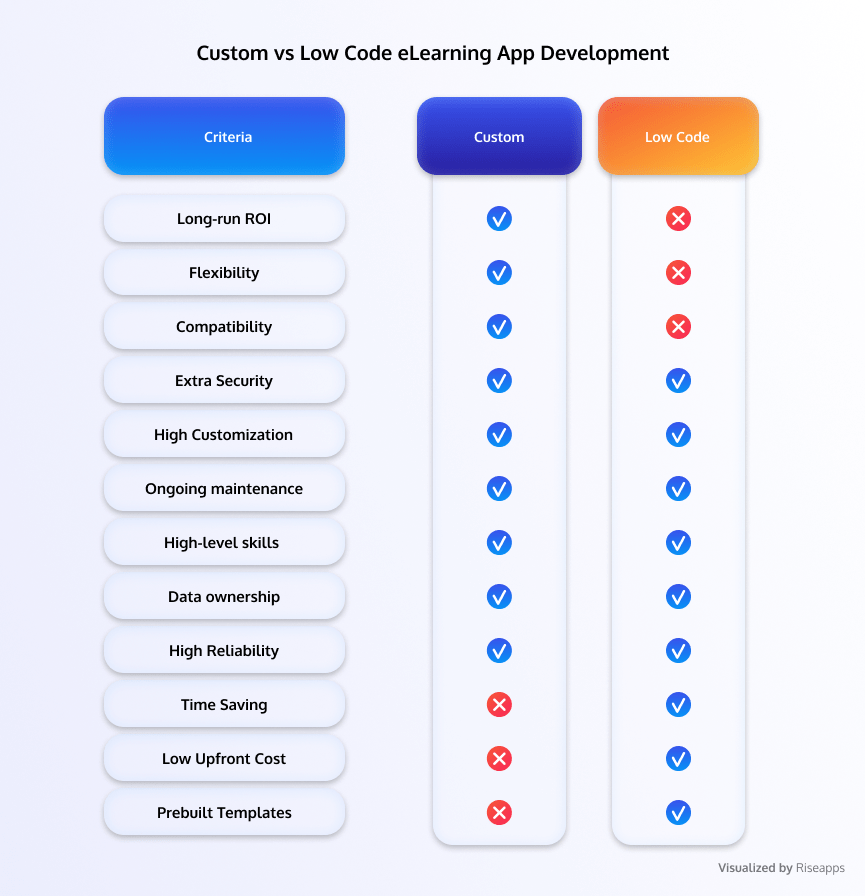
Low-Code vs Custom E-learning Apps: Pros & Cons
Low-Code eLearning App Development Pros:
- Reduced time and cost
- Easy to use
- Pre-built templates and integrations
- Scalable and flexible
- Faster prototyping and iterations
- Simplified maintenance and updates
Cons:
- Limited customization
- Restrictions on functionality
- Possible security risks
- Performance limitations
- Dependency on provider roadmap
- Difficulty integrating with legacy systems.
Custom eLearning App Development Pros:
- Complete control
- Tailored user experience
- No restrictions on customization
- Higher performance and scalability
- Greater flexibility to integrate
- Potential for competitive advantage.
Cons:
- Higher cost
- Greater technical expertise required
- Longer time to market
- Complex maintenance and updates
- Need for ongoing technical support
- Risk of project failure or scope creep.
OutSystems and Appian exemplify low-code platforms for app creation, whereas custom-developed platforms address specific organizational and learner needs through in-house teams or contracted developers.
Best Instances for Custom Development
Scalable & Feature-rich Solutions
Custom development suits organizations requiring scalable learning apps with tailored features, ensuring adaptability to growing and evolving needs, such as advanced LMS for large enterprises.
Specialized & Industry-specific Apps
A bespoke approach is ideal for highly specialized, industry-specific apps requiring modern features, integrations, and customizations, like medical training platforms with VR/AR simulations.
Optimal Conditions for Low-Code Implementation
Rapid Prototyping & Validation
Low-code development enables quick MVP or prototype creation for concept validation and feedback without significant resource investment, like testing new language learning apps.
Limited Budget & Expertise
Applying minimal coding is apt for organizations with budget constraints and minimal technical expertise, empowering non-technical professionals to create functional apps, such as simple onboarding apps for small businesses.
Approaching Each Scenario
Here are the steps involved in low code development of eLearning apps.
Define requirements
Start by clearly outlining the application’s business needs, user requirements, and objectives. This step ensures that the final product will effectively address the specific problem or functionality you aim to solve or provide.
Choose a low-code platform
Select a suitable low-code platform that aligns with your requirements, budget, and technical expertise. When deciding, consider factors like ease of use, scalability, integration capabilities, and platform support.
Design the user interface
Utilize the visual interface provided by the low-code platform to design the application’s user interface (UI). Low-code platforms simplify this process and include drag-and-drop features and pre-built UI components.
