25 LMS Features to Engage, Train, and Retain Students and Employees in 2025

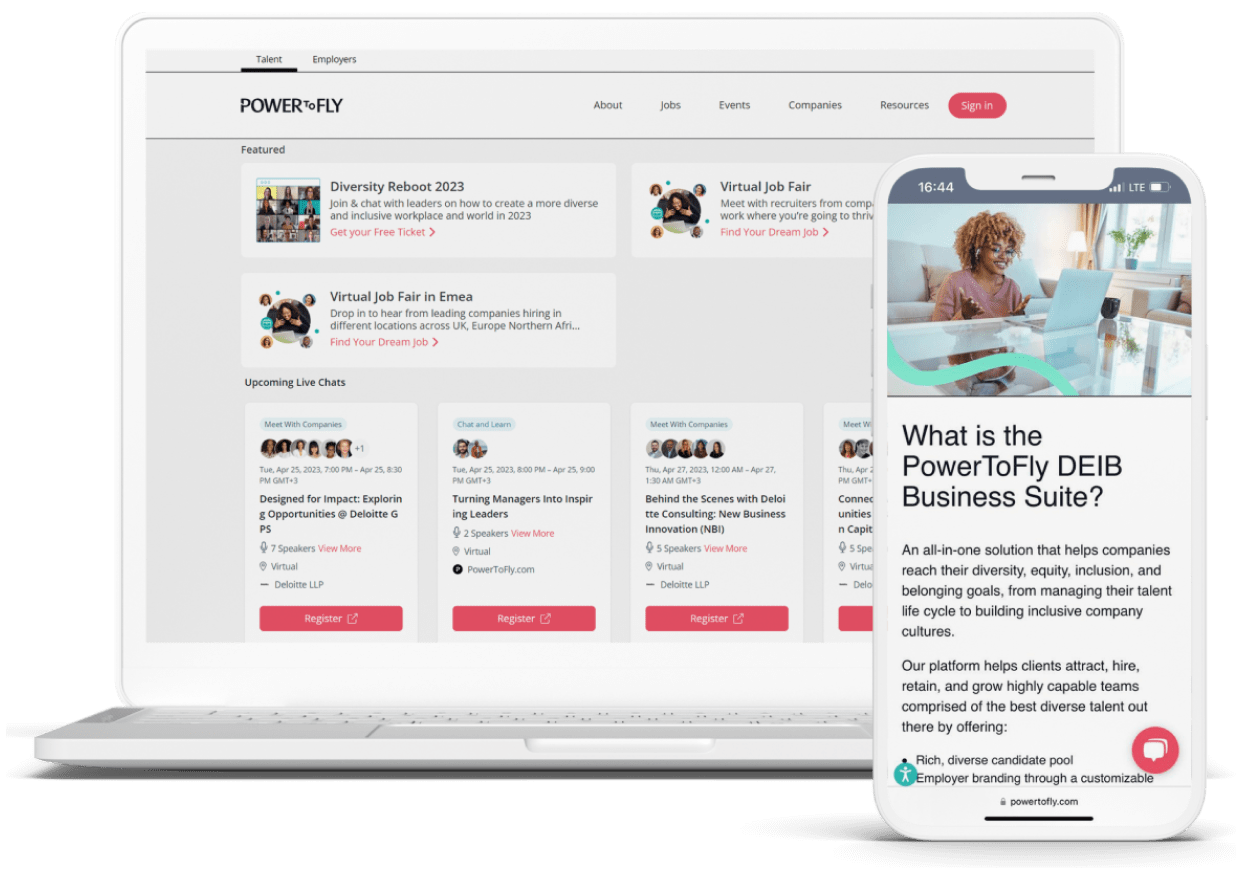
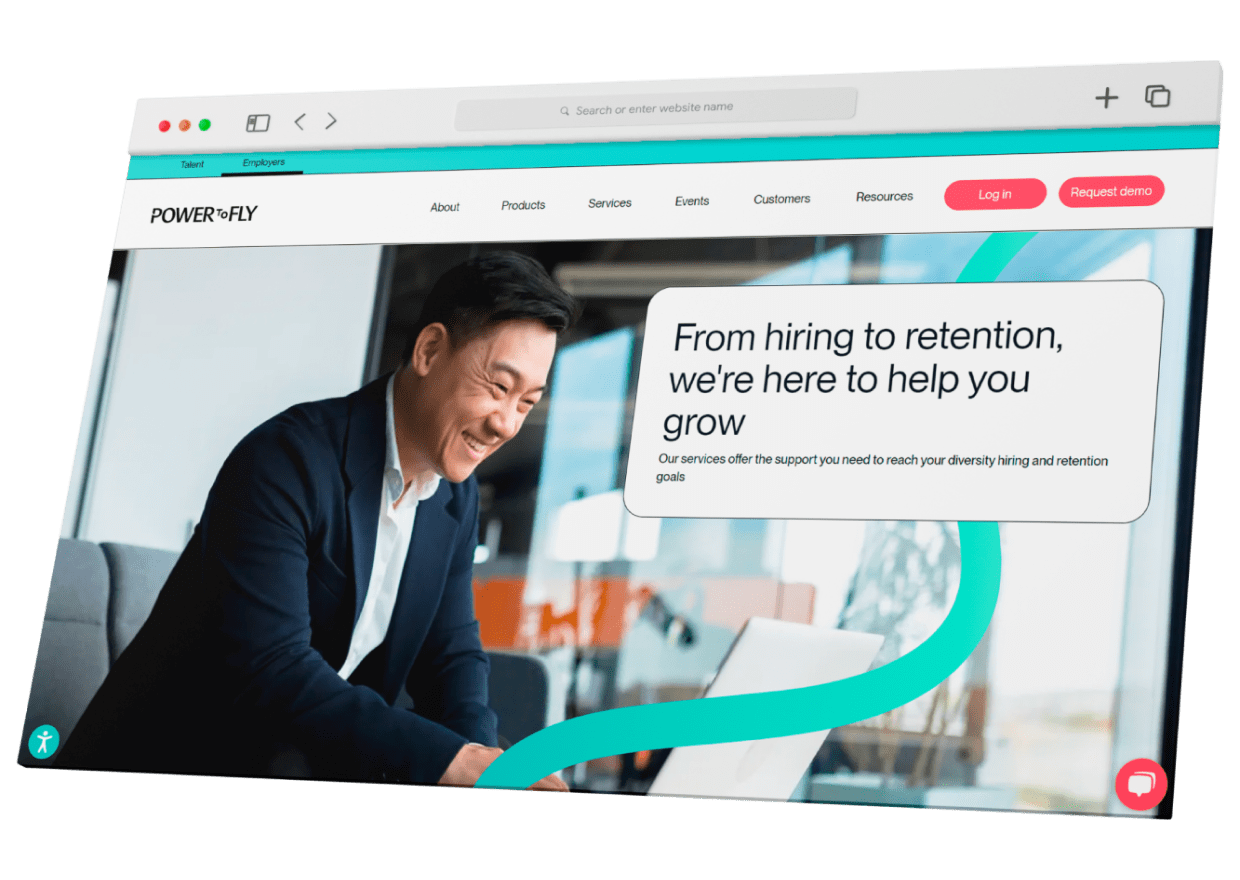
Whether you’re developing a solution for employee onboarding, professional upskilling, or remote classrooms, the features you choose for your learning management system (LMS) will define the platform’s value from day one. Riseapps helped PowerToFly expand their market reach to top-tier enterprises such as Facebook and Amazon, thanks to a wide range of relevant B2B features in a corporate LMS platform.
In this guide, we break down 25 essential LMS features and benefits — grouped into core functionality, engagement and personalization, scalability, and admin tools. We’ll show how each LMS features checklist contributes to a high-performing platform, referencing real LMS projects we’ve delivered at Riseapps and the best practices of global EdTech leaders.
Why organizations are turning to LMS platforms
Let’s take a closer look at the core issues driving LMS adoption in both business and academic environments and how the right features can directly address them.
Identifying corporate needs
The best way to identify corporate organizations’ educational needs is to analyze what challenges they’re currently facing. If your company experiences the problems listed below, you definitely need a learning management system:
- Fragmented employee training. New hires require structured onboarding. Teams need continuous upskilling. But when learning happens via scattered documents, spreadsheets, or Zoom recordings, tracking who learned what and when becomes nearly impossible. Managers often receive incomplete or outdated progress reports, limiting their ability to assess team readiness.
- High and repetitive training costs. Live training sessions come with recurring costs: speaker fees, travel, venue rental, printed materials, and they must be repeated every time a new hire joins. The average cost to train a new employee can reach almost $1,300 (Indeed).
- Inconsistent learning experiences. Without a structured agenda, employees may drag out training. A course designed for 2 weeks stretches into 2 months, diminishing its impact. Disconnected experiences lead to fragmented knowledge retention.
- Disorganized learning materials. In large organizations, training assets live in dozens of folders across SharePoint, Google Drive, or legacy tools. Outdated PDFs mix with current policy slides. The result? Confusion and low adoption.
Identifying the education system’s needs
Digitally enhanced learning and teaching (DELT) tools and solutions are used in 75% of institutions across the European Higher Education Area (The DIGI-HE project co-funded by the Erasmus+ Programme of the European Union). Still, challenges remain, and a well-designed LMS can solve them.
- Outdated or inconsistent course content. Teachers struggle to keep course material updated across multiple tools. Some institutions still rely on PDFs, email threads, and outdated portals that aren’t built for real-time edits or version tracking.
- Admissions and onboarding under pressure. Many schools still use in-person exams or paperwork-heavy enrollment. In a post-COVID world, that’s no longer sustainable, especially when recruiting international students or offering online degree programs.
