Telehealth App Development Guide: Key Phases, Costs, and Examples

The United States will likely face a shortage of up to 86,000 physicians by 2036. This healthcare crisis explains why telehealth app development has become one of the fastest-growing sectors in digital health.
The market numbers tell a compelling story: recent research shows that 65% of patients become repeat users after their first telemedicine experience, with first-time caller ratios dropping from 60% to just 30% as users discover the convenience of virtual care.
What makes telemedicine so sticky? The numbers speak for themselves. A comprehensive study found that 67% of telemedicine consultations are fully resolved online, with only 10.8% requiring in-person follow-up.
This efficiency has driven explosive growth: resolved consultations increased by 235% during peak adoption periods, while follow-up appointments surged by 305%.
However, successful telemedicine app development requires careful attention to technical requirements, regulatory compliance, and user experience.
This article guides you through every phase of software development, from average costs to real-world examples, helping you learn from industry leaders.
- According to Fortune Business, the global telehealth market is projected to hit $504 billion by 2030, with North America commanding 48% share and 85% of U.S. doctors offering virtual visits (up from just 9%) in 2025, delivering over 25% of care virtually in 2023 (a 133% surge).
- Based on OECD Health Working Paper, 55.7% of telemedicine visits focus on mental health, and patients using AI-enhanced platforms show 65% better treatment adherence, with 40% higher satisfaction rates when features like pre-visit digital intake forms are included. It highlights virtual care’s edge in convenience and access over traditional appointments.
- Teladoc Health survey in 2025 says that essential components like HD video consultations, secure messaging, EHR integration prioritized by 75% of organizations, (up from 55% in 2023), and e-prescriptions are now in over 51% of telehealth software products.
- According to CTeL research, advanced features like AI-powered diagnostics (e.g., symptom checkers with 93% accuracy in dermatology) and AR/VR for remote exams are optional but already boosting leaders like Teladoc (via acquisitions) and SkinVision (95% sensitivity for skin cancer detection).
- Galen Growth research highlights that $12.1 billion invested in digital health in H1 2025 (51% in mega-deals) and mature adopters seeing 2x higher ROI making 2025 year the right time to build innovative telehealth apps.
Telemedicine Market Landscape in 2025
Telemedicine has grown from a pandemic necessity into the foundation of modern healthcare delivery. Multiple researches show a mature market that’s growing faster than ever before and set to expand throughout this decade.
Key Telehealth Market Trends and Growth Projections
The global embrace of virtual care is not merely a fleeting trend. It represents a sustained and accelerating movement.McKinsey analysis suggests that up to $250 billion of US healthcare expenditures could be virtualized.
Fortune Business Insights forecasts the global telehealth market to reach $504 billion by 2030.
The Global Telemedicine Map: Who’s Leading and Why in 2025
The telemedicine boom looks different everywhere. These differences matter to anyone building in this space.
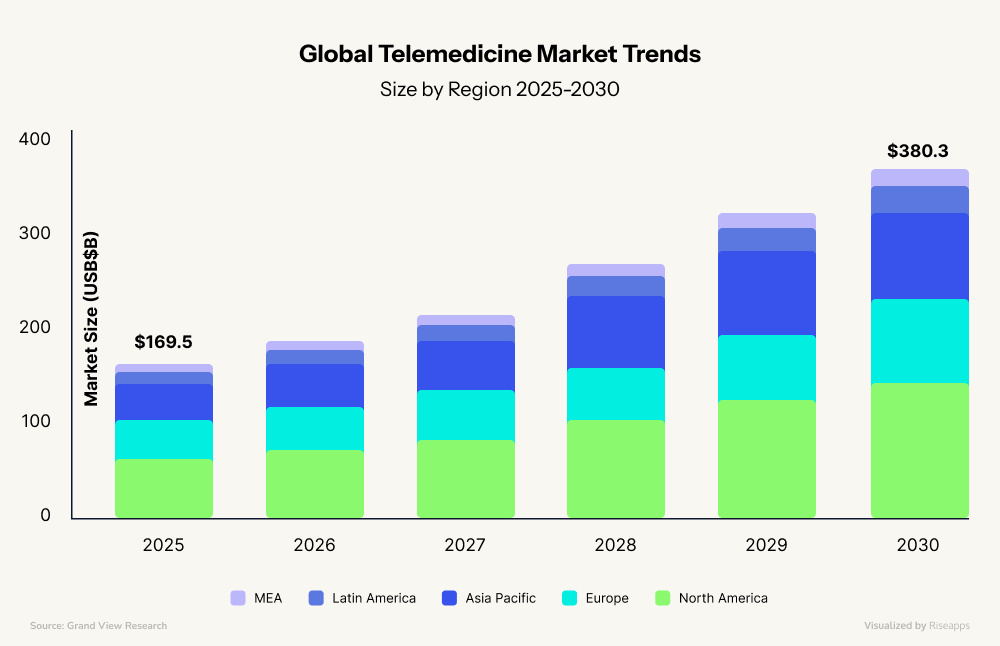
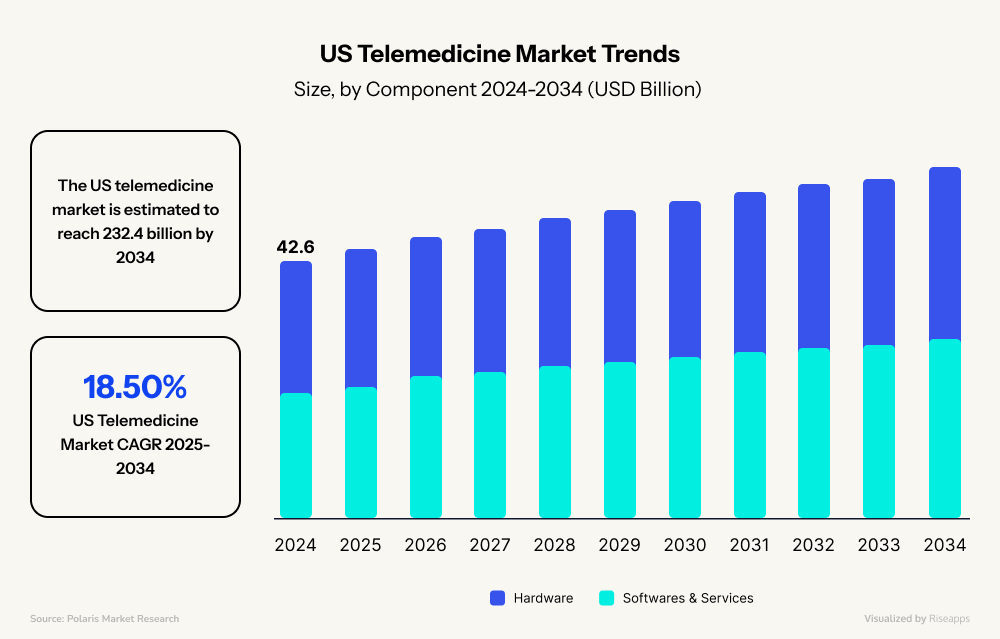
- North America owns 48% of the market, with 85% of U.S. doctors now offering virtual visits. The telemedicine market is projected to continue growing and soar to $232.4 billion by 2034, demonstrating a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 18.5% from 2025 to 2034.
- Western Europe takes a government-led approach. The UK’s NHS and Germany’s Digital Healthcare Act have integrated telemedicine directly into public healthcare systems, creating stable, predictable markets.
- China holds a 25.2% market share on a massive scale: Ping An Good Doctor serves hundreds of millions using AI-powered consultations.
- India grows 16% yearly by bringing first-time healthcare to rural villages through platforms like eSanjeevani.
- Southeast Asia, Brazil, and Mexico are building mobile-first telemedicine platforms, skipping desktop entirely. Limited traditional infrastructure becomes an advantage in these markets, which are designed for smartphones from day one.
- The Middle East combines ambitious digital transformation goals with substantial funding.
- Africa faces connectivity challenges but shows promise, just as it leapfrogged traditional banking with mobile money, it might do the same with healthcare.
But not every market is ready. Rural areas lack basic internet, some countries ban cross-border consultations, and low-income regions (those who need telemedicine most) often can’t access it.
However, constraints evolve. Today’s challenges become tomorrow’s opportunities for developers who build with specific regional needs. Success means building for the market you’re serving, not the one you wish existed.
More Telehealth Market Trends in 2025
- Mental health care accounts for 55.7% of telemedicine visits. Teladoc Health’s recent acquisition of UpLift (a tech-enabled provider of virtual mental health therapy, psychiatry, and medication management services) only proves this emerging trend.
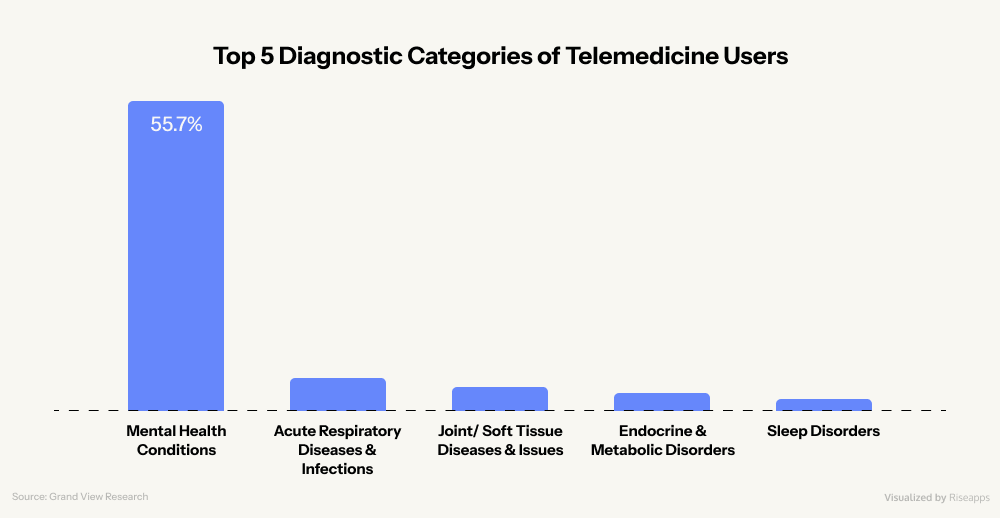
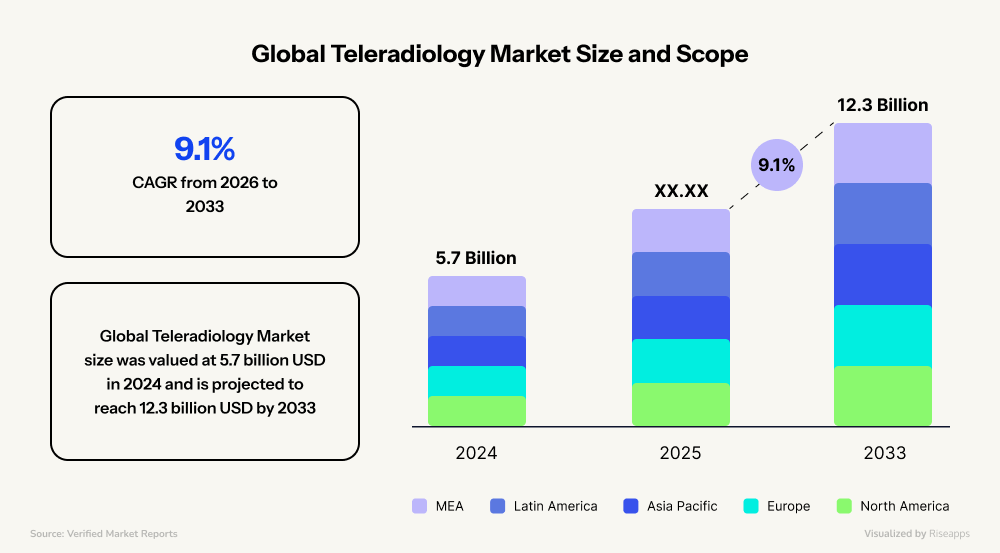
- Teleradiology holds the most significant slice at 24.30%, followed by behavioral health and chronic disease management. This segment was expected to reach $12.3 billion by 2033.