Configure data models
Define the data models and structures that will be used within the application. Many low-code platforms offer visual modeling tools that enable you to create, edit, and manage data models without writing complex code.
Set up business logic
Implement the business logic and processes that dictate how the application functions. Use the platform’s built-in tools and components to define workflows, rules, and algorithms that govern application behavior.
Integrate with external systems
Connect your low-code application with other systems, such as databases, APIs, or third-party services. Low-code platforms often provide pre-built connectors and integration tools to simplify this step.
Test the application
Conduct thorough application testing to ensure its functionality, performance, and security meet the defined requirements. Many low-code platforms include testing tools and features that can help streamline this process.
Deploy the application
Once the application has been tested and refined, deploy it to the target environment, such as a cloud server, on-premises server, or mobile application store.
Monitor and maintain
After deployment, monitor the application’s performance and usage, addressing any issues and implementing updates or improvements as needed.
Iterate and scale
Continuously iterate on the application, incorporating user feedback and scaling the solution as your business needs evolve. Low-code platforms often simplify updating and expanding applications, allowing faster and more efficient iterations.
OutSystems and Appian exemplify low-code platforms for app creation, whereas custom-developed platforms address specific organizational and learner needs through in-house teams or contracted developers. Here’s how to go about it.
Requirement Analysis
Thoroughly analyze and document the specific needs of the eLearning app, including target audience, educational objectives, and desired features, to create a clear vision for the project.
Design and Architecture
Develop a comprehensive blueprint for the app’s structure, layout, and user experience, considering UI/UX best practices, accessibility, and compatibility with various devices and platforms.
Technology Stack Selection
Choose the most suitable programming languages, frameworks, databases, and tools to build a robust, scalable, and secure eLearning app.
Development Process
Utilize agile methodologies and iterative development cycles to incrementally build the learning app, incorporating regular feedback from stakeholders, subject matter experts, and potential users.
Functional testing
This focuses on verifying that the application’s features, functionalities, and components are working as intended according to the specified requirements. Functional tests are typically initiated during the early stages of the mobile or software app development life cycle (SDLC) and continue throughout the development process. Examples of functional testing include:
- Unit testing
- Integration testing
- System testing
- Acceptance testing
Non-functional testing
On the other hand, this type of testing assesses the application’s performance, usability, reliability, and other attributes that contribute to the overall user experience. Non-functional testing typically starts after the functional testing phase once the application’s core features have been implemented and verified. Examples of non-functional testing include:
- Performance testing
- Load testing
- Stress testing
- Security testing
- Usability testing
Deployment and Integration
Launch the eLearning app on the appropriate platforms and integrate it with relevant third-party services, such as learning management systems, analytics tools, or payment gateways.
Post-launch Support and Maintenance
Provide ongoing technical support, address user feedback, and release updates to fix bugs, improve performance, and introduce new features, ensuring the elearning mobile app remains relevant and competitive in the e-learning app market.
Why Riseapps is Worth a Peek: eLearning App Development Cases
Riseapps is a full-cycle edtech development company that focuses on creating innovative elearning solutions. We ensure a smooth client experience during the SDLC by fostering clear communication channels, involving clients in decision-making, and utilizing agile project management for adaptability and iterative development. Our success is evident in our accomplished projects.
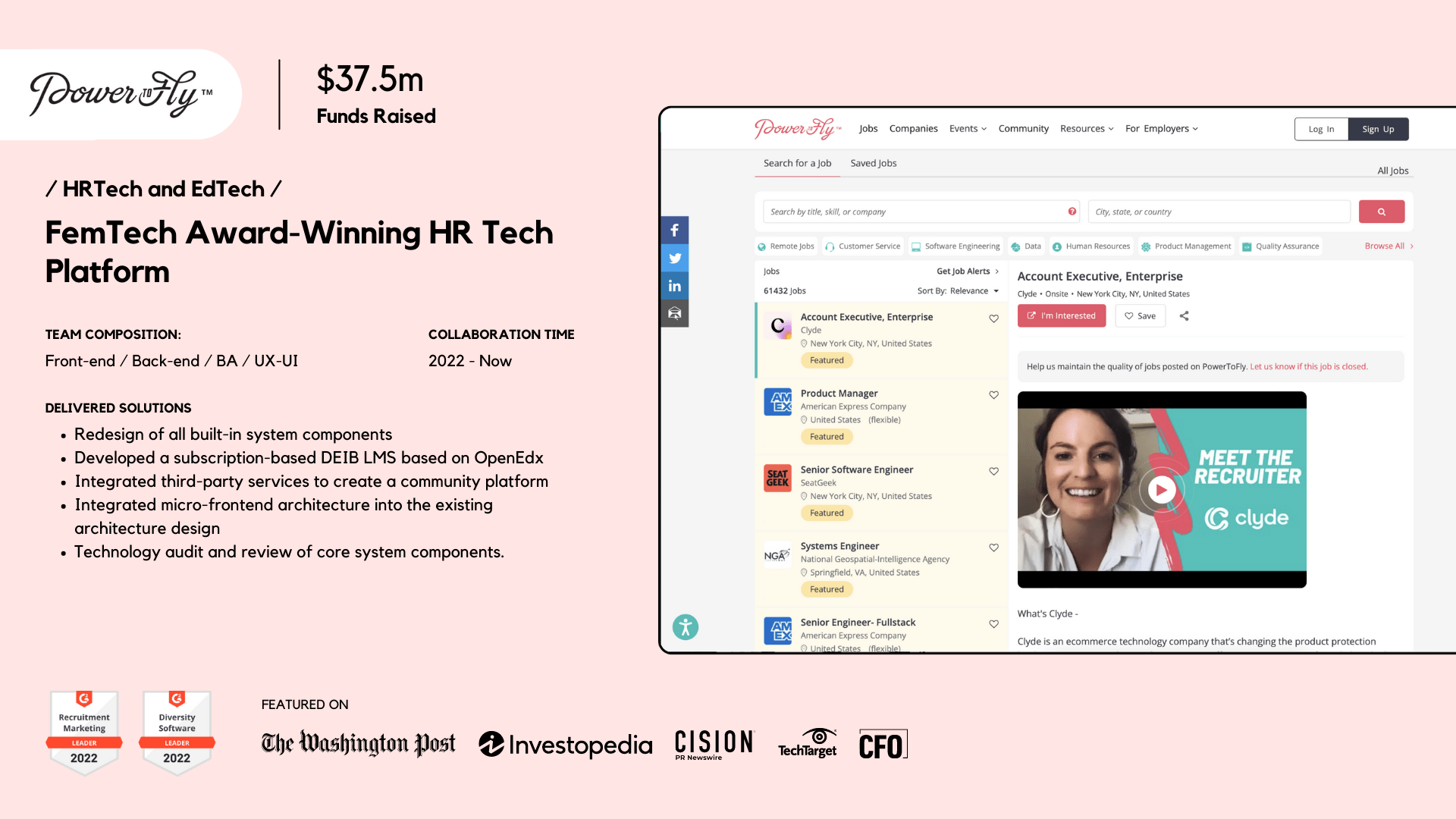
PowerToFly
PowerToFly, a renowned platform for Diversity and Inclusion (D&I) professionals in the B2B EdTech space, is one of the beneficiaries of our elearning application development services.
- We created a subscription model DEIB LMS based on OpenEdx.
- Redesigned the system components in their built-in corporate training platform.
- Integrated external services into the community platform.
- As a result of our services, PowerToFly secured $37.5M in funding and won the trust of global giants like Google, Amazon, Siemens, Facebook, and StackOverflow.
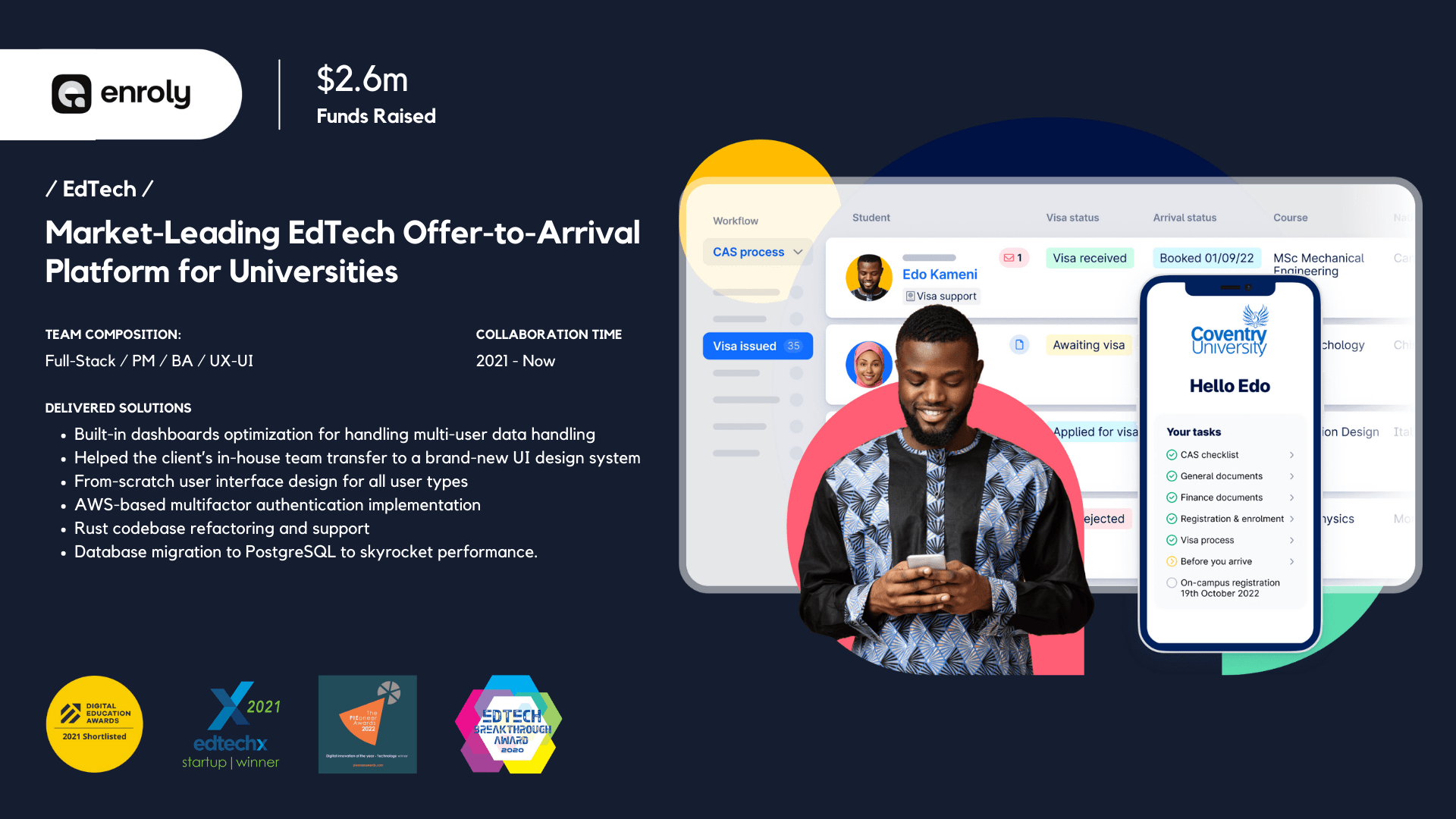
Enroly
Enroly is one of the market leaders in the Edtech space. Their offer-to-arrival university platform annually helps more than 150,000 international students in the UK.
Riseapps executed an app development project for Enroly and delivered the following solutions:
- We optimized the built-in dashboards to manage multi-user data effectively.
- Transferred the in-house team to a new and more functional UI design system.
- Created a user interface design from scratch to cater to all user types.
- Implemented a multi-factor authentication based on AWS to optimize security.
FAQ
What is an e-learning platform?