- Unequal access to online learning. Not every student has a high-end laptop or constant internet access. Digital divide challenges still affect more than 20% of students in rural parts of Europe (Eurostat).
- Social isolation in online classrooms. Educators worry that online classes reduce peer-to-peer interaction. A lack of live communication can lead to disengagement, loneliness, and lower academic performance.
How a learning management system solves common issues found in organizations
For big corporations that seek e-learning solutions for staff training, learning management system features help centralize monitoring progress, save money on in-person seminars, and increase employees’ engagement rates.
A centralized learning management system automates tracking, sends real-time performance data to team leads, and ensures no learner falls through the cracks. LMS platforms offer timed modules, built-in quizzes, and gamification tools that help learners stay accountable and interested. LMS feature list covers:
- progress control,
- content centralization,
- analytics and reporting,
- personalized learning paths for employees, etc.
For schools and universities, LMS functionality can provide tools for quick content creation and task assessment. The LMS system features can include social learning to give students the power of teamwork.
1–10 features: Key features of LMS for a seamless learning experience
These LMS features form the functional foundation of any learning management system. Without them, your learning management system can’t deliver structured, measurable, or scalable education. Let’s break them down:
1. Content and course management
At the heart of any LMS is the ability to build and deliver training content. A robust system must support all major formats — video, audio, and PDFs — and let educators structure that content into courses, chapters, and lessons.
Key functionality includes:
- Drag-and-drop course builder
- Support for SCORM/xAPI packages
- Rich media embedding (YouTube, Vimeo, presentations)
- Content tagging and search
Riseapps example: In the PowerToFly LMS, DEIB-focused (diversity, equity, inclusion, belonging) course creators could quickly create lesson templates, upload assets, and publish new modules. This was essential for scaling across their major corporate clients like Facebook, Amazon, and Google.
Also seen in: Canvas, Thinkific, Open edX.
2. User management