- In 2025, 75% of organizations consider EHR bidirectional integration with telemedicine apps important (up from 55% in 2023)
- Now, 21% of organizations deliver more than 25% of patient visits virtually (up from 9% in 2023 with a 133% increase), and 41% of clinics believe they can provide more than 20% of care virtually (up from 37%) (Source: Teladoc Health’s survey).
- There is a 91% increase in telehealth software implementations for primary care, specialty care, behavioral health, and neurology (compared to 2023) (Source: Teladoc Health’s survey).
- Mature adopters of telehealth technology (5+ years) are 2x more likely to report over 10% of ROI (Source: Teladoc Health’s survey).
- In 2025, rapid growth areas (with 70-80% of adoption) remain to be: remote patient monitoring (78%), chronic care management (78%), hospital at home (73%), and pre-/post-surgical care (73%) (Source: Teladoc Health’s survey).
- The top five players in the global telehealth market (Teladoc Health, American Well, Cisco Systems, Koninklijke Philips, and Siemens Healthineers) still account for 40-45% of the market’s share.
- Web-based platforms dominate 45.37% of the market, though mobile apps are growing faster.
- Telemedicine software products lead with 51.57% of market share, while development services comprise about 47.13%.
The data above reveals that virtual care is becoming the core infrastructure, system integration is non-negotiable, and patient visit volume growth will require more comprehensive care models in the future.
Another significant trend is that major health tech players aren’t developing new software products. They’re acquiring them.
- UniDoc Health Corp. acquired AGNES Connect (a secure, cloud-based clinical examination platform) to enhance its existing NEIL Connect platform and expand its telehealth offerings with EHR integration, real-time data exchange, and video conferencing features.
- Commure is in the process of acquiring Augmedix (an AI medical scribing solution).
- Innovaccer acquired Humbi AI for analytics & automation.
It shows a clear message: companies are investing in innovation and integrating with existing infrastructure rather than building solutions from scratch.
Why Now is the Right Time to Start your Own Telehealth Business
The telehealth sector’s ability to attract substantial funding demonstrates its evolution from experimental technology to essential healthcare infrastructure.
The first half of 2025 saw a total investment of $12.1 billion in digital health funding, a clear signal of robust momentum.
This period was marked by a strong wave of strategic mergers and acquisitions (M&A) and significant venture funding, with mega-deals exceeding $100 million accounting for 51% of all funding.
This influx of capital demonstrates that investors are actively seeking and funding platforms that are poised for long-term growth.
The H1 of 2025 has witnessed purposeful acquisitions that reveal how established players are building comprehensive care ecosystems:
- Teladoc Health’s expansion strategy exemplifies this trend. In Q1 2025, they acquired Catapult Health for $65 million, which brought at-home diagnostic capabilities directly into their chronic and preventive care programs. By April 2025, they added UpLift to their portfolio, significantly expanding their behavioral health services.
- Iris Telehealth’s strategic move to acquire innovaTel from Quartet Health addresses a critical gap: nearly 160 million Americans currently lack access to adequate mental health providers. This acquisition extends their telepsychiatry reach precisely where it’s needed most.
In 2025, other health tech companies like Commure, Datavant, Hinge Health, and Innovaccer are also channeling investments into strategic growth rather than mere expansion.
The financial return on investment (ROI) for healthcare providers is another key driver. A meta-analysis of 1,247 healthcare facilities revealed that telehealth delivered a staggering $42 billion in annual healthcare savings.
The analysis also found that providers saw a 225% ROI in primary care within two years and a 275% ROI in dermatology, accompanied by a 93% diagnostic accuracy rate.
Finally, another significant trend of 2025 is the evolution of telehealth from simple video visits to intelligent care orchestration systems. Now, artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer an optional differentiator but a core component of a modern telehealth platform.
In 2025, the rapid adoption of generative AI:
- streamlines clinical documentation and medical data summarization,
- listens to provider-patient conversations and generating clinical notes in real time,
- reduces administrative burdens.
These and other AI-powered features are now being placed on the 2025 Watch List for telemedicine application developers. Integrating them, alongside features like wearable health device integration, will be essential for any platform seeking to lead the market.
Why Telemedicine Matters: Benefits for Patients and Providers
The healthcare landscape is experiencing a revolutionary transformation through the adoption of telemedicine platforms. This creates unprecedented value for both patients and healthcare providers, addressing longstanding challenges while opening new possibilities for care delivery.
The Patient Experience Revolution
Enhanced Access Meets Modern Convenience
Telemedicine eliminates traditional healthcare barriers, particularly benefiting patients in rural or underserved areas. Geographic limitations no longer determine access to quality medical care or specialist consultations. So, patients can enjoy:
- reduced wait times,
- 24/7 care availability,
- the convenience of receiving treatment from home.
The financial impact proves equally significant. Patients save substantially on:
- travel expenses,
- parking fees,
- childcare arrangements,
- time away from work.
These cost reductions make healthcare more accessible to individuals who might otherwise delay necessary medical attention due to financial constraints.
Key Fact: Successful telemedicine programs see 40% higher patient satisfaction when they implement pre-visit digital intake forms, reducing actual consultation time while improving care quality.
Personalized Care Through Technology
Modern telemedicine platforms leverage artificial intelligence to deliver truly individualized healthcare experiences. AI-driven analysis enables providers to create tailored treatment plans based on comprehensive patient data and real-time health metrics.
This technological integration supports better medication adherence through:
- automated reminders,
- continuous monitoring for chronic conditions,
- enhanced patient engagement through regular digital check-ins.
For sensitive health issues, particularly mental health concerns, telemedicine provides a private, stigma-free environment that encourages open communication.
Key Fact: Patients using AI-enhanced telemedicine platforms show 65% better treatment adherence than traditional care models.
Provider Benefits: Efficiency Meets Excellence
Operational Transformation and Cost Management
Healthcare providers experience dramatic operational improvements through telemedicine implementation. Reduced overhead costs, minimized need for physical infrastructure, and decreased administrative burden allow practices to allocate resources more effectively toward direct patient care.
Eliminating the high setup costs associated with traditional clinics particularly benefits new practices. The reduced risk of missed appointments due to travel or scheduling conflicts further improves operational efficiency and revenue predictability.
Key Fact: Top-performing telemedicine practices maintain an 85% show-rate by implementing automated reminder systems 48 hours and 2 hours before appointments, significantly outperforming the industry average of 72%.
The Synergistic Healthcare Ecosystem
The true power of telemedicine lies in creating mutually reinforcing benefits. When patients experience improved access and cost savings, they demonstrate higher engagement levels and better treatment compliance.
This increased engagement directly benefits providers through improved patient outcomes and satisfaction scores.
Key Fact: Healthcare organizations implementing comprehensive telemedicine programs report an average ROI of 200-400% within 18 months, primarily driven by increased patient volume and reduced operational costs.
Telemedicine addresses critical systemic challenges including healthcare workforce shortages and rising costs.
By enabling efficient resource allocation and remote consultations, the technology helps distribute limited medical expertise across populations that need it most.
As chronic disease prevalence increases globally, telemedicine provides essential tools for continuous monitoring and management, supporting both patient outcomes and healthcare system sustainability.
Global Telemedicine Use Cases in Healthcare
In 2025, telemedicine use cases span across virtual AI-powered symptom checks, remote monitoring, and digital care plans. Startups prefer focusing on primary care, mental health, and dermatology the most.
Here are 4 most common directions of telemedicine app development:
Telepsychiatry and Telepsychology
Telepsychiatry and telepsychology deliver remote mental healthcare through secure digital platforms that significantly improve access to specialized care while ensuring patient privacy.
Their primary use cases include:
- virtual therapy and counseling sessions (e.g., CBT),
- psychiatric medication management,
- continuous mood monitoring,
- crisis intervention, etc.
And one of the noteworthy telepsychiatry & telepsychology platforms is Talkiatry. It is a fast-growing behavioral healthcare startup offering virtual psychiatry and therapy for anxiety, depression, PTSD, and more.
Recently it secured a $130 million investment from Andreessen Horowitz to scale its operations. Talkiatry is built to support:
- telemedicine consultations,
- secure messaging,
- prescribing,
- lab/result sharing.
Talkiatry utilizes HIPAA-compliant telehealth via the Healow app for conducting video sessions, managing appointments, and accessing records. Moreover, it supports insurance verification and billing.
Teledermatology
Teledermatology allows specialists to remotely evaluate skin conditions.
Its most impactful use cases involve:
- screening suspicious moles for cancer risk,
- AI triaging acute rashes,
- managing chronic ailments like psoriasis,
- effectively bridging the distance between patients and expert dermatological care.
SkinVision is an AI-powered skin health monitoring app example, primarily used for skin cancer detection. It enables tracking of changes over time and provides reminders for skin checks.
SkinVision boasts up to 95% sensitivity for detecting common skin cancers, offers reminders, and allows tracking over time.
Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) uses digital technology to collect health data from patients outside traditional healthcare settings.
This technology may include features like:
- vital signs monitoring of heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose for managing chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes,
- real-time health alerts for clinicians and caregivers,
- integration with wearable and IoT medical devices for monitoring elderly patients,
- clinician dashboards for patient health trend analysis.
Notable examples of such apps are Dexcom G6, which revolutionizes diabetes care through continuous glucose monitoring with smartphone integration, and Whoop Strap, which serves athletes and fitness enthusiasts with advanced recovery and strain metrics.
Telepharmacy
Telepharmacy technology is also created to enable pharmacies to deliver digital telepharmacy services end-to-end with strong patient engagement tools.
Its most frequently used features include:
- remote prescription verification and dispensing,
- virtual patient consultations on medication use and adherence,
- automated medication management through integration with electronic prescribing (eRx) systems.
A good example is DigitalPharmacy.io – a platform for pharmacies and chains, which provides a full e-commerce pharmacy portal, prescription order management, AI-powered pill reminders, health record maintenance, and secure pharmacist–patient chat.