An e-learning platform is a destination for those who need or want to acquire new knowledge in the fastest way possible. It’s usually a website with a library of courses by individual accredited instructors or academic institutions.
How to build an online learning platform?
There are six main steps to create your own e-learning platform:
- Select the platform type
- Choose a monetization strategy
- Decide on the functionality
- Create a solid UX/UI design
- Develop your platform
- Launch
How to make money with an e-learning platform?
There are many ways to monetize your platform, including paid courses, paid certificates, subscriptions, corporate cooperation, affiliate model, and donations.
What is the best tech stack for an e-learning website?
Here are some of the commonly used frameworks and languages for such a website: JavaScript, Typescript, PHP, React, Angular, HTML, CSS for the frontend and Python, Django, Node.js, MySQL, AWS for the backend.
How much does it cost to develop an e-learning platform?
The price tag for an online learning platform depends on three main variables: the complexity of the project, the number of developers in your team, and their hourly rate. For example, if there are six team members with a $50/hour rate who have to complete 1500 hours of work in total, the final cost would be $75,000.
If you have any further questions about how to build an online learning platform, don’t hesitate to contact us.
FAQ
What is an e-learning platform?
An e-learning platform is a destination for those who need or want to acquire new knowledge in the fastest way possible. It's usually a website with a library of courses by individual accredited instructors or academic institutions.
How to build an online learning platform?
There are six main steps to create your own e-learning platform:
- Select the platform type
- Choose a monetization strategy
- Decide on the functionality
- Create a solid UX/UI design
- Develop your platform
- Launch
How to make money with an e-learning platform?
There are many ways to monetize your platform, including paid courses, paid certificates, subscriptions, corporate cooperation, affiliate model, and donations.
What is the best tech stack for an e-learning website?
Here are some of the commonly used frameworks and languages for such a website: JavaScript, Typescript, PHP, React, Angular, HTML, CSS for the frontend and Python, Django, Node.js, MySQL, AWS for the backend.
How much does it cost to develop an e-learning platform?
The price tag for an online learning platform depends on three main variables: the complexity of the project, the number of developers in your team, and their hourly rate. For example, if there are six team members with a $50/hour rate who have to complete 1500 hours of work in total, the final cost would be $75,000.
If you have any further questions about how to build an online learning platform, don't hesitate to contact us.
Contact Us