Your learning management system must allow admins to manage user roles, permissions, and organizational structures, whether it’s a company with departments or a school with classes.
Core elements:
- Role-based access control (learners, instructors, reviewers, admins)
- Manual or bulk user enrollment
- CSV import/export
- Group and cohort management
Riseapps example: In LMS for schools, we created a system that facilitates the management of different user roles—teachers, students, and parents—allowing for tailored access and interactions within the platform.
Also seen in: Moodle (very granular permissions), TalentLMS (group-based assignments).
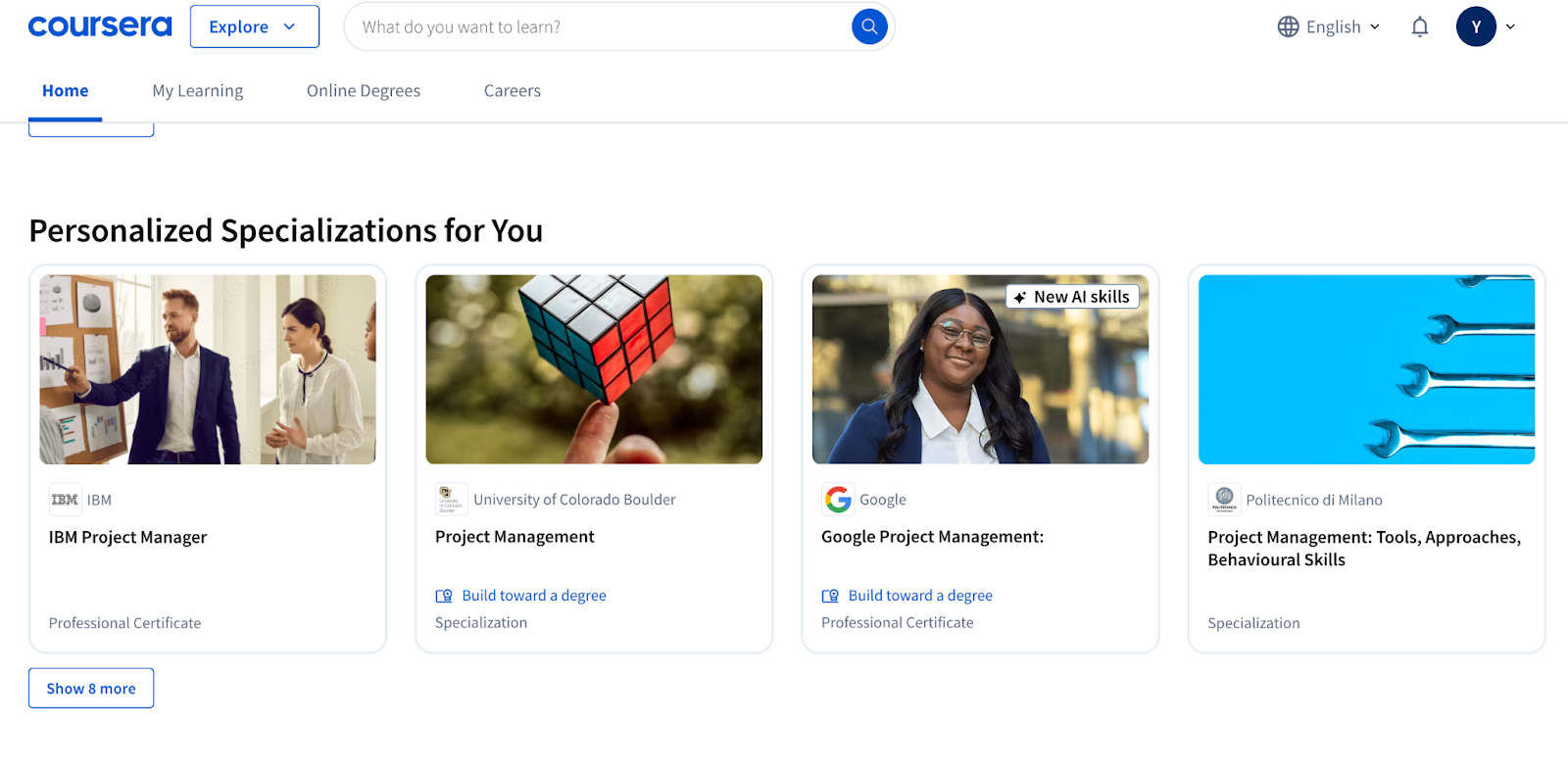
3. Learning paths and course modules
Rather than standalone courses, most platforms now offer learning paths — sequences of courses or lessons unlocked step-by-step based on progress or rules.
Key use cases:
- Sequential module completion
- Prerequisite enforcement
- Certification tracks
Riseapps example: On PowerToFly, learning paths could be customized per client company.
Also seen in: Coursera (specializations), Teachable (course bundles), Moodle (conditional activities).

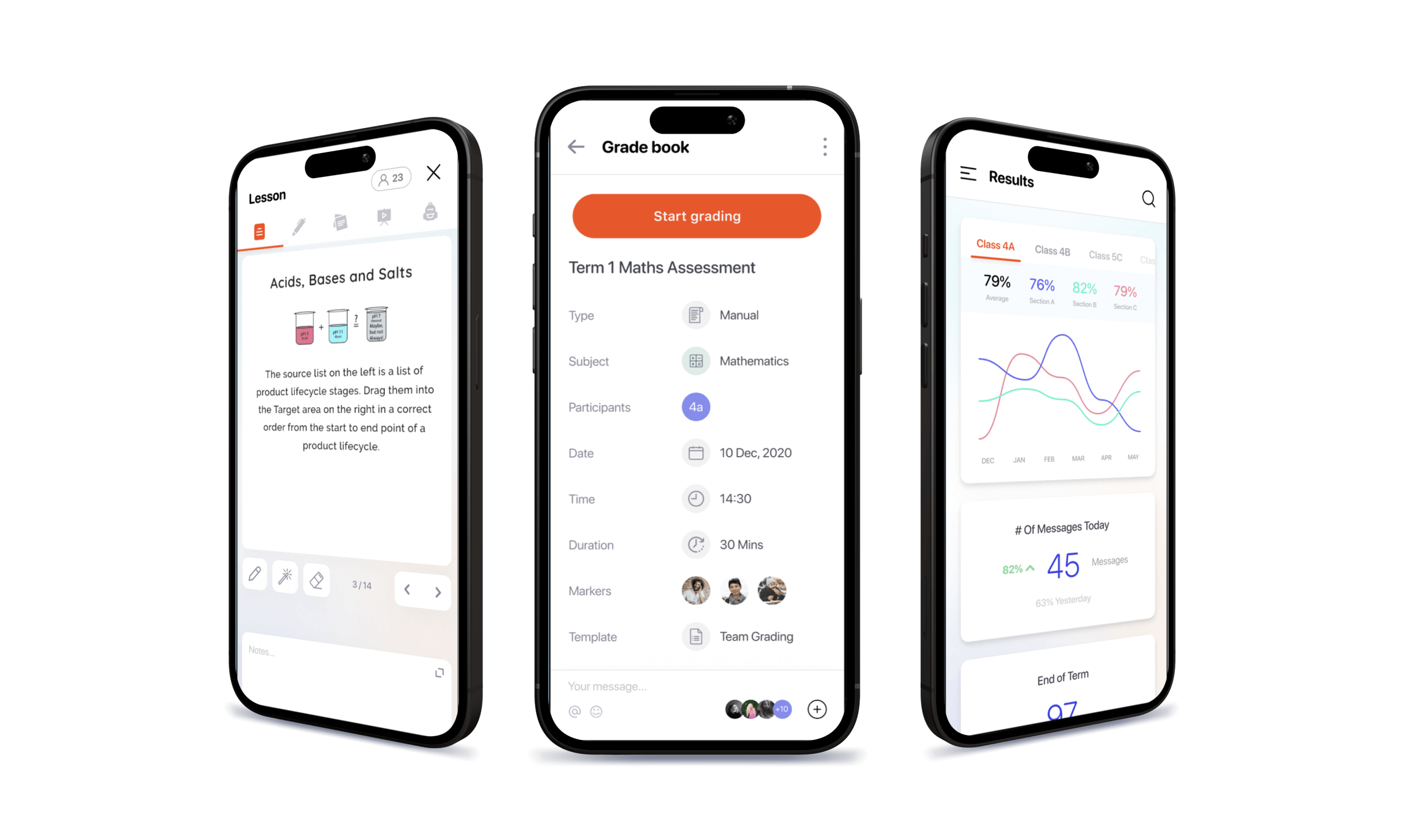
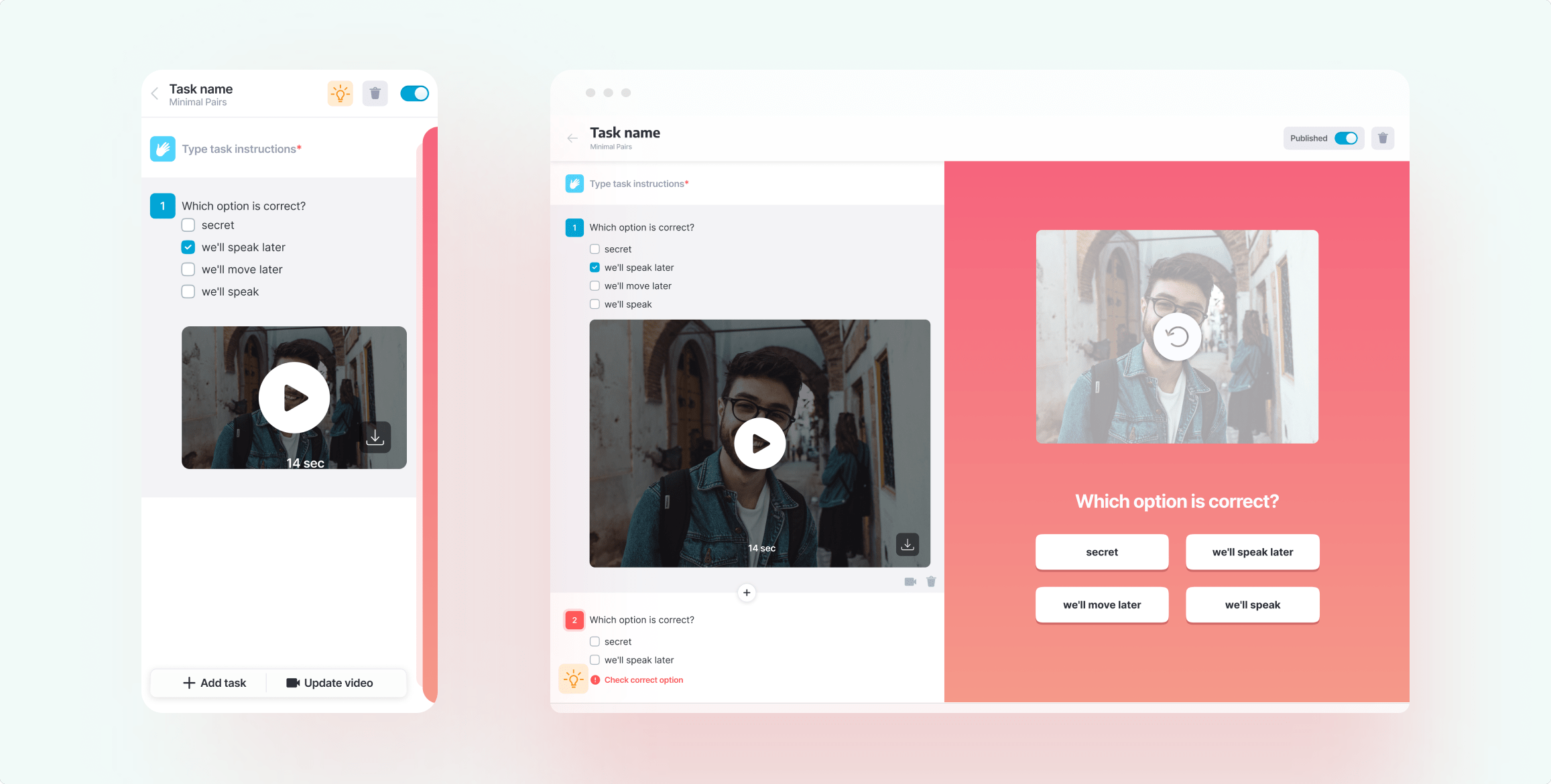
4. Assessments and quizzes
Testing comprehension is essential. Your LMS software features should include tools to create various types of quizzes and exams, from self-checks to final evaluations.
Feature checklist:
- MCQs, short answers, drag-and-drop, matching, and multimedia questions
- Randomized question pools
- Time limits and pass thresholds
- Auto-grading with feedback
- Manual grading with comment options
Riseapps example: In our language learning LMS, we minimized the onboarding steps to allow students to start their language level assessment right away.
Also seen in: Moodle, LearnWorlds, Edmodo
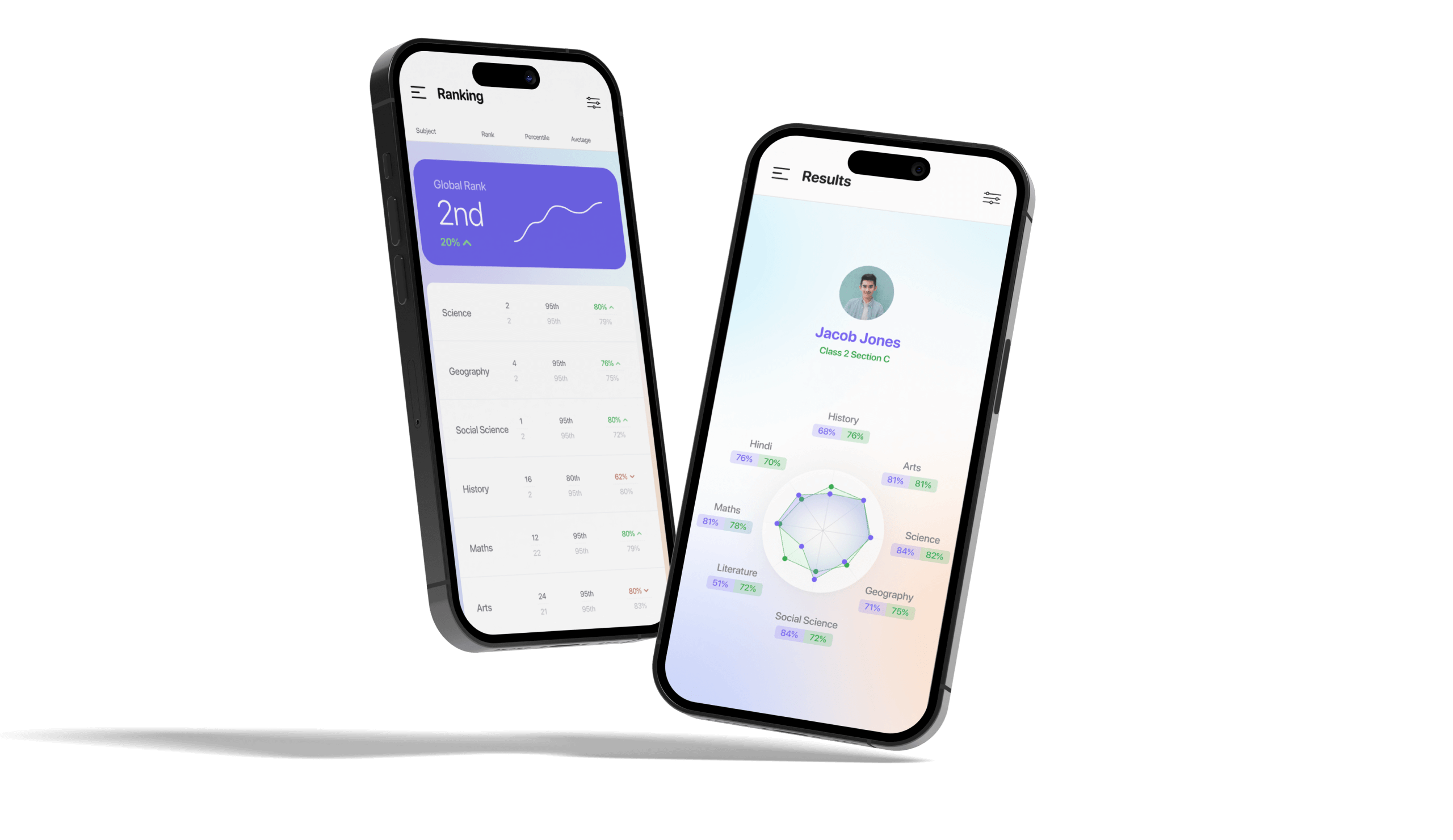
5. Progress tracking and reporting
A learning management system without reporting is like a car without a dashboard. Admins should be able to track learner activity, identify struggling users, and optimize content based on results.
Core metrics include:
- Course completion rates
- Quiz scores and attempts
- Time spent on content
- Active/inactive users
- Heatmaps of user engagement
Riseapps example: A learning management system for schools included advanced LMS reporting features with easy-to-configure dashboards to provide learners and admins with an opportunity to evaluate training progress and build customized reports.