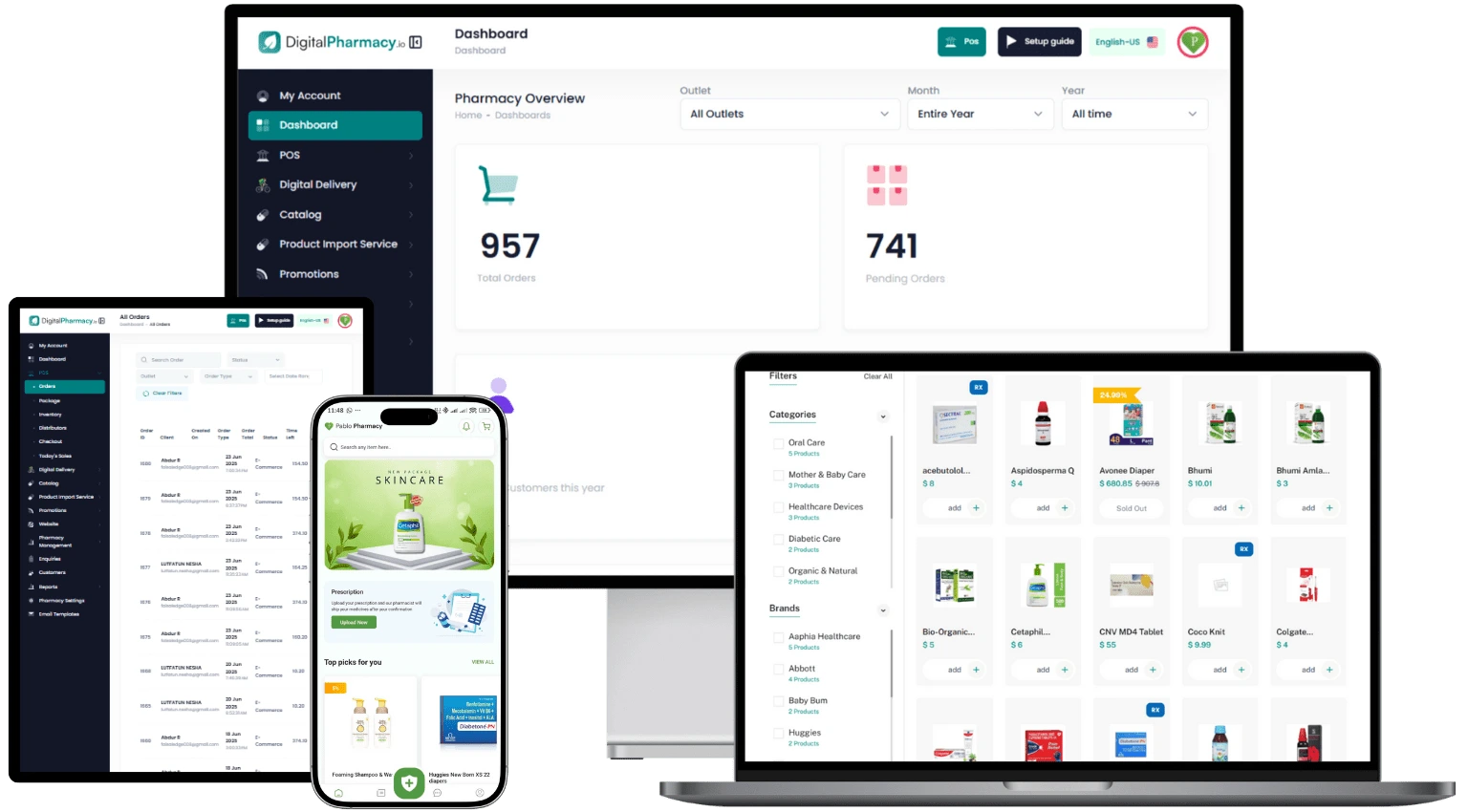
As these telemedicine tools successfully shift healthcare from the clinic to the cloud, the next frontier lies in seamlessly integrating this wealth of data to create a truly holistic and predictive model of human health.
AI Technologies Changing the Telemedicine Market
For telemedicine startups, adopting AI is no longer a choice but a critical evolution, determining whether they will become the architects of predictive, personalized healthcare or the digital fossils of a reactive past.
Here are the key AI-powered telehealth applications that you can be inspired by:
AI-Powered Triage and Symptom Checker
AI-powered triage and symptom checkers are intelligent tools in telemedicine that use AI algorithms to evaluate user-reported symptoms via chat or apps.
They provide:
- preliminary diagnoses,
- urgency (triage) prioritization,
- virtual consultations.
Moreover, they integrate with human oversight, enhancing access, reducing wait times, and streamlining care, as seen in platforms like Doctronic.
Doctronic is a U.S.-based healthcare AI startup offering an AI-driven symptom checker that guides users through an anonymous chat and provides up to four likely diagnoses and plans of action.
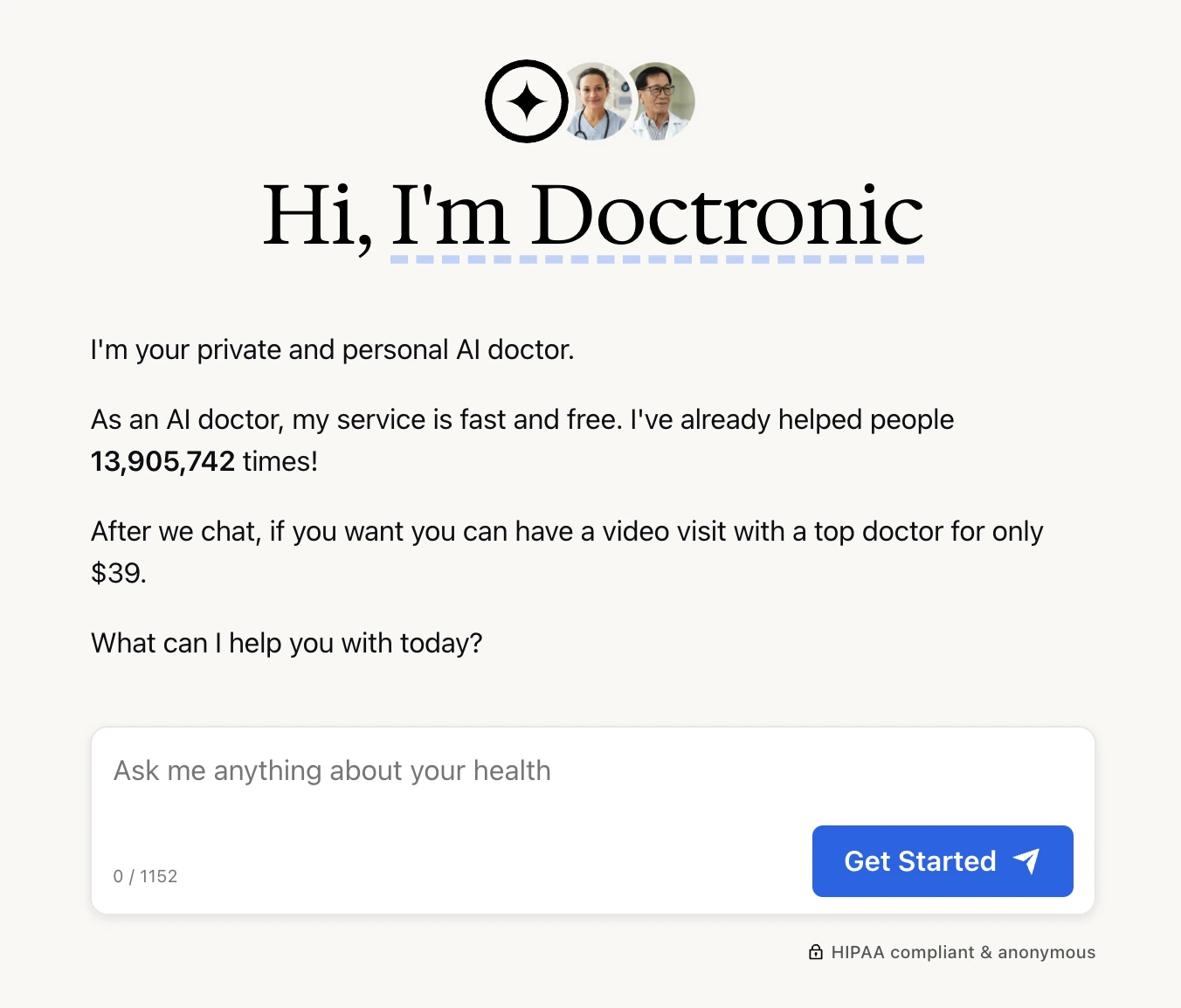
Their app enables immediate booking of video consultations with licensed physicians (typically within 30 minutes) and utilizes a multi-agent AI framework that debates diagnoses internally. Doctronic is model-agnostic (e.g., OpenAI, Anthropic), with a human clinician validating outcomes.
As of early 2025, the platform handles ~50,000 users weekly, has conducted over 10 million consultations, and raised $5 million in seed funding.
At Riseapps, we developed “Amina,” a 24/7 virtual assistant using Infermedica’s engine, which triages symptoms, automates patient queries, and accelerates diagnosis by 65%.
Check how we helped Dr. Bill Releford, a distinguished podiatric physician and surgeon, to develop telemedicine solutions fueled with AI in a 6-month period.
Real-time Documentation and Scribing
These tools use AI to listen to provider-patient conversations during telemedicine sessions, automatically transcribing and generating structured clinical notes, summaries, and documentation.
It reduces administrative burdens, and enhances efficiency, as seen in platforms like Heidi Health.
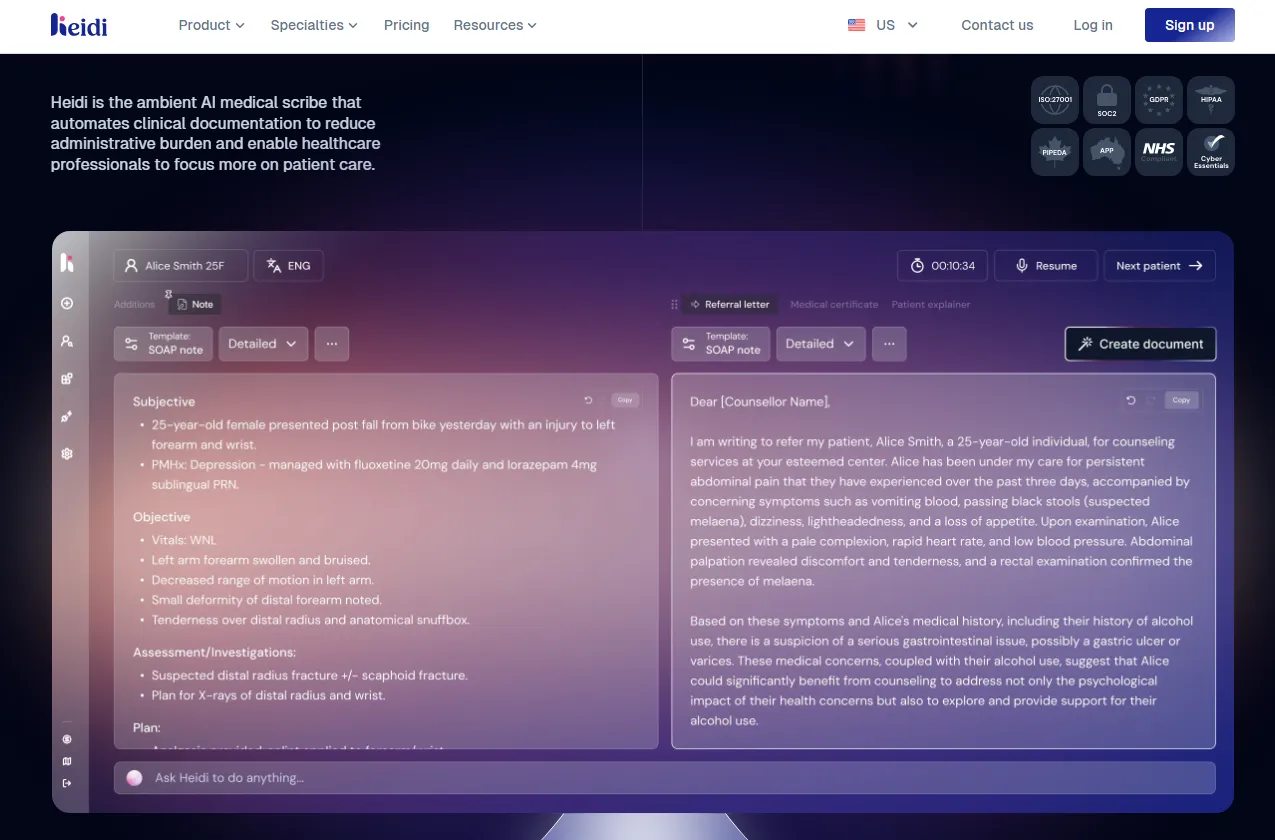
Heidi Health is an Australian-based startup that as of March 2025, raised AUD 16.6 million in Series A funding to expand AI scribe capabilities and grew to support over two million patient interactions per week.