Also seen in: Docebo (AI-driven analytics), Canvas (instructor analytics dashboard)
6. Certificate generation
Issuing branded, trackable certificates is a key feature for both employee training and academic LMSs. These should be auto-generated and customizable.
Must-haves:
- Dynamic data (learner name, course name, date)
- Company/school logo
- Downloadable PDF
- QR code or unique verification link
Riseapps example: In PowerToFly, we built a certificate engine that produced compliance-ready certificates.
Also seen in: Udemy, TalentLMS, EdApp
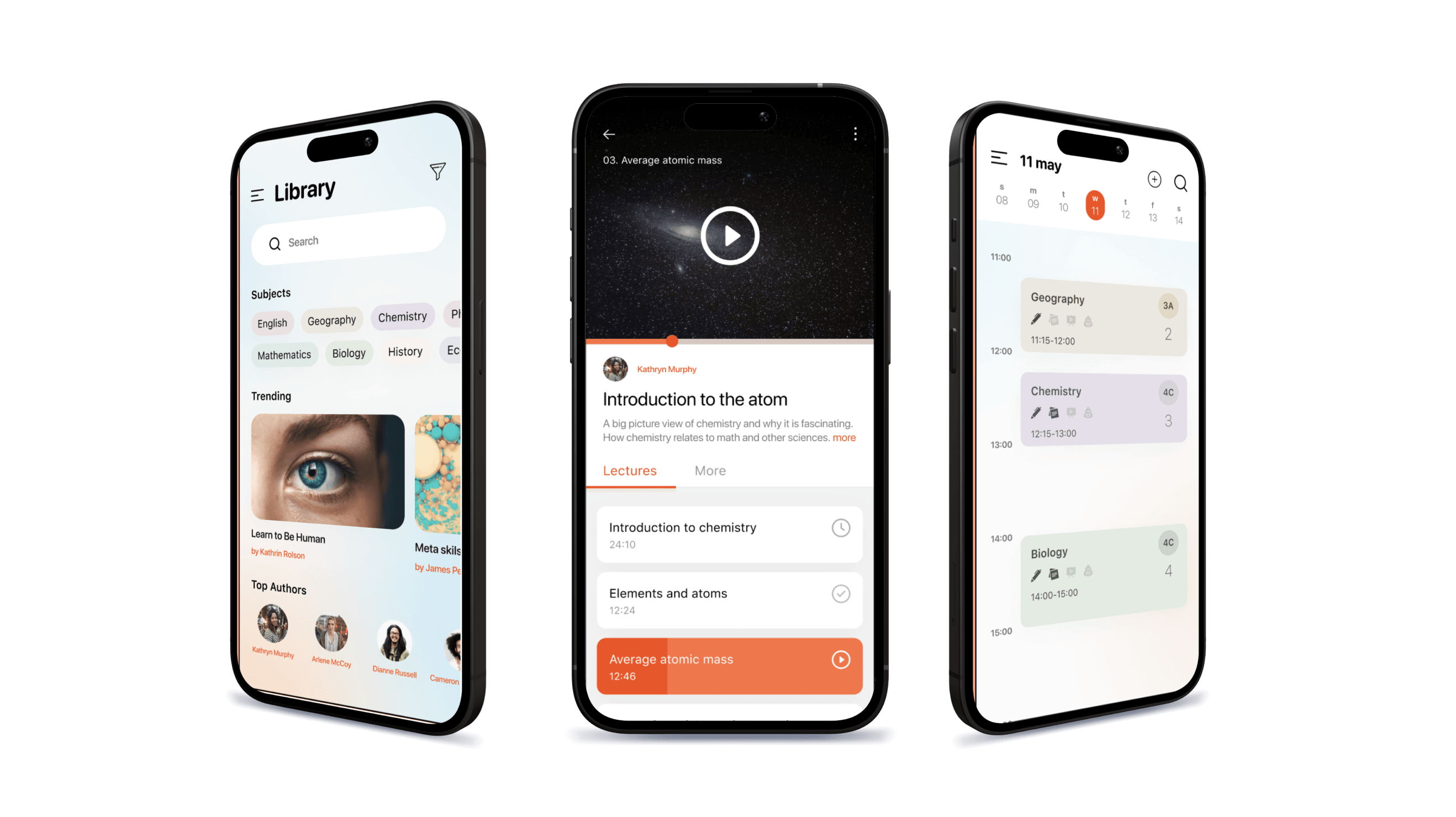
7. Mobile learning (responsive or native app)
In 2025, mobile learning will continue gaining traction and winning over users. According to Statista, a language learning mobile app, Duolingo, has reached $32 million in revenue in 2024.
Key options:
- Mobile-optimized web app
- Native app with offline mode and push notifications
- Full feature parity with desktop
Riseapps example: For the school-focused LMS, we used React Native and Flutter to build Android and iOS apps that allowed students to easily complete assignments at home and on the go.
Also seen in: Moodle Mobile App, Coursera, Rise (by Articulate)
8. Offline access
Offline learning is crucial for users in areas with limited or unreliable internet access, from students in rural schools to healthcare workers and field technicians. Without it, continuous learning becomes impossible in disconnected environments.
Required capabilities:
- Downloadable lessons, videos, and files for offline access
- Local data storage with automatic sync upon reconnecting
- Error handling and progress caching to prevent data loss
Use cases: Rural education programs, military or emergency training programs, oil and gas field workers, and humanitarian organizations.
Example: Khan Academy’s mobile app allows users to download videos and exercises for offline study. Learners can complete lessons offline, and their progress is synced when they go back online — a critical feature for the platform’s global education mission, especially in underserved regions.
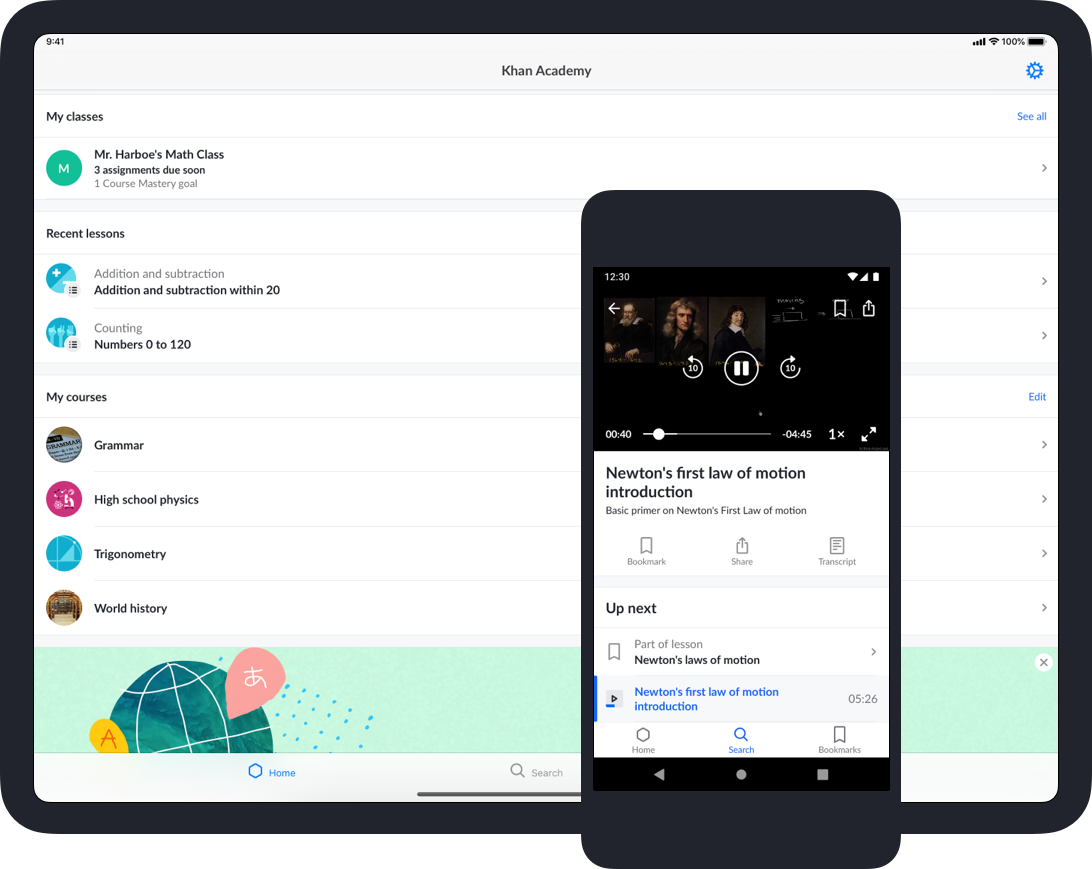
Also seen in:
- TalentCards: Offers complete offline training modules, especially designed for frontline workers.
- Edmodo: Supports offline assignments for students in areas with inconsistent internet.
9. Content versioning
As training courses evolve, instructors need the ability to update materials while retaining access to previous versions for audits, compliance, or reusing past structures.
Feature checklist:
- Draft and publish modes
- Automatic version tracking with timestamps and user attribution
- Rollback options to previous versions
- Change logs and content diffs
Example: Canvas LMS allows instructors to view the full history of any course page, including edits and who made them. You can restore earlier versions with one click, making it easier to fix mistakes or revisit prior content.

Also seen in:
- Moodle: Via plugins such as Content Versioning, which offer audit trails and revision logs.
- Rise 360: Provides robust version control for course creators using their authoring tool.
10. Multilingual support
Global learning platforms — or even regional ones with diverse populations — must provide multilingual capabilities for both UI and content delivery. This is especially important for public education, NGOs, and platforms with international reach.