It offers AI-powered scribe software that automatically transcribes patient consultations into structured clinical notes, case histories, and other documentation.
Heidi Health also supports integration with major EHR platforms such as Epic Systems, Athenahealth, MediRecords, and more.
AI Treatment Plan Generation and Decision Support
These solutions use AI analytics to create personalized treatment plans and assist clinicians with guideline-based recommendations.
It includes features like:
- imaging triage and oncology planning,
- analyzing patient data to suggest optimal therapies,
- predicting patient outcomes.
AI treatment plan generators enhance decision-making, reducing errors and improving efficiency in telemedicine workflows.
Varico, a Canadian healthtech startup employs AI to generate personalized treatment plans specifically for varicocele and male infertility. This software:
- assesses patient condition data,
- suggests tailored care strategies,
- supports disease monitoring,
- optimizes treatment plans remotely.
Thanks to their features, Varico helps facilitate telemedicine-based personalized medicine.
At Riseapps, we offer an AI treatment plan generator that helps to save 3 hours and $400 per patient by generating care plans in only 4 mins. Want to see this app in action?
Core Features of a High-Performing Telemedicine App in 2025
A successful telemedicine application must integrate a comprehensive suite of features designed to cater to the distinct needs of:
- patients,
- healthcare providers,
- administrative staff.
These functionalities, from foundational elements to cutting-edge innovations, ensure a secure, efficient, and user-friendly experience.
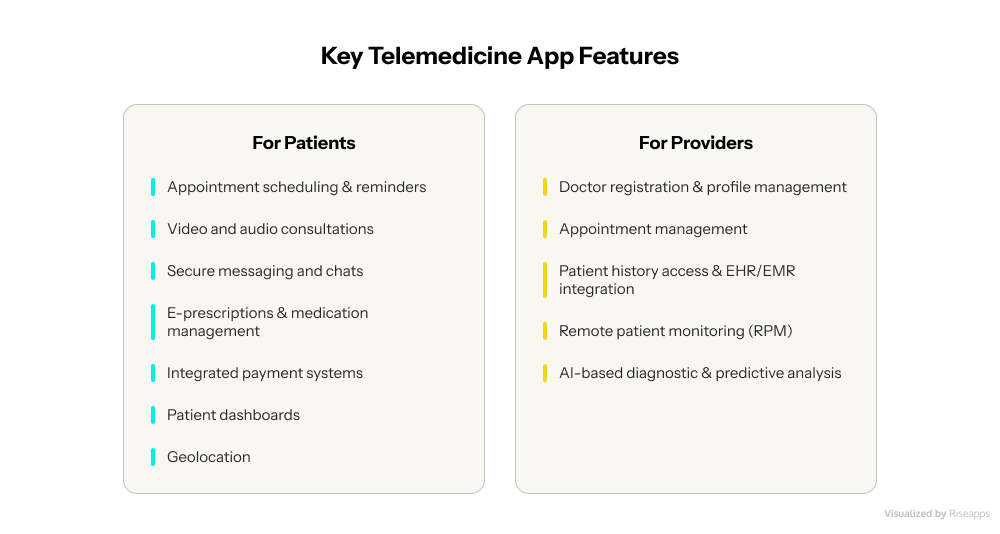
Essential Patient-Facing Features of a Telehealth Application
The telemedicine app should offer patients a seamless and intuitive experience, mirroring the convenience of modern digital services while upholding the highest standards of healthcare.
Appointment Scheduling & Reminders
A user-friendly interface is paramount for patients to effortlessly:
- book,
- reschedule,
- cancel appointments.
This system should include automated email, SMS, or in-app notifications to reduce missed appointments. Calendar synchronization is also key to helping patients manage their schedules effectively.
Video and Audio Consultations
HD video calling is the foundation of any good telemedicine platform. Video quality is vital because it helps medical professionals spot more details during patient examinations and diagnose accurately.
Your system should include:
- backup audio channels when patients have poor internet or connection issues
- quick transmission with AI-improved noise reduction and background silence
- support for multiple devices so patients can switch mid-consultation without losing connection
Research shows patients find video visits more effective than audio-only calls. They can show their health conditions and pick up visual cues. So, reliable video is a must-have for any serious telemedicine app.
Secure Messaging and Chat
Text messaging lets patients get quick advice without booking full video or audio sessions. This works well to ask questions, update providers about health changes, or book appointments.
Your messaging system needs:
- end-to-end encryption,
- message expiration options,
- delivery confirmation.
Studies show AI chatbots paired with secure messaging can cut doctor workload by 20–30%. Yes, it is true that built-in chats make communication easier and improve patient engagement and staff output.
E-Prescriptions & Medication Management
Healthcare providers must be able to send prescriptions electronically. The app should ideally include built-in trackers that notify patients when their prescription is ready for pickup from the pharmacy or if home delivery is an option.
Automated reminders for medication adherence also play a crucial role in improving patient outcomes.
Integrated Payment Systems
Secure payment gateways like Stripe, PayPal, Braintree, and Square are essential for processing consultation fees and other services.
Multiple payment options, including credit cards, insurance plans, employer coverage, and coupons, enhance convenience. Automated invoicing further streamlines the billing process.
Patient Dashboard
A comprehensive dashboard provides patients with a consolidated view of their:
- health history,
- recent visits,
- ongoing treatments,
- contact information,
- insurance details,
- medical record number.
This central hub empowers patients with easy access to their vital health information.
Geolocation
This feature allows the app to identify nearby pharmacies and hospitals, provide directions, and estimate arrival times, reducing unnecessary patient travel.
Critical Provider-Side Functionalities
For healthcare providers, the telemedicine app must offer robust tools that enhance their workflow, improve patient management, and facilitate informed decision-making.
Doctor Registration & Profile Management
Healthcare professionals require secure profile creation, enabling them to manage their availability, specify their specializations, and upload credentials.
Appointment Management
Comprehensive tools are needed for providers to manage appointments and patient consultations efficiently and customize their workflows to suit their practice needs.
Patient History Access & EHR/EMR Integration
Real-time access to patient medical histories and records is fundamental for effective consultations. Seamless integration with existing Electronic Health Records (EHR) and Electronic Medical Records (EMR) systems, such as Epic and Cerner, is crucial for workflow efficiency and data accuracy.
This ensures that all patient information from telemedicine visits is automatically added to the existing EHR system.
This allows healthcare professionals to view a complete and updated health record, streamlines administrative tasks, and reduces data entry errors.
Prescription Management & Templates
Providers need robust facilities to efficiently create, send, and manage digital prescriptions.
Also, pre-designed templates for common illnesses and digital prescriptions can significantly save doctors’ time during consultations.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) uses connected medical devices to send patient health data to providers. This helps manage chronic conditions well.
Medicare covers RPM data collection for both chronic and acute conditions.
RPM needs three main parts:
- setup and training,
- device provision (getting at least 16 readings every 30 days),
- treatment management.
Modern RPM can use AI to check data for warning signs and alert physicians when readings exceed set limits.
AI-Based Diagnostic & Predictive Analysis
Advanced algorithms can:
- analyze patient data to speed up the diagnostic process,
- increase accuracy,
- forecast health risks,
- recommend preventive measures,
- optimize treatments.
Examples include AI-powered symptom checkers, automated pre-session primers, and AI alerts for suicide risk prevention (as seen in Talkspace).
AI-powered patient interviews (like HealthTap’s Dr.A.I.) can efficiently gather patient data before a consultation.
Robust Administrative & Backend Features
Behind the scenes, a telemedicine app requires powerful administrative and backend functionalities to ensure smooth operation, data integrity, and compliance.
- User management: Administrators must have comprehensive tools to manage both patient and provider accounts within the application, overseeing access and permissions.
- Analytics & reporting: AI-driven dashboards are crucial for providing actionable data, including patient trends, treatment outcomes, and overall app usage patterns. This data is vital for strategic decision-making and continuous improvement.
- Compliance & security management: Features specifically designed to ensure adherence to regulatory compliance and maintain robust data security are non-negotiable. This includes detailed audit trails and message retention policies to track data access and modifications.
- Queue management: Systems that inform patients of their estimated wait times and provide real-time updates on their appointment status can significantly reduce patient anxiety and improve their overall experience.
- Content management system (CMS): A robust CMS is necessary for efficiently managing and updating educational content, medical instructions, and other informational resources provided within the app.
Integrating cutting-edge technologies is paramount to truly differentiating and future-proofing a telemedicine app.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is rapidly becoming a transformative force, moving beyond simple automation. It is increasingly deployed for:
- clinical decision support,
- fraud detection,
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) for medical records,
- sophisticated predictive analytics.
AI agents can automate routine tasks, provide immediate insights, and offer personalized attention to users, allowing doctors to intervene where their expertise is most needed.
AI-driven dashboards and predictive analysis empower healthcare providers with actionable data, allowing them to optimize their workflows and focus on more complex patient cases.
For patients, AI promises continuous support from “tech assistants” and highly personalized treatment plans, addressing their increasing desire for greater control over their health.
This indicates that artificial intelligence is indispensable for scaling personalized care and improving diagnostic accuracy, securing its long-term viability and competitive advantage in the market.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The seamless connection with wearable devices and various health trackers is crucial for advanced remote patient monitoring, enabling continuous data collection and proactive health management.
Augmented Reality (AR) & Virtual Reality (VR)
These immersive technologies are poised to revolutionize telemedicine by enhancing diagnostic capabilities and treatment experiences, offering new avenues for remote examinations and therapeutic interventions.
Multi-language Support
The app should offer services in multiple languages to ensure inclusivity and broader accessibility, removing communication barriers for diverse patient populations.
API Extensibility
A well-designed app architecture allows easy integration with other software and services through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs, enhancing the app’s ecosystem and functionality). This includes:
- payment gateways,
- social media platforms,
- calendar services.
A Step-by-Step Blueprint for Telemedicine App Development
Developing a telemedicine application is a complex undertaking that requires a structured, multi-phase approach. From initial conceptualization to ongoing maintenance, each step is critical for building a robust, compliant, and user-centric digital healthcare platform.
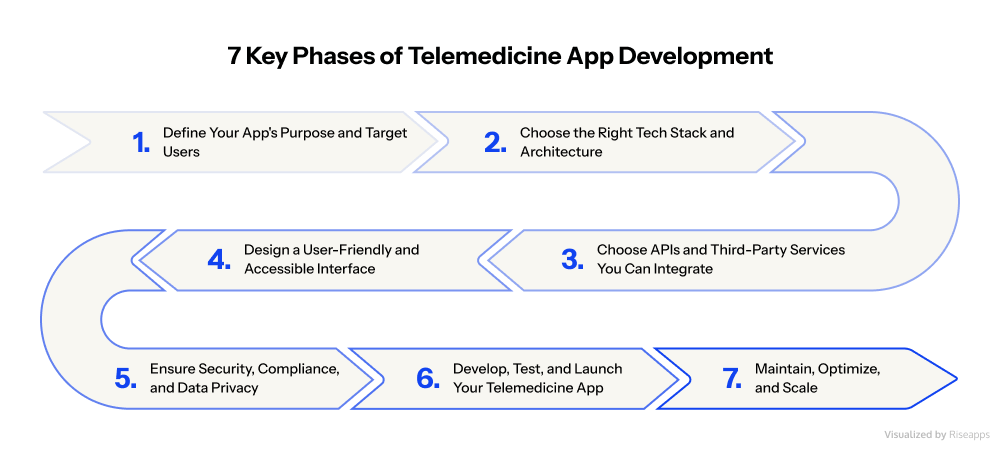
Phase #1: Define Your App’s Purpose and Target Users
Success in telemedicine starts with knowing exactly who you’re building for. Your users typically fall into three categories:
- patients seeking remote care,
- healthcare providers streamlining workflows,
- dual platforms serving both groups.
But dig deeper. An app for elderly cardiac patients needs different features than one for busy parents managing their children’s health. Consider your users’ tech skills, preferred devices, and when they typically need care.
These details shape every development decision. There are other vital steps you need to take:
Research the Competition
Study both direct competitors (other telehealth apps) and indirect ones (alternative healthcare solutions). Analyze their core features, user experience, pricing model, and market positioning for each.
This research reveals crucial gaps like:
- current apps ignore certain specialties,
- lack proper integrations,
- miss specific patient needs.
These gaps become your opportunities.
Find Your Niche
General telehealth platforms face fierce competition. Consider focusing on specific areas like:
- mental health,
- chronic disease management,
- pediatric care,
- underserved populations like rural communities or correctional facilities.
A targeted approach means less competition and more focused solutions. Becoming the best teletherapy app is easier than competing with established all-purpose platforms.
Define Your Mission
Your app needs more than features. It needs purpose. Will you reduce ER visits? Improve medication adherence? Connect specialists with rural patients?
This clear vision guides development and helps communicate your value to users and investors.
Remember: successful telemedicine apps don’t try to be everything to everyone. They solve specific problems exceptionally well.
Phase #2: Choose the Right Tech Stack and Architecture
Your current technology choices will determine whether your telemedicine app thrives or struggles. Get it right, and you’ll build faster, scale easier, and adapt to whatever healthcare throws at you.
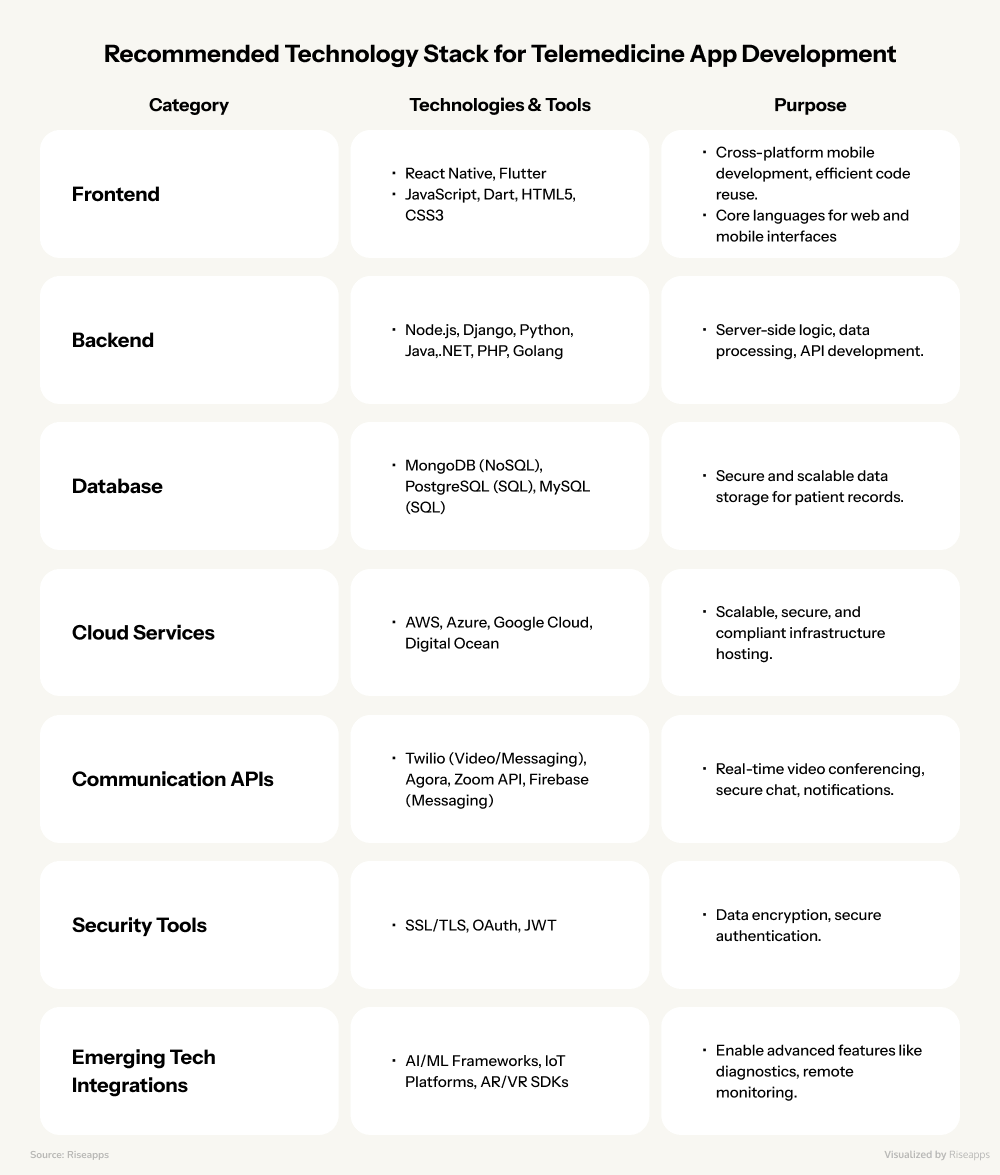
Here is the list of the most commonly recommended tech stacks for telemedicine developers.
Building What Users See
You face a classic dilemma for the frontend: build once or twice?
Cross-platform frameworks like React Native and Flutter let you create one app that works everywhere. React Native excels at video calls (the heart of telemedicine) while Flutter gives you pixel-perfect control over your app’s appearance.
You’ll save time and money, but might sacrifice some performance.
Going native with Swift (iOS) and Kotlin (Android) means building separate apps, but you’ll get buttery-smooth video calls and seamless device integration. When milliseconds matter in a medical consultation, Native often wins.
The Engine Room
Your backend needs to handle everything from storing medical records to streaming video without breaking a sweat.
- Node.js shines for real-time features like live consultations.
- Python opens doors to AI diagnostics and smart symptom checkers.
- Ruby on Rails helps startups launch fast and iterate quickly.
For databases, PostgreSQL keeps medical records organized and compliant, while MongoDB handles the messy stuff:
- chat logs,
- images,
- unstructured notes.
Many apps use both.
Why Cloud Matters
Forget managing servers. AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud handle the heavy lifting while you focus on building features.
- AWS brings HIPAA-ready infrastructure out of the box.
- Azure plays nice with international regulations.
- Google Cloud makes AI integration almost trivial.
Cloud platforms scale automatically when a health crisis hits and usage spikes 10x overnight. No crashed servers, no angry patients, no emergency calls to your tech team.
But here’s the truth: there’s no perfect stack. A startup proving its concept needs tools that are different from those of an established health system in terms of upgrading its infrastructure.
So, whatever you choose, think beyond today. Pick technologies that grow with you, support emerging standards, and won’t lock you into expensive dead ends.
Phase #3: Choose APIs and Third-Party Services You Can Integrate
Based on current trends in 2025 we mentioned above, integrating with third-party services can enhance functionality in areas like video consultations, electronic health records (EHR), payments, wearables, and AI-powered diagnostics where you don’t need to reinvent the wheel.
Key apps and tools we recommend to integrate include:
- EHR systems like Epic or Cerner via APIs like Redox,
- Video communication apps like Zoom, Twilio, or Agora API
- AI chatbots via GetStream API,
- Wearable and device ecosystems like Apple Health or Google Fit,
- Payment gateways like Stripe,
- Pharmacy services like Truepill,
- Scheduling tools like Calendly or custom via APIs.
And below you’ll find the overview of 5 APIs we recommend to explore in 2025.

Phase #4: Design a User-Friendly and Accessible Interface
The importance of user experience extends beyond mere aesthetics; it is intrinsically linked to the app’s ability to achieve widespread adoption and maintain data security.
When 90% of users abandon apps after poor experiences, we’re not talking about lost revenue. We’re talking about missed diagnoses and untreated conditions.
Design for Real Healthcare Scenarios
Your emergency room doctor needs different features at 3 AM than your elderly patient scheduling a routine checkup. Both deserve interfaces that work flawlessly.
- Simplicity saves lives. Strip away everything non-essential. That extra menu? Those fancy animations? They’re obstacles when a provider needs patient vitals fast. Healthcare workers already face video fatigue. University of Galway research confirms that seeing yourself on screen exhausts users faster. Hide self-view by default. Minimize clicks. Make every interaction count.
- Build for your most vulnerable users. If your 85-year-old patient with arthritis can navigate your app, everyone can. This means a minimum of 14-point fonts, buttons you can hit with shaky hands, and contrast that works for aging eyes. Voice commands and screen readers transform your app from “usable” to universal.
- Communicate clearly. In healthcare, uncertainty creates anxiety. Show users exactly what’s happening: “Doctor Johnson will join in 2 minutes.” “Prescription sent to Walgreens on Main Street.” “Upload is successful. Your doctor can now see your test results.”
Test with Real Users, Not Assumptions
Paper sketches beat perfect code when you’re still figuring out workflows. Start with basic wireframes, then build clickable prototypes.
Most importantly, test with actual users: the night-shift nurse who’ll use your app between emergencies, the rural patient with spotty internet, the specialist juggling 20 consultations.
Their feedback reveals what developers miss: the button placement that causes accidental logouts, the form that’s impossible to complete on a phone, and the critical feature buried three menus deep.
Phase #5: Ensure Security, Compliance, and Data Privacy
In healthcare, security isn’t a feature. It’s the foundation. One data breach doesn’t just trigger fines; it destroys the trust that takes years to build.
Here is the list of the most common regulations and standards telemedicine providers should comply with, depending on the geography.