Key features:
- Interface language switching for users
- Right-to-left (RTL) language support for Arabic, Hebrew
- Segmented course libraries based on user location or preferences
- Translation workflows and content duplication tools
Example: Open edX supports multilingual user interfaces, allowing each learner to select their preferred language. Course content can also be localized or duplicated in multiple languages, which is why the platform has been adopted by large institutions like MIT, Harvard, and various UN training programs.
Also seen in:
- Moodle: Features over 100 language packs, with strong community translation support.
- Thinkific: Supports multilingual content with site-level localization and multi-language course options.
11–18 features: Engagement, personalization, and motivation
The main challenge when developing an LMS isn’t just getting users to sign up — it’s keeping them engaged. For instance, a case study by TalentLMS highlighted how Wider Circle achieved a 56% increase in learner engagement by using TalentLMS’s AI course creator and ready-made courses.
The following LMS platform features are designed to withstand this head-on, turning passive users into active participants.
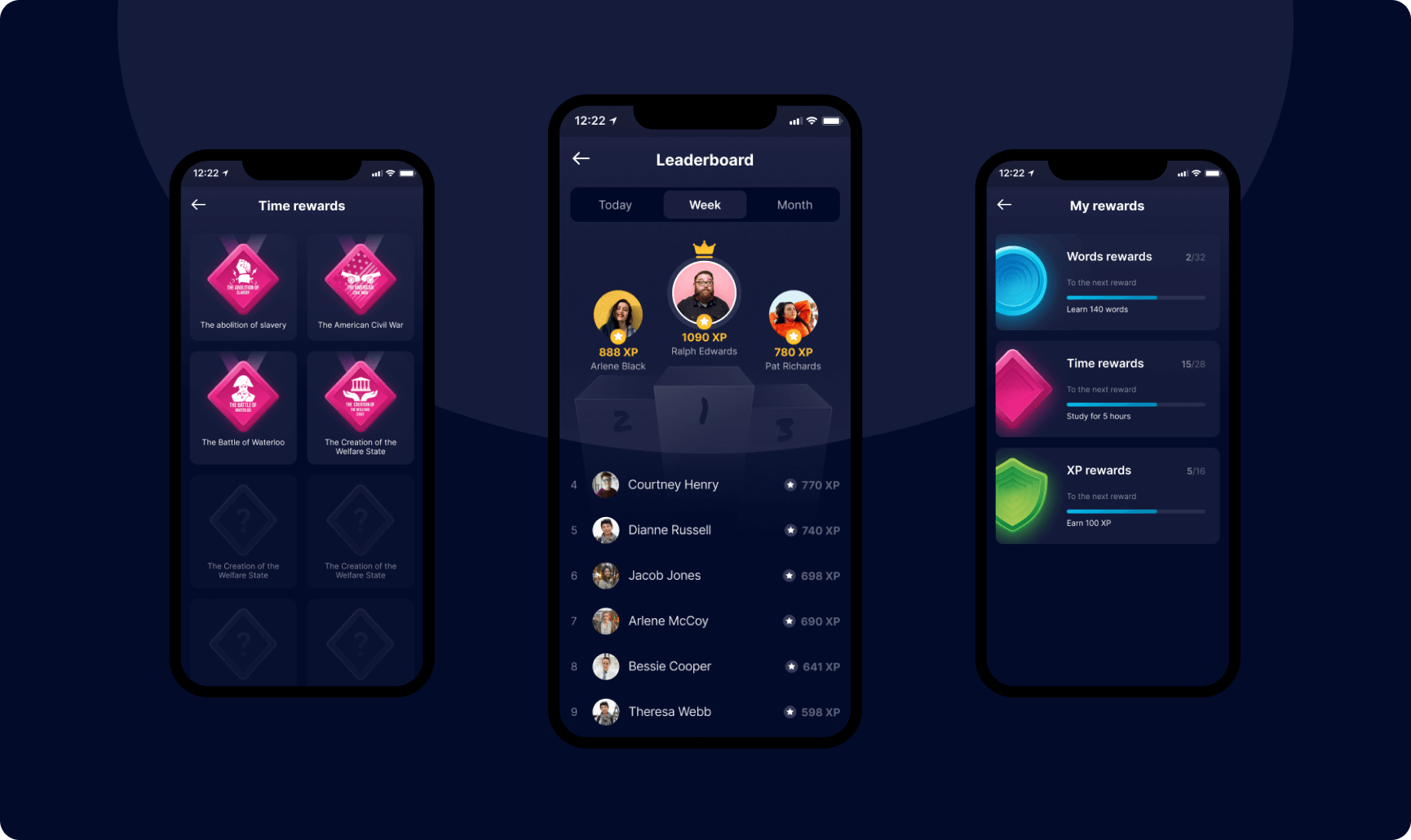
11. Gamification
Gamification adds fun, structure, and achievement incentives to the learning process. An LMS with a gamification feature should provide interactive tasks, levels, and leaderboards, virtual rewards, and points to create healthy competition and a positive learner experience.
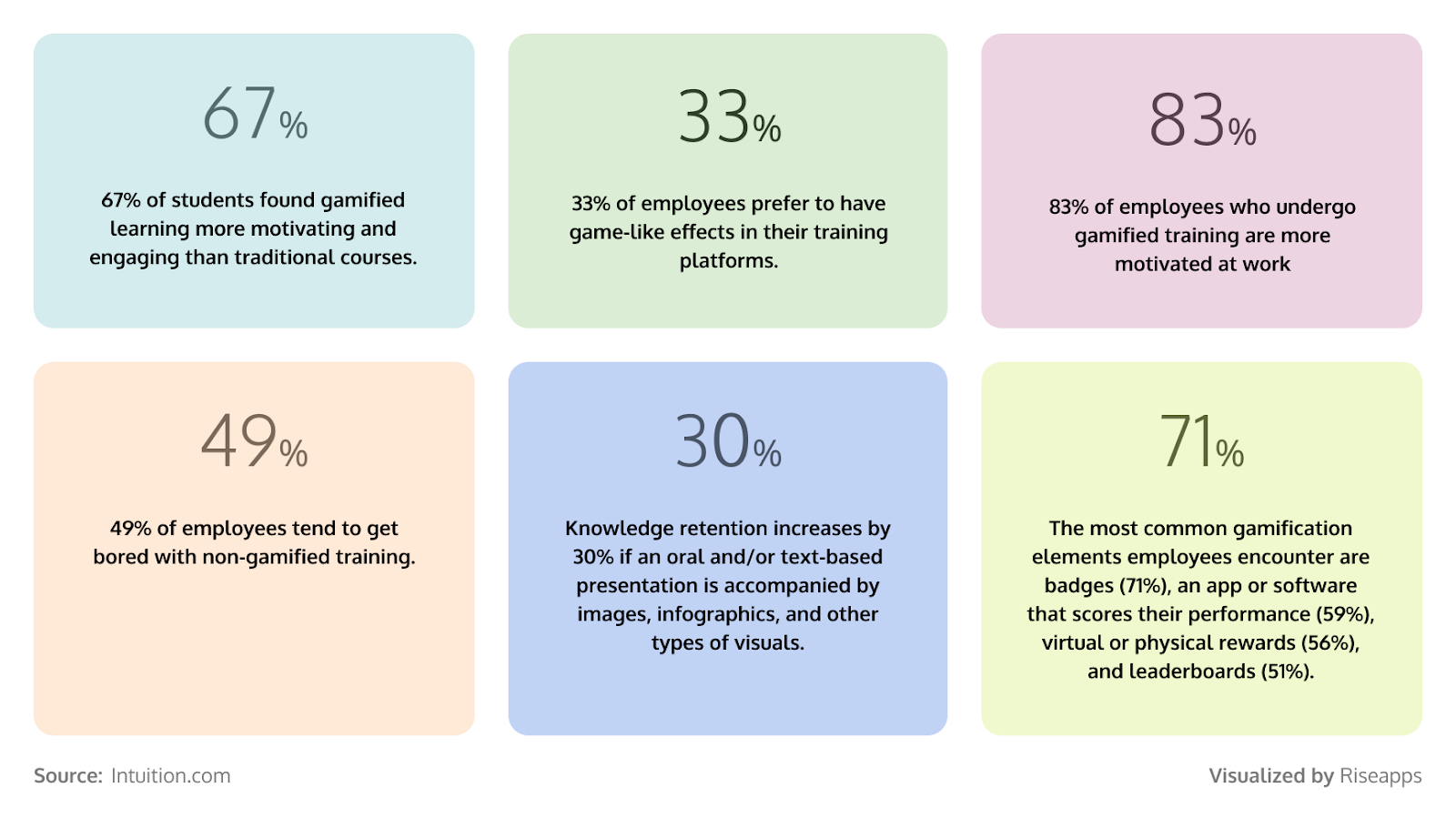
Riseapps example: Here’s how Riseapps created a leaderboard for a language learning platform.
Also seen in:
- TalentLMS: Offers a complete gamification suite out-of-the-box.
- Kahoot!: A popular platform using quizzes and visual badges to engage learners of all ages.
12. AI-driven recommendations
Artificial intelligence can enhance personalization by analyzing learning behavior and recommending the most relevant content based on previous interactions, skill gaps, and learning preferences. This reduces content fatigue and increases engagement.
Core functions:
- Suggest new courses or lessons
- Flag struggling learners for intervention
- Adjust difficulty level or content type
Examples:
- LinkedIn Learning: Recommends courses based on professional roles, skills, and user behavior.
- Docebo: Uses AI to recommend content and create automated learning paths for each user.
- Coursera: Offers AI-driven personalized recommendations and assessments that increase in difficulty as users perform better.
13. Adaptive learning
Adaptive learning goes beyond recommendations. It actively adjusts the learning experience based on real-time data, altering the course difficulty, content sequence, or even the format to fit each learner’s pace and performance. A Gates Foundation-funded study found that adaptive learning can improve student outcomes by 16–30% compared to traditional e-learning models.
Benefits:
- Supports self-paced and personalized journeys
- Reduces dropout by matching content with capability
- Accelerates mastery through smart repetition
Examples:
- Khan Academy: Uses adaptive algorithms to guide students to areas they’re struggling with.
- Knewton Alta: Offers adaptive college-level courseware, especially in math and science.
14. Social learning tools
Learning doesn’t happen in isolation. Peer learning has been shown to improve retention and engagement by 25% or more (LearnKhana), especially in cohort-based programs. Social features replicate classroom or workplace collaboration through:
- Discussion forums and threads
- Peer reviews and group assignments
- Public Q&A under course modules
- Chat and real-time collaboration tools
Examples:
- Moodle: Forums and wikis are built-in, often used in blended learning.
- Edmodo: Designed for K–12, with social learning at its core.
- Thinkific Communities: Allows course creators to build topic-specific groups.
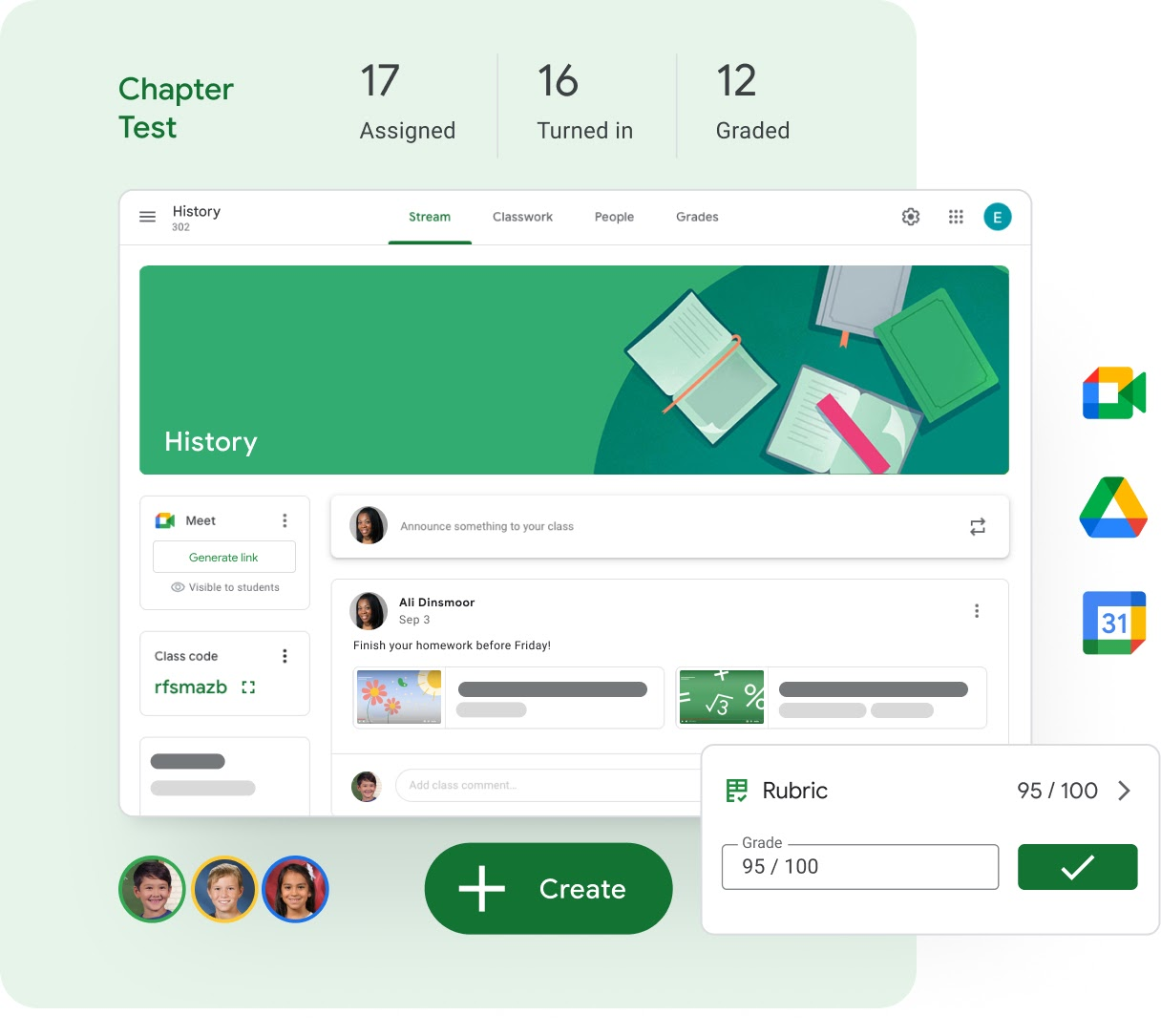
15. Live class integration
Synchronous learning remains important, particularly for onboarding, workshops, and high-touch academic experiences. Live class features include:
- Integration with Zoom, MS Teams, or Google Meet
- Calendar invites and attendance tracking
- Session recordings for later access
Examples:
- Canvas LMS: Seamlessly integrates with Zoom and BigBlueButton.
- Teachable: Supports live webinars through Zapier and third-party tools.
- Google Classroom: Fully integrated with Google Meet for real-time teaching.
16. Push notifications
Notifications keep learners informed and on track. According to the Airship report, 95% of new users who don’t receive push notifications within 90 days will eventually churn. Whether through in-app popups, mobile alerts, or email summaries, this feature improves attendance and course completion.
Essential triggers:
- New content added
- Assignment deadlines
- Scheduled live sessions
- Inactivity reminders
Examples:
- TalentCards: Sends mobile push notifications for microlearning courses.
- Blackboard App: Offers SMS and push alerts.
- Duolingo: Uses app notifications to boost engagement.
17. Calendar and scheduling
A centralized calendar helps learners stay organized and reduces drop-off due to missed deadlines or confusion. Ideal calendar tools include:
- Event syncing with Google or Outlook
- Personalized due dates and reminders
- Visibility of upcoming live sessions and tests
Examples:
- Canvas: Offers a powerful calendar for instructors and students with color coding, drag-and-drop scheduling, and task reminders.
- LearnUpon: Uses personalized dashboards with calendar widgets for learners and trainers.
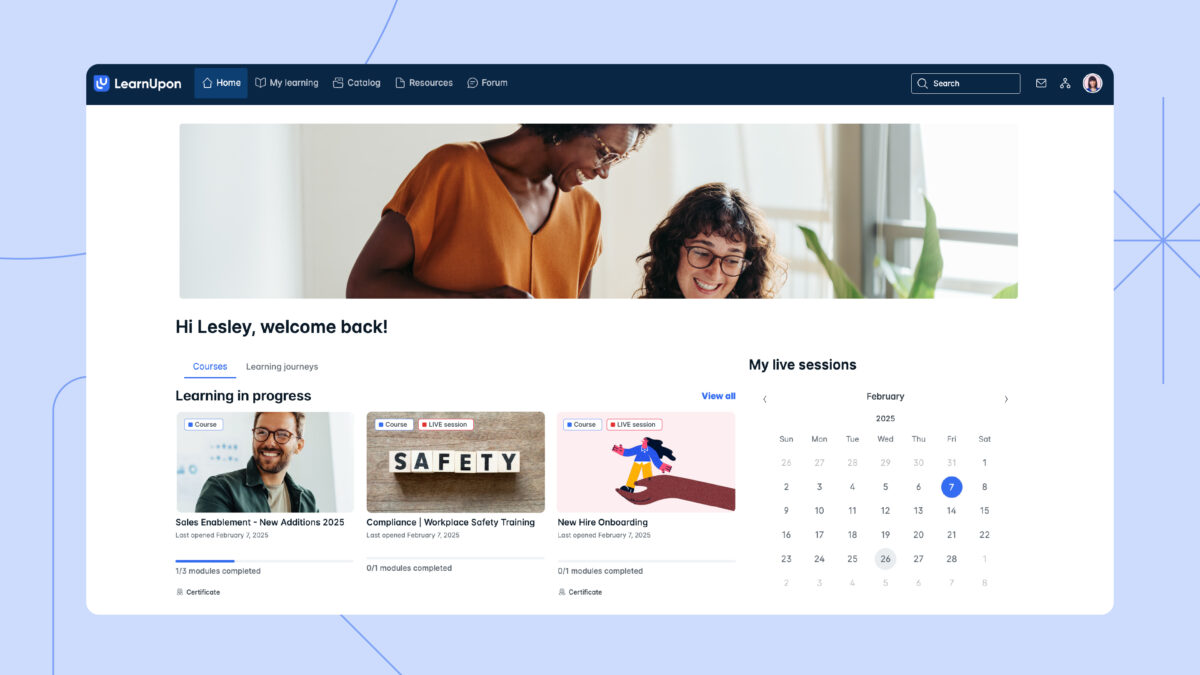
18. Feedback and ratings
Transparent feedback mechanisms allow learners to evaluate courses, flag issues, and share testimonials. It also gives instructors valuable input to iterate and improve. Gartner reveals that 86% of businesses consider reviews and social proof a crucial aspect of their purchase decisions.
Features to include:
- Star ratings
- Open-ended comments
- Anonymous feedback options
- Admin dashboards with average course scores
Examples:
- Udemy: Learners rate courses, and ratings are prominently displayed to help new users choose.
- Thinkific: Course reviews and feedback modules can be embedded directly within the course flow.
- Coursera: Students rate every module and assignment, not just the full course.