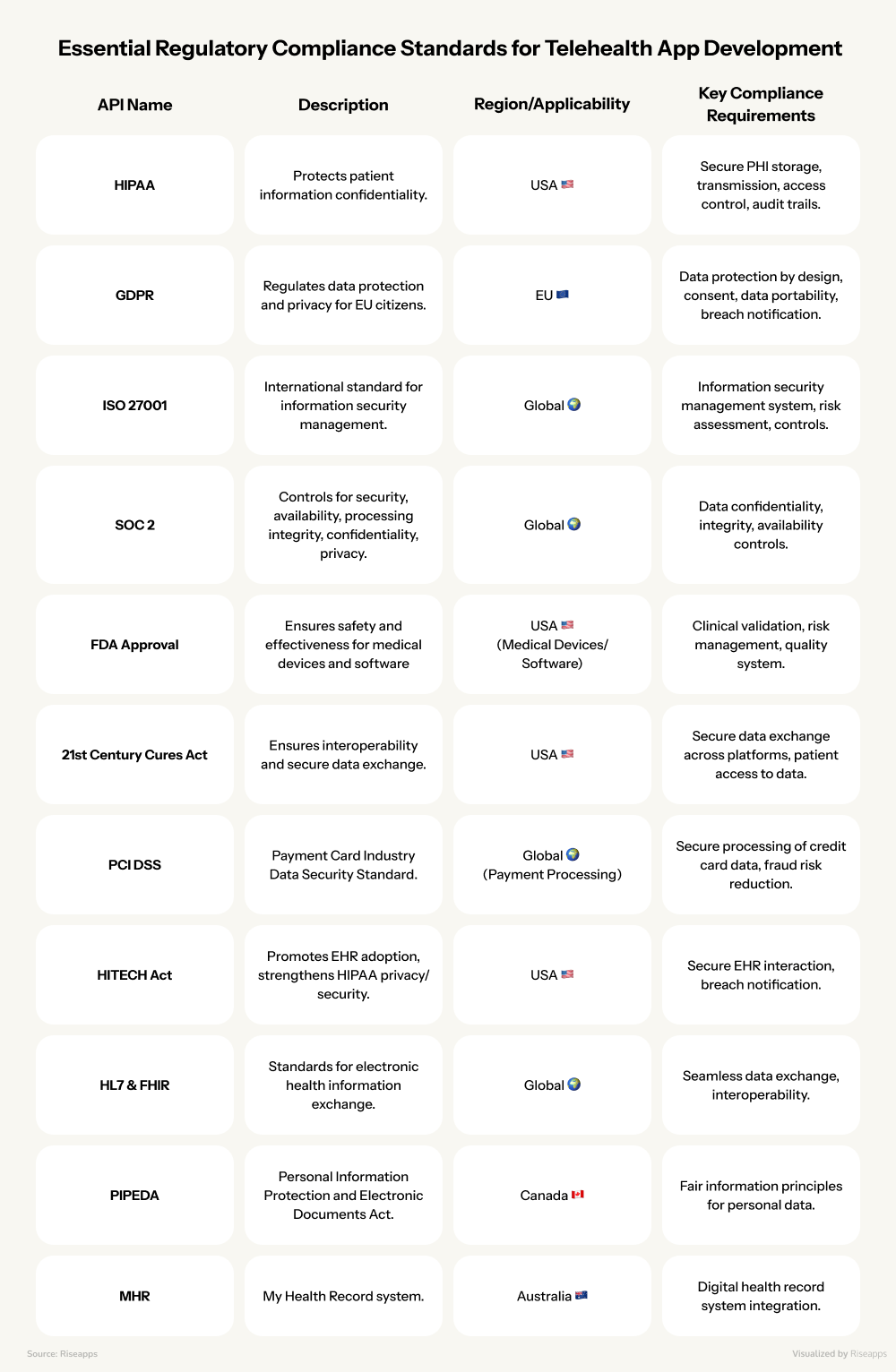
HIPAA Compliance (USA)
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is the cornerstone of patient data protection in the United States. It mandates strict confidentiality, secure storage, transmission, and access control of Protected
Health Information (PHI). Compliance is an absolute requirement for any telemedicine application handling medical data.
GDPR Compliance (EU)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) governs the handling and movement of personal data for operations within the European Union, aiming to significantly enhance individuals’ rights in the digital era.
Other Regional/Industry-Specific Regulations
Beyond these major frameworks, developers must contend with many other regional and industry-specific regulations. These include PIPEDA in Canada, the Data Protection Directive 1995/46/EC and e-Privacy 2002/58/EC/IEC 62304 in Europe, and the My Health Record (MHR) system in Australia.
Industry Standards & Certifications
Adherence to broader industry standards and certifications further reinforces compliance and trustworthiness. These include:
- ISO 27001 for international information security,
- SOC 2 for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data,
- FDA Approval for apps that function as medical devices or aid clinical decision-making.
- The 21st Century Cures Act promotes interoperability,
- PCI DSS is essential for processing secure payment information,
- The HITECH Act governs interactions with EHRs.
- HL7 and FHIR support seamless data exchange across diverse healthcare systems.
The varying and complex regulatory landscape across different regions constitutes a significant barrier to international expansion for telemedicine platforms. A company aspiring for global reach cannot simply apply one set of rules uniformly.
Each new market necessitates a deep dive into its specific:
- telemedicine laws,
- data privacy acts,
- medical device regulations.
This implies substantial legal and technical overhead for multi-country operations, often requiring a modular compliance architecture and potentially localized application versions.
This regulatory fragmentation also influences the choice of development partners, favoring those with “full-spectrum delivery” capabilities that support various regional requirements.
Phase #6: Develop, Test, and Launch Your Telemedicine App
Building a working telemedicine app from your concept needs a well-laid-out development plan. Your final product should meet user needs, run smoothly, and follow healthcare standards through several key development steps.
Set Agile Development Process
Agile methodology gives you significant advantages in telemedicine development through step-by-step improvements. A well-laid-out Agile process splits work into two-week sprints that have these parts:
- Sprint planning: Teams pick tasks from the product backlog
- Daily scrum meetings: Quick updates to solve roadblocks
- Sprint reviews: Teams show completed features
- Sprint retrospectives: Teams share feedback to get better
This approach helps teams test and integrate continuously. They can spot and fix bugs early in development. This constant feedback becomes vital for telemedicine apps where reliability matters most.
Choose between MVP vs a Full Product Development
Your strategy is shaped by your choice between an MVP (Minimum Viable Product) and full-scale development. A good telehealth MVP takes 3-6 months to build and costs $20,000-$50,000.
Full-scale development usually takes more than 12 months.
Most businesses should start with an MVP with core features to get user feedback at lower costs. This makes sense in telemedicine, where healthcare apps cost a lot to develop.
Conduct Rigorous Quality Assurance (QA) and testing
Quality Assurance (QA) and testing are indispensable to ensure the app’s reliability, security, and performance before launch. Below are the types of testing we recommend you go through:
- Comprehensive testing: This phase involves thorough testing for usability, functionality, security, and overall performance. This includes various testing types such as unit testing, integration testing, system testing, security testing, performance testing, and user acceptance testing.
- Cross-device and cross-platform compatibility: It is essential to ensure that the app functions flawlessly across all intended devices and platforms, providing a consistent user experience.
- HIPAA-aware testing: Given the sensitive nature of healthcare data, all manual and automated testing must be HIPAA-aware to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities, thereby reducing bugs and increasing the app’s reliability.
Phase #7: Maintain and Optimize
Your telemedicine app’s launch is just the start of your development trip. Successful applications must evolve based on real-life usage patterns and changing healthcare needs.
Here are the steps you must take once you’ve completed the testing phase.
- Deploy: The final, tested application is deployed on target platforms, typically Android and iOS app stores.
- Collect user feedback: Multiple channels help collect user feedback after launch. The app interface should let users report issues or suggest improvements directly. Monthly updates fix bugs and performance problems at $500-$1000 per update. These updates total around $18,000 yearly, with 4-5 monthly updates. Your app needs biannual feature releases to stay competitive. The budget should include $8,000-$12,000 yearly for these releases.
- Monitor and analyze performance: The success measurement of your telehealth program depends on key performance indicators. The essential metrics include no-show rates, virtual patient wait times, successful encounters, connectivity quality, and provider adoption.
- Post-launch growth strategies: Beyond initial deployment, sustained growth requires improving patient engagement, minimizing misdiagnosis risks, ensuring immediate access to care, and enhancing prescription alerts. Automating routine operations, such as appointment reminders, is vital for improving patient communication and operational efficiency.
- Post-launch engagement represents a continuous development cycle, where growth is not merely a function of marketing but of ongoing feature refinement and service expansion driven by user needs and market feedback
Cost of Telemedicine App Development: A Comprehensive Breakdown
Understanding the financial investment required for telemedicine app development is crucial for strategic planning.
The cost is not a fixed figure but varies significantly based on numerous factors, from the app’s complexity of features to the location of the development team.
Cost Estimates by App Complexity and Development Phase
When considering building a telemedicine app, the first question that likely comes to mind is: “What will this cost me?” It’s a fair question, and while there’s no one-size-fits-all answer, understanding the cost breakdown can help you plan smarter and avoid budget surprises.
Telemedicine app development costs can range anywhere from $30,000 to well over $200,000. But don’t let that wide range discourage you. Let’s break down exactly what drives these costs and how you can make informed decisions for your project.
Cost Variations by App Complexity
Think of app complexity like building a house. A studio apartment costs less than a mansion, right? The same principle applies here:
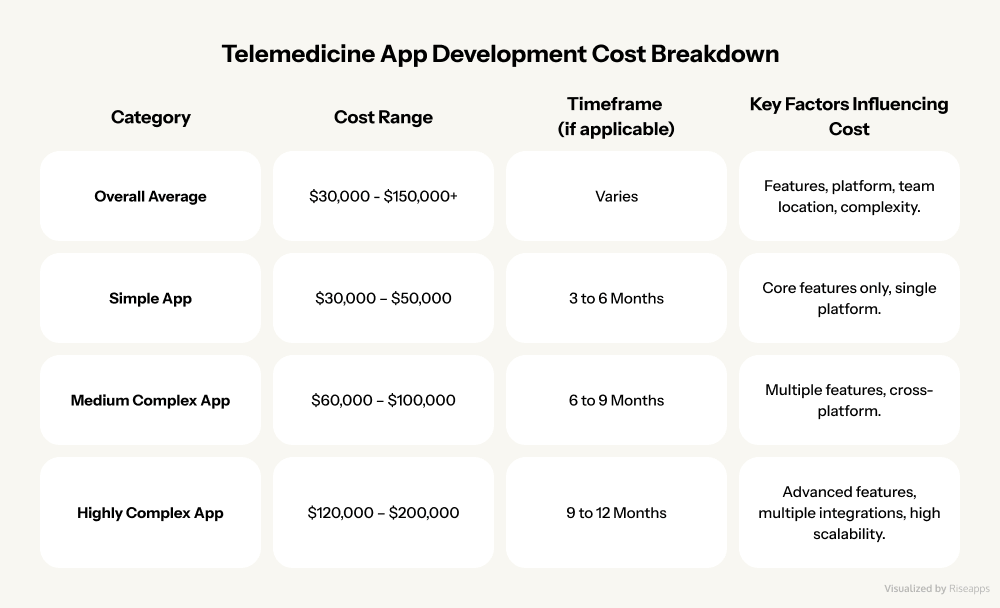
- Simple telemedicine apps ($30,000 – $50,000): Perfect for startups testing the waters, these apps handle the essentials:video consultations, basic scheduling, and simple patient profiles. Development typically takes 3-6 months, making them ideal for quick market entry.
- Medium-complexity apps ($60,000 – $100,000): These are your “sweet spot” solutions, featuring advanced scheduling, electronic prescriptions, payment integration, and basic analytics. Expect 6-9 months of development time.
- Highly complex apps ($120,000 – $200,000+): We’re talking enterprise-level solutions here: AI-powered diagnostics, multi-provider networks, advanced analytics, and seamless EHR integration. These powerhouses take 9-12 months to build but deliver unmatched functionality.
Breaking Down Costs by Development Phase
Ever wondered where your money actually goes during development? Here’s the inside scoop on how costs distribute across a typical high-end telemedicine project:
- Research & planning ($15,000 – $25,000): This foundational phase involves market analysis, competitor research, and technical architecture planning. While it might seem like a hefty upfront cost, proper planning can save you thousands in costly pivots later.
- UI/UX design ($20,000 – $40,000): Great design isn’t just about looking pretty. It’s about creating intuitive experiences that patients and doctors actually want to use. This phase includes user research, wireframing, prototyping, and creating a cohesive visual design system.
- Front-end development ($40,000 – $70,000): This is where your app comes to life visually. Developers create responsive interfaces that work seamlessly across devices, ensuring smooth navigation and lightning-fast load times.
- Back-end development ($60,000 – $100,000): The engine under the hood. This covers server infrastructure, database design, API development, and all the complex logic that makes your app tick. It’s typically the most expensive phase, but also the most critical.
- QA & testing ($10,000 – $20,000): Nobody wants a buggy healthcare app. Comprehensive testing ensures HIPAA compliance, security protocols, and flawless functionality across different devices and scenarios.
- Post-launch maintenance ($20,000 – $50,000/year): The journey doesn’t end at launch. Regular updates, security patches, feature enhancements, and server maintenance keep your app running smoothly and competitively.
Cost Variations by Telemedicine App Type
Not all telemedicine apps are created equal. Your specific use case significantly impacts development costs:
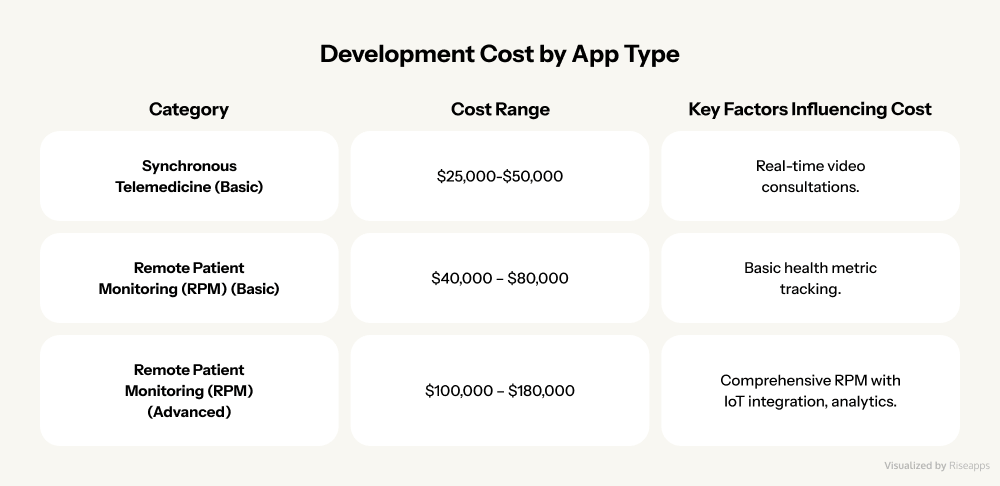
- Synchronous telemedicine apps ($25,000 – $50,000): These real-time consultation platforms are the bread and butter of telehealth, offering live video calls, instant messaging, and immediate provider-patient interaction.
- Basic remote patient monitoring (RPM) apps ($40,000 – $80,000): Ideal for chronic disease management, these apps track vital signs, medication adherence, and send alerts for anomalies. All without requiring constant provider attention.
- Advanced RPM solutions ($100,000 – $180,000): These sophisticated systems integrate multiple medical devices, use predictive analytics, and often include AI-powered insights for proactive care management.
Check our table with a telemedicine solution development cost overview.
How Riseapps Approaches Telemedicine Solutions
The telemedicine revolution isn’t just about moving healthcare online. It’s about reimagining how care is delivered, accessed, and experienced.
At Riseapps, we help telehealth market leaders demonstrate that success comes from solving real healthcare challenges with innovative technology.
But we don’t just develop telemedicine apps. We architect healthcare transformations that deliver measurable impact through:
- Proven results: From 40x efficiency gains to 300% faster clinical outcomes
- Speed to market: Full platforms delivered in 6-8 months, not years
- Compliance excellence: ISO 27001, ISO 9001, and 100% HIPAA compliance guaranteed
- Healthcare expertise: Supporting 100,000+ doctors and 1M+ patients globally
- End-to-end solutions: From AI integration and EHR connectivity to custom workflows
Let’s explore how we helped these companies transform their visions into thriving platforms that serve millions.
1. Black Doctor 24/7: Healthcare Without Barriers
Built for: African-American patients seeking physicians who understand their health risks, individuals in healthcare deserts, and anyone who’s ever felt unheard in a traditional medical setting.
Dr. Bill Releford, a podiatric surgeon, recognized a painful truth: healthcare disparities in the African-American community weren’t just statistics. They were preventable tragedies. His response? Black Doctor 24/7, a telemedicine platform.
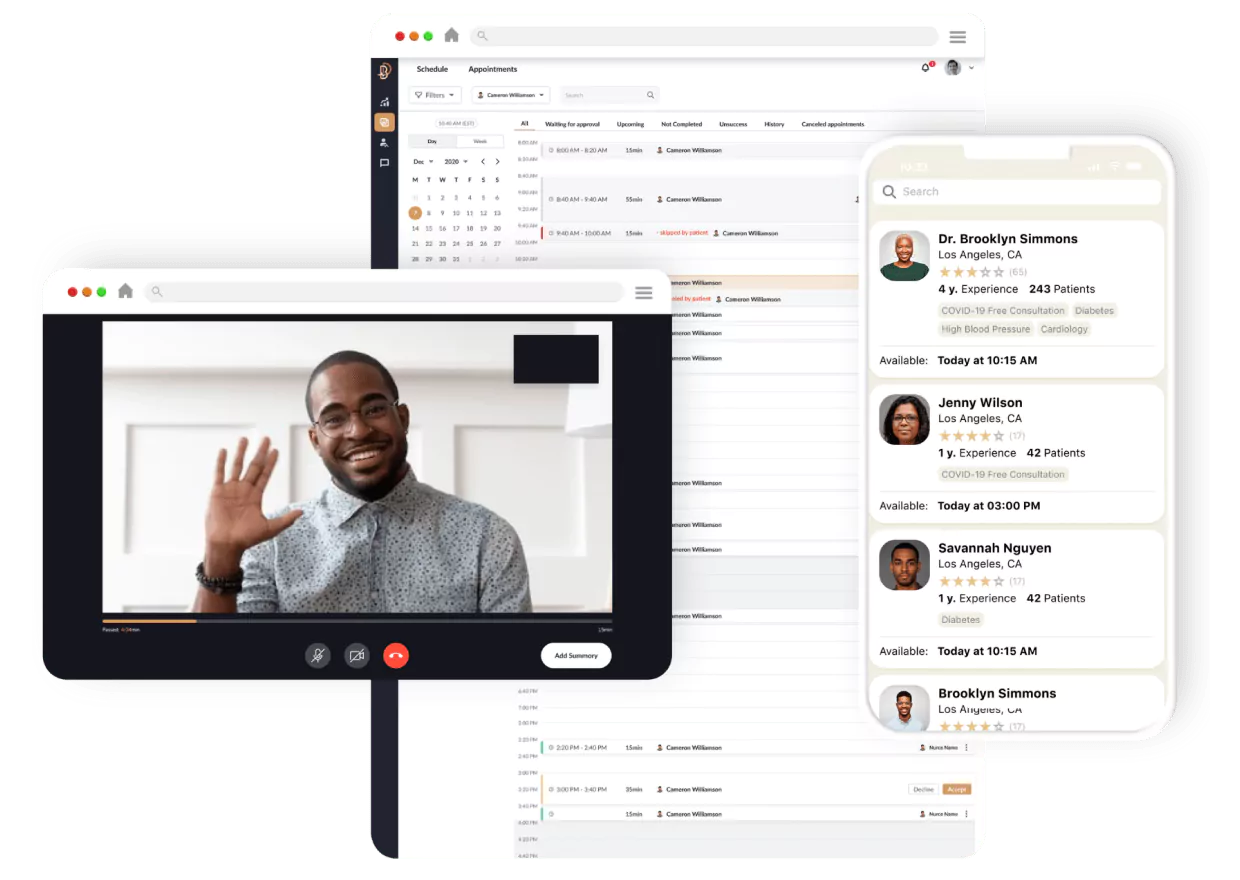
What sets it apart: Black Doctor 24/7 uniquely combines cultural competency with cutting-edge technology.
By focusing specifically on the African-American community’s healthcare needs (where cardiovascular disease and diabetes rates are disproportionately high) the platform provides a trusted alternative to traditional healthcare systems while maintaining 100% HIPAA compliance.

How Riseapps made it happen: Faced with an ambitious 6-month launch timeline, Riseapps delivered what typically takes a year or more.
For a Black Doctor 24/7, the Riseapps team delivered:
- AI virtual assistant “Amina” powered by Infermedica for 24/7 symptom triage
- High-quality video consultations via Agora integration
- Secure real-time messaging through GetStream integration
- Flexible appointment scheduling with provider selection
- Multi-component physician dashboard for streamlined workflows
- Automated patient queries and prescription management
- A HIPAA-compliant infrastructure on AWS
- Separate experiences for patients and physicians.
As a result, the Black Doctor 24/7 platform achieved 100% HIPAA compliance on its first review and helped reduce care delivery costs by 40%.
2. Skinpick: Transforming Mental Health Through Specialized Care
Built for: Individuals battling dermatillomania, trichotillomania, or OCD who need specialized treatment and therapists seeking evidence-based digital tools.
The Israeli mental health startup Skinpick had a noble mission to innovate its treatment approach of dermatillomania (compulsive skin picking), trichotillomania (hair pulling), and OCD (conditions affecting millions yet rarely discussed).

What sets it apart: By creating Skinpick, laser-focused on excoriation disorders, they provide targeted interventions that general platforms can’t match. The 46% reduction in OCD-related symptoms within 120 days speaks volumes about their specialized approach.
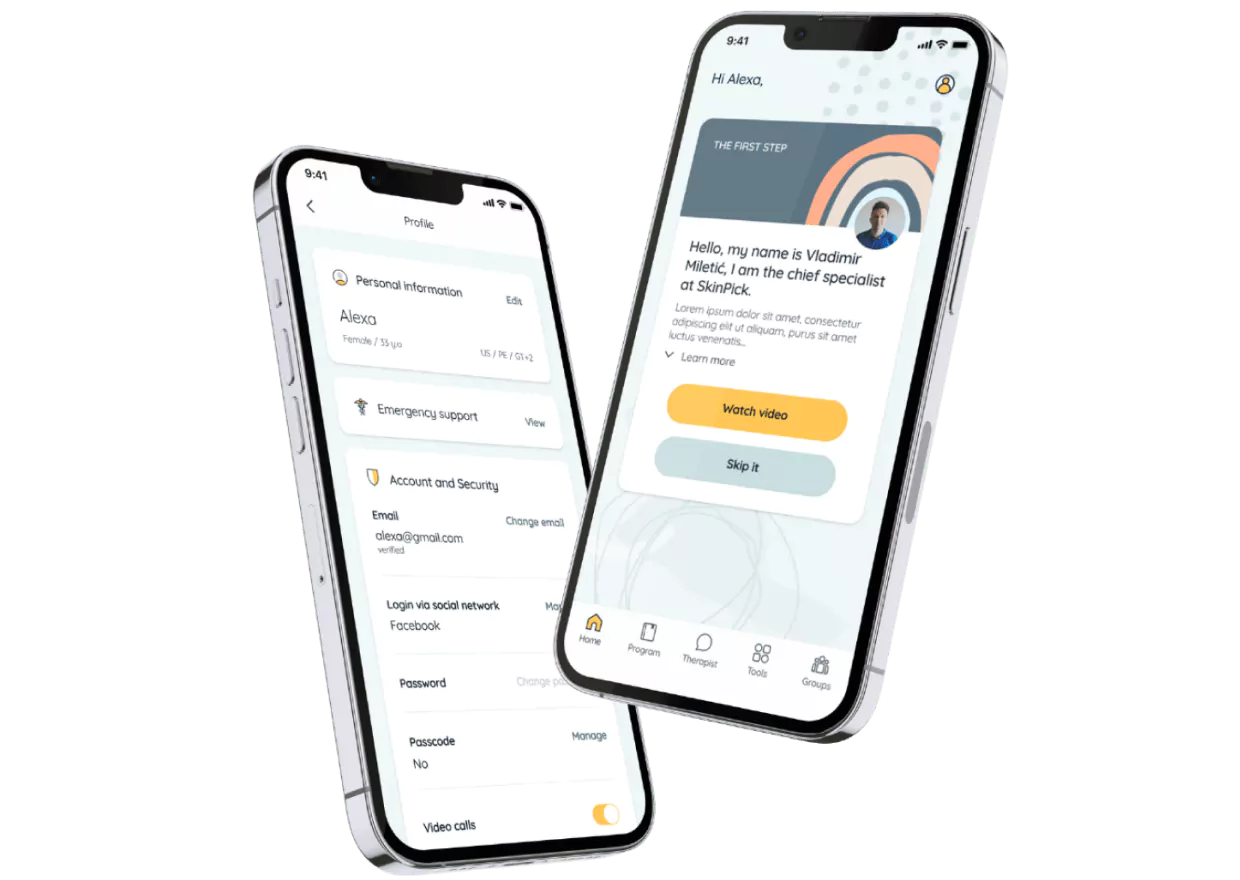
How Riseapps made it happen: Starting with an 8-year-old desktop-only platform, Riseapps completely reimagined the user experience. They delivered:
- Mobile-first therapeutic modules that transform desktop-only content into engaging, accessible experiences
- 5x expansion in therapy tools, including mindfulness practices, progressive muscle relaxation, and R.A.I.N. training
- Smart session constructor allowing therapists to customize treatment plans 3.5x faster
- Real-time peer support rooms organized by topics for community healing
- Interactive progress tracking with visual analytics showing improvement patterns
- A cloud-based patient-physician chat, replacing outdated PDF-based communication

As a result, a mobile-first design made therapy accessible anywhere, expanded therapeutic tools by 400%, and reduced clinician workload by 47% through intelligent automation.