19–25 features: Admin and scalability tools
A great LMS should be as seamless for a 10-person training team as it is for an international university with 100,000 users. A set of admin and scalability features ensures your platform is future-ready, whether you’re adding new users, selling courses, or analyzing performance at scale.
19. Single sign-on (SSO)
SSO simplifies access and strengthens security by allowing users to log in using credentials from systems they already trust. It’s especially useful for enterprise LMSs and institutions where users already operate in centralized environments.
Why it matters:
- Reduces password fatigue and IT support burden
- Accelerates onboarding for teams
- Enables secure access across platforms
Example:
- Docebo: Offers SAML 2.0, OpenID, and social login options.
- Canvas: Supports institution-wide SSO via LDAP and OAuth.
20. SCORM/xAPI support
Support for SCORM (Sharable Content Object Reference Model) and xAPI (Experience API) allows the LMS to deliver and track standardized e-learning modules from third-party vendors or authoring tools like Articulate, Rise 360, or Captivate.
Why it matters:
- Ensures compatibility with existing course libraries
- Enables detailed learning analytics (especially via xAPI)
- Required by many corporate clients and institutions
Examples:
- TalentLMS: Offers built-in SCORM and xAPI support.
- Moodle: Long-standing SCORM compatibility, extendable with plugins.
- SAP Litmos: Commonly used in regulated industries like healthcare and finance.
21. Asynchronous learning
Asynchronous learning is a core requirement for modern LMS platforms. 69% of online learners prefer asynchronous formats because they allow a better balance between education, work, and life responsibilities (Inside Higher Ed). In 2025, users expect to learn on their own schedule, at their own pace, and from any location. That means your LMS must support content delivery and user interaction without requiring real-time participation.
Key capabilities include:
- Self-paced course progression
- Pre-recorded video lectures and downloadable materials
- Scheduled release of course modules (drip content)
- Asynchronous discussions and forums
- Time-independent assessments and assignments
Why it matters:
- Enables learners to revisit content and study when it’s most effective for them
- Accommodates users in different time zones or with busy schedules
- Reduces dropout by removing rigid time constraints
Examples:
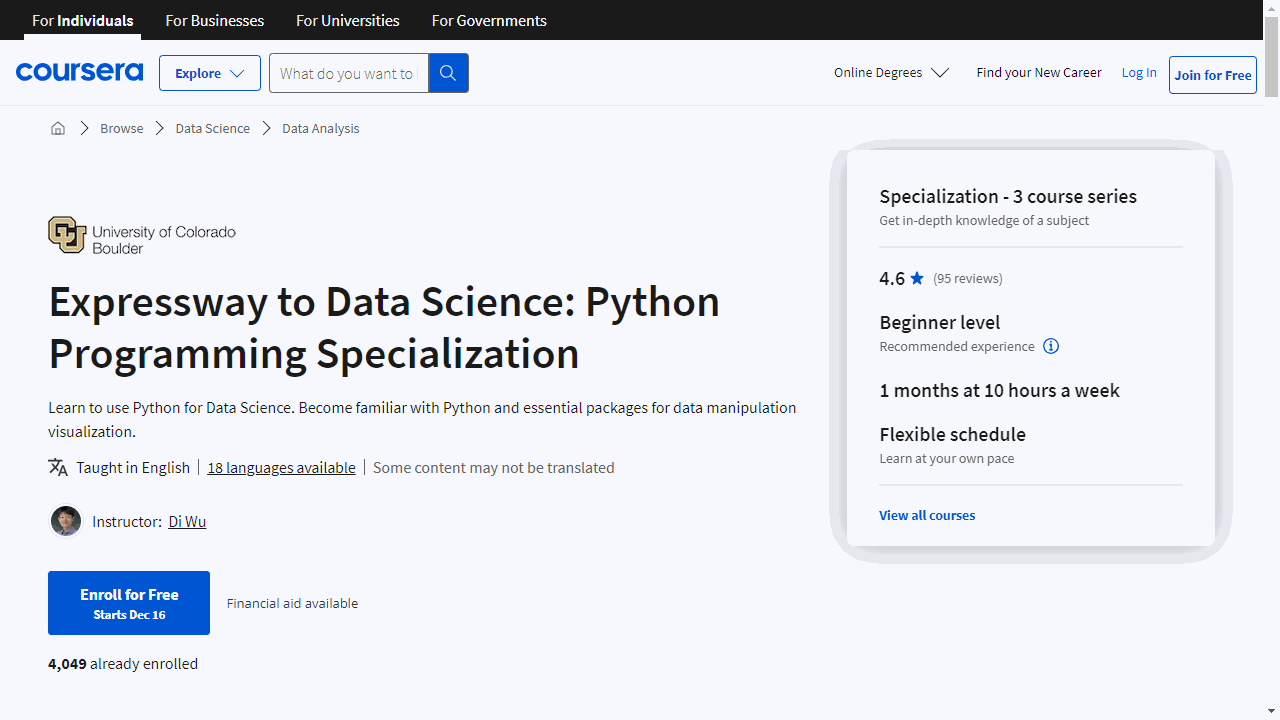
- Coursera: Offers fully asynchronous programs with deadlines, optional live check-ins, and flexible pacing.
- Moodle: Provides robust support for asynchronous delivery through forums, quizzes, and timed module release.
- edX: Allows learners to follow entire degree programs asynchronously while still earning verified certificates or credentials.
22. E-commerce and monetization modules
If your LMS is built for public audiences or paid content, you’ll need built-in monetization features:
- One-time course purchases
- Subscription models
- Coupon codes
- Checkout and tax management
- Payment gateway integrations
You can integrate sales dashboards for instructors or course owners to track revenue per course and lifetime value.
Examples:
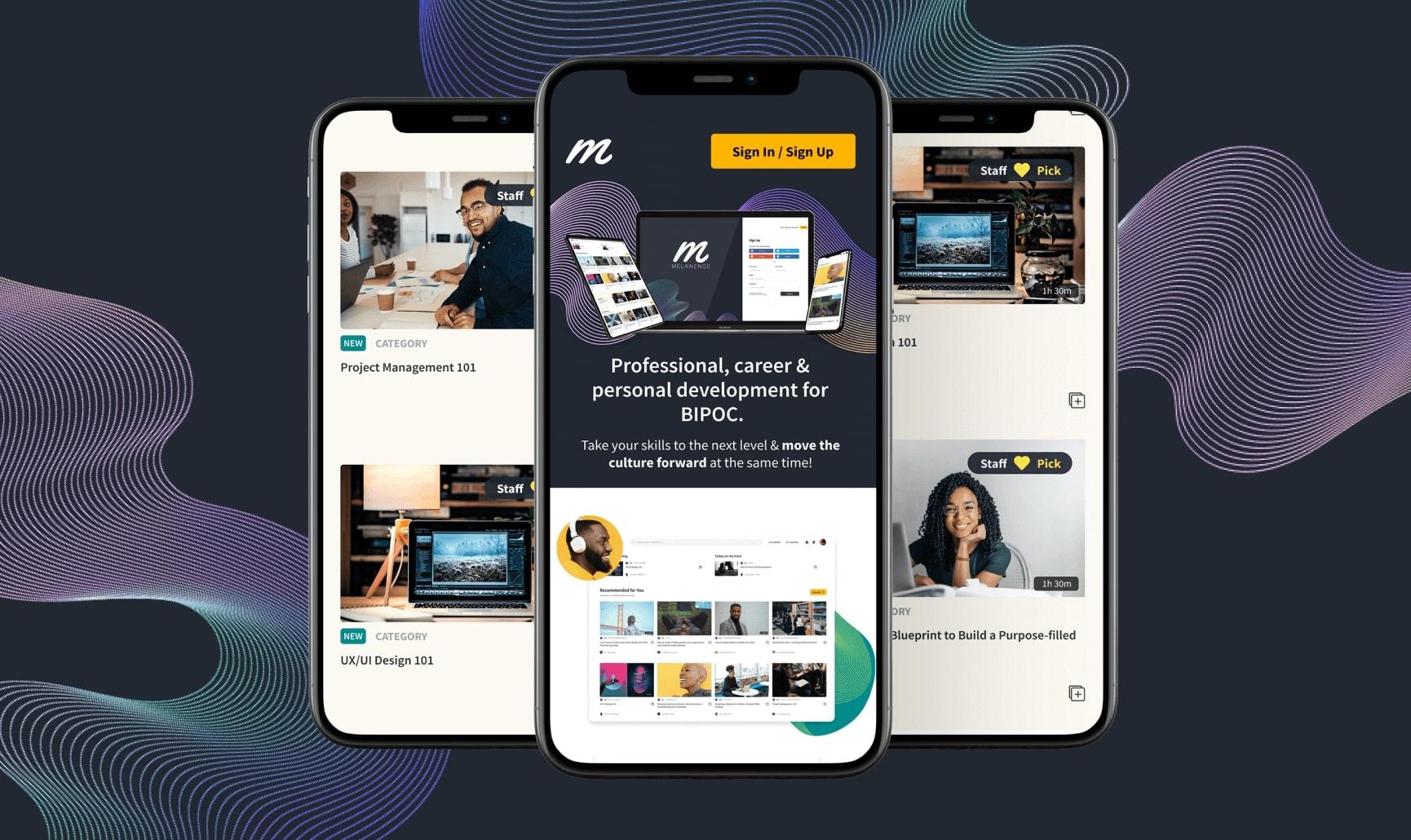
- Melanence (by Riseapps): Included PayPal integration for subscription-based revenue.
- Thinkific: Built-in e-commerce engine, with Shopify and Stripe integrations.
- Kajabi: Supports full business suite — courses, checkouts, and CRM.
23. Data visualization and learning analytics
Data is only useful when it’s actionable. LMS Admins and instructors need intuitive dashboards to monitor engagement, identify bottlenecks, and prove ROI to stakeholders. A study published in the Springer Open found that the use of Learning Analytics Dashboards (LADs) led to a significant increase in student engagement with course materials immediately after interacting with the dashboard.
Recommended metrics:
- Completion rates by course and user group
- Quiz performance trends
- Learner inactivity alerts
- Average time spent per module
- Sales performance (for e-commerce platforms)
Examples:
- Docebo: Provides AI-powered insights for both L&D and business outcomes.
- Canvas Analytics: Includes student-specific drill-down reports and visual dashboards.
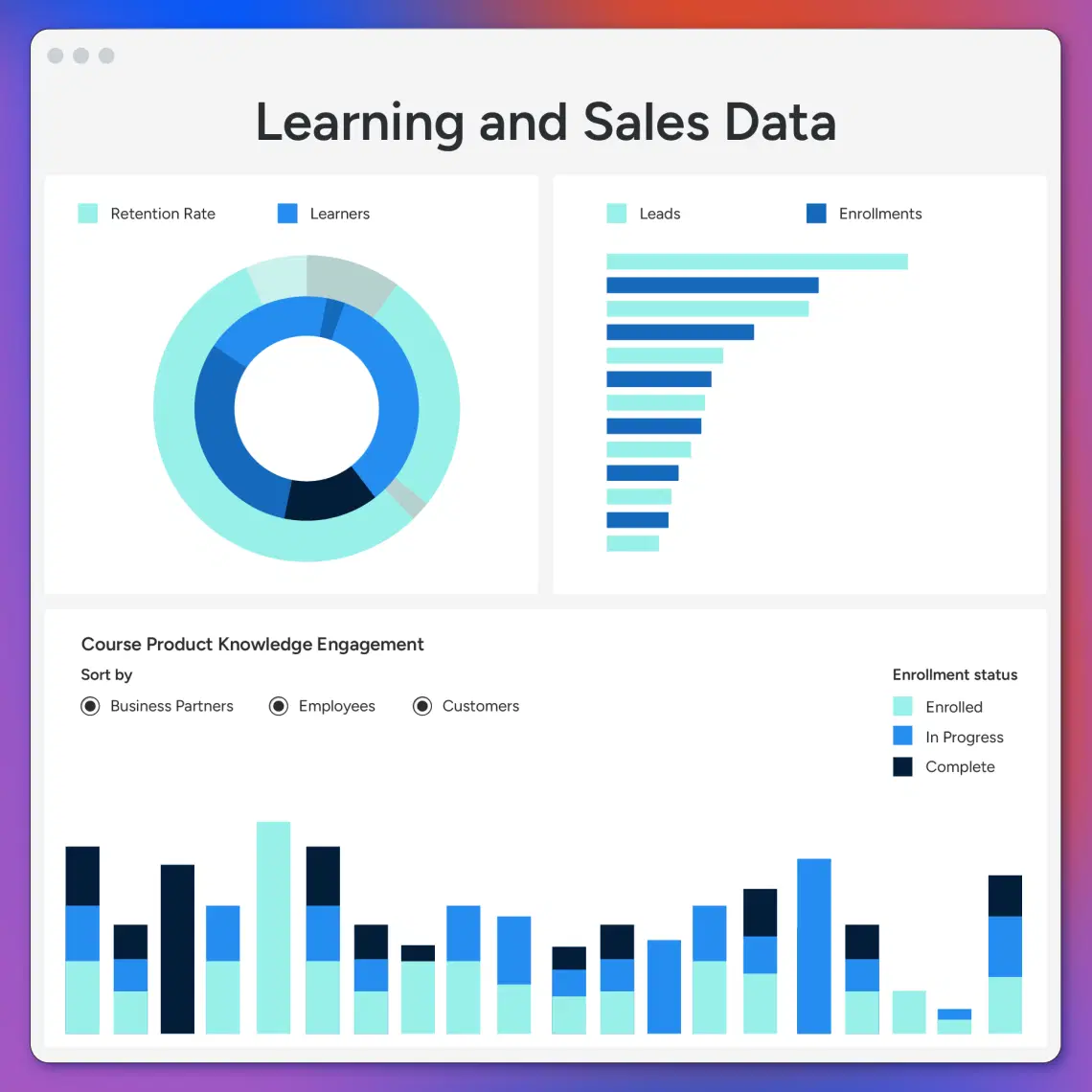
Docebo insights
24. Public API and developer tools
Offering an open API allows your LMS to grow beyond its original purpose — integrating with CRMs, HRIS systems, custom dashboards, or mobile apps.
Features to look for:
- RESTful or GraphQL API
- Authentication via tokens or OAuth
- API documentation and sandbox environment
- Webhooks for real-time updates
Examples:
- Open edX: Extensively API-driven, with support for third-party app integrations.
- Teachable & Thinkific: Offer APIs for syncing data across marketing and user platforms.
- Riseapps-built LMSs: We’ve integrated open APIs for partners and analytics pipelines.
25. Customizable admin dashboards
Unlike role-based access alone, customizable dashboards allow every admin, instructor, or team lead to see exactly the data or tools they care about, without clutter. It puts relevant data front and center, whether it’s an instructor looking for grading alerts or a department head watching team progress.
Must-have capabilities:
- Widget-based dashboard layout
- Saved views and filters
- User-specific KPIs (e.g., instructor vs. team lead vs. platform owner)
- Modular plugin integration
Examples:
- Canvas: Each role has its own dashboard experience, including to-do lists and course insights.
- Absorb LMS: Offers custom dashboard builders for L&D teams.
- LearnUpon: Allows segmentation by business unit or learner cohort.
Core LMS integrations
While it’s tempting to build everything custom, smart LMS development starts with strategic integrations. At Riseapps, we help clients prioritize integrations that maximize value early on, ensuring your MVP delivers a seamless user experience without overcomplicating infrastructure.
Here are the eight integration categories we recommend prioritizing:
| Integration type | Popular tools | Why it matters |
| Single sign-on (SSO) | Google Workspace, Okta, Microsoft Azure | Streamlines login across platforms. Critical for scaling in enterprise or EDU use cases. Reduces support tickets and speeds up onboarding. |
| Video conferencing | Zoom, Microsoft Teams, Google Meet | Enables seamless live learning sessions, webinars, and virtual classrooms without leaving the LMS. |
| Payment gateways | Stripe, PayPal, Paddle | Allows you to monetize your content from day one. Supports subscriptions, one-time payments, or course bundles. |
| Analytics / BI | Mixpanel, Amplitude, Google Analytics | Offers real-time tracking of learner engagement and behavior, conversion funnels, and engagement drop-off points — essential for scaling. |
| HRIS / CRM | BambooHR, Salesforce, HubSpot | Syncs user data, learning history, and performance with existing enterprise tools. Ideal for corporate training or partner education platforms. |
| Messaging tools | Slack, MS Teams, Discord | Encourages peer-to-peer communication, community-building, and cohort collaboration. |
| Project management tools | Trello, Asana, Notion, ClickUp | Enables task tracking for project-based learning and instructor workflows. |
| ERP Systems | SAP, Oracle NetSuite, Odoo | Useful for large-scale academic or enterprise LMSs to sync finance, HR, and scheduling functions. |
Many platforms we’ve built at Riseapps start with 2–3 core integrations and expand as user needs evolve. With proper API planning, you can future-proof your LMS without overbuilding at launch.
LMS development cost: MVP vs. full-featured platform
Whether you’re building an MVP to test the market or a full-scale LMS to support thousands of users, we tailor our approach to meet your business goals, without amplifying the timeline or the budget.
Here’s how we typically scope LMS projects at Riseapps:
| LMS type | Timeline | Estimated budget (USD) | What’s included |
| MVP LMS | 3–6 months | $60K–$80K | 10–12 core features (course builder, user management, assessments), mobile-friendly UI, key integrations (e.g., Zoom, Stripe, SSO). Built for early traction. |
| Full-featured LMS | 6–10+ months | $80K–$100K | All 25+ features, including mobile apps, AI-driven analytics, adaptive learning, certification engine, gamification, multi-language support, and API access. Built for scale. |
Tech stack we rely on:
- Web: React or Next.js for a responsive and performant frontend
- Mobile: React Native or Flutter for cross-platform speed and native-like experience
- Backend: Node.js, NestJS, or Django (depending on needs)
- Open-source foundation: When appropriate, we build on top of Open edX, Moodle, or other modular LMS frameworks to accelerate development and reduce costs
Every LMS we develop is designed to grow with you, from 100 users to more than 100,000. We build cloud-ready, API-friendly architectures from day one, so you’re not paying twice when it’s time to scale.
FAQ
What are the basic features of an LMS?
Basic features of a learning management system should cover primary user requirements. When creating an LMS portal, provide learners and teachers with:
- Content support system
- Personalized learning path
- E-learning management
- Mobile learning
- Social learning tools
- Assessment tools
- Analytics and reports
- Gamification
What is LMS reporting?
The list of ideal LMS features includes reporting and analysis tools. LMS analytics helps to measure engagement rates and control course quality. L&D professionals can get course program data and analyze each stage of the program to estimate the influence of course structure and content on particular learning results.
What does an LMS typically provide?
An LMS typically provides a centralized platform to:
- Host and deliver online courses
- Track learner progress and certifications
- Automate enrollment, grading, and reporting
- Facilitate both synchronous (live) and asynchronous (self-paced) learning
- Integrate with tools like Zoom, Google Workspace, or Stripe for a seamless experience
Contact Us