3. Almond Health: Reimagining Women’s Healthcare
Built for: Women tired of the traditional healthcare runaround and those managing complex conditions like PCOS or endometriosis.
Healthcare visionary Tara Raffi experienced firsthand the frustrations millions of women face:
- weeks-long waits for OB-GYN appointments,
- rushed visits,
- dismissed concerns.
Her answer was Almond Health. This platform makes quality women’s healthcare as accessible as ordering lunch.
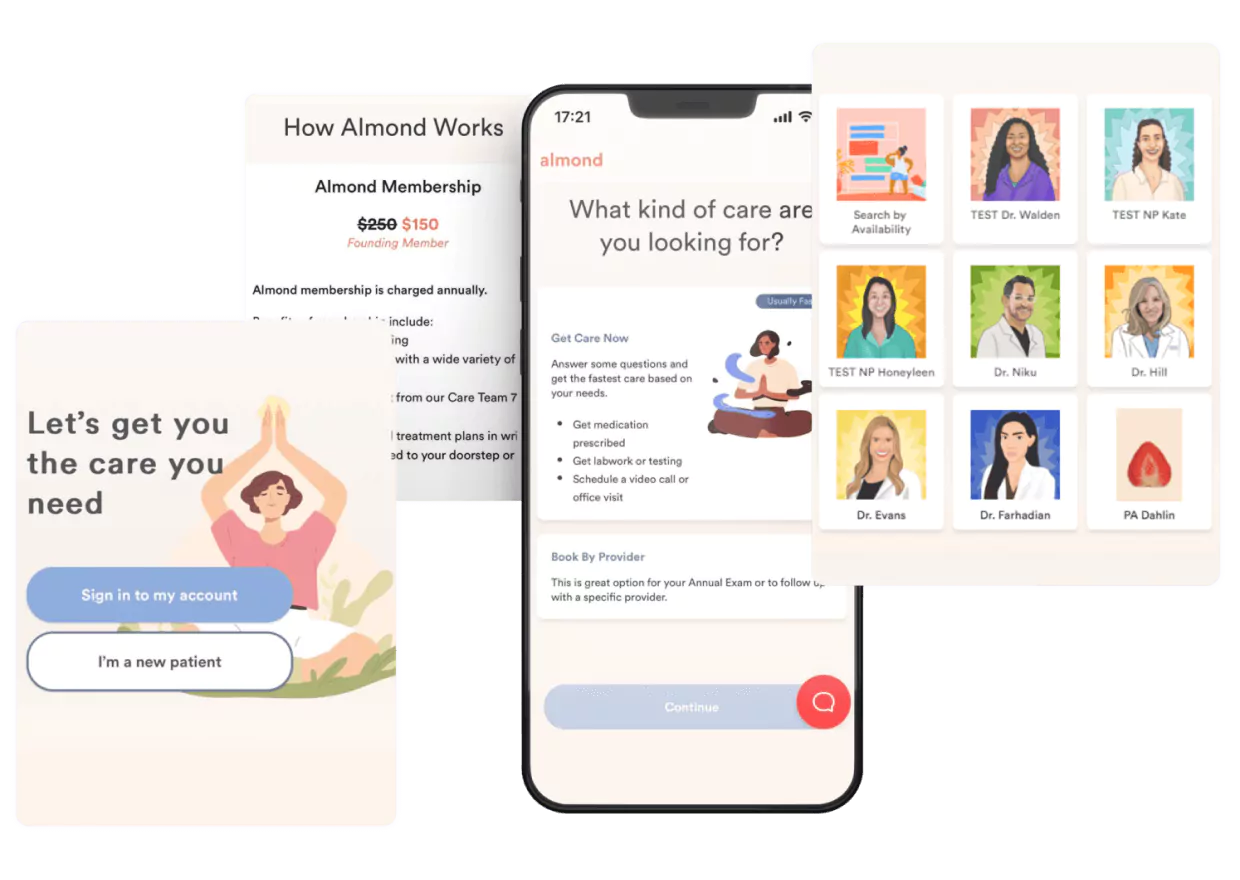
What sets it apart: Almond Health‘s unique combination of gamification, accessibility, and integrated care approaches sets it apart. The platform successfully addresses the common frustration of long wait times and offers on-demand booking and comprehensive care options.
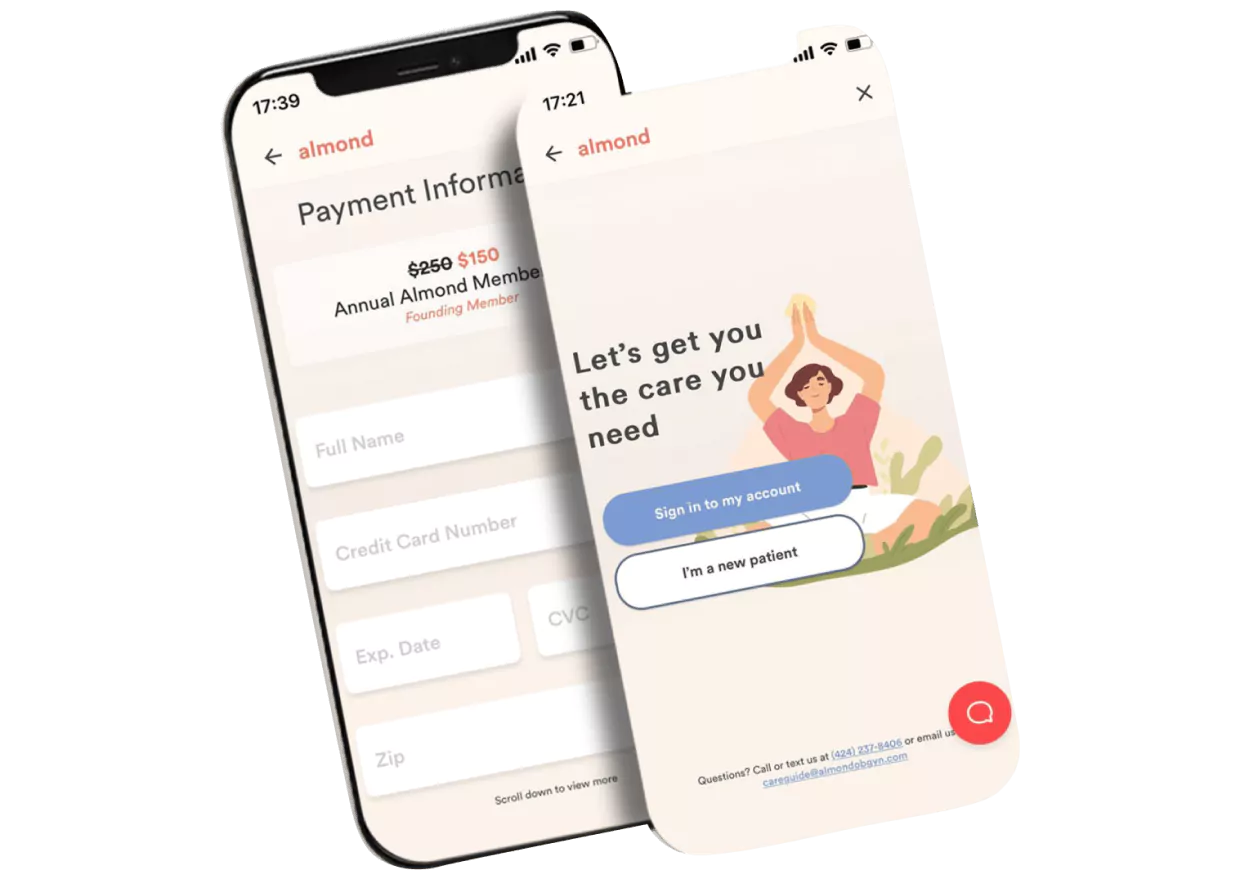
How Riseapps made it happen: The team developed a platform that feels more like a wellness app than a medical tool, with tools like:
- Gamified patient onboarding flows with interactive questionnaires
- 24/7 online appointment booking for virtual and in-person visits
- Integrated traditional and functional medicine approaches
- Secure profile and medical history management
- Real-time messaging for pre- and post-appointment care
- Patient progress tracking with visual health dashboards
- Automated appointment reminders and follow-ups

The result? 462 new appointments booked in the first month alone, and $7M in funding to fuel expansion.
Want to build an innovative AI-powered telemedicine app like Black Doctor 24/7, Skinpick, or Almond Health?
FAQ
How to create a telemedicine app?
Follow 6 essential steps: conduct market analysis, design HIPAA-compliant architecture, integrate core features (video consultations, e-prescriptions, payment gateway), develop using React Native or Flutter (saves 30% time), perform penetration testing, deploy on AWS/Azure. Timeline: 16-24 weeks with $75,000-$250,000 investment.
How much does it cost to build a telehealth app?
MVP telehealth apps cost $55,000-$95,000 (3-4 months development). Enterprise solutions with AI triage, blockchain records, and 10+ integrations range $200,000-$450,000 (6-12 months). Hourly rates: US developers $150-$250, Eastern Europe $50-$100, reducing costs by 60%.
How to develop a telehealth program?
Launch in 90 days: secure state licenses (2-4 weeks), implement encrypted platform supporting 500+ concurrent sessions, train staff (95% competency required), establish 5-7 insurance partnerships, create clinical protocols. Successful programs achieve 89% patient retention and 4.8/5 satisfaction scores.
How profitable is telemedicine?
Telemedicine generates $79.7 billion annually (2024), with practices earning $150-$300 per virtual visit. Operating costs drop 68% compared to physical clinics. Average practice ROI: 320% within 24 months, serving 3x more patients with 50% less staff overhead.
How to start your own telehealth business?
Invest $75,000-$200,000 initially: form LLC/corporation ($500-$2,000), obtain multi-state licenses ($5,000-$15,000), secure cyber liability insurance ($2,500-$7,500/year), hire 2-3 providers. Reach profitability serving 1,000+ patients monthly within 14-16 months.
Contact Us








