Connected Medical Devices in 2025: Definition, Examples, Benefits
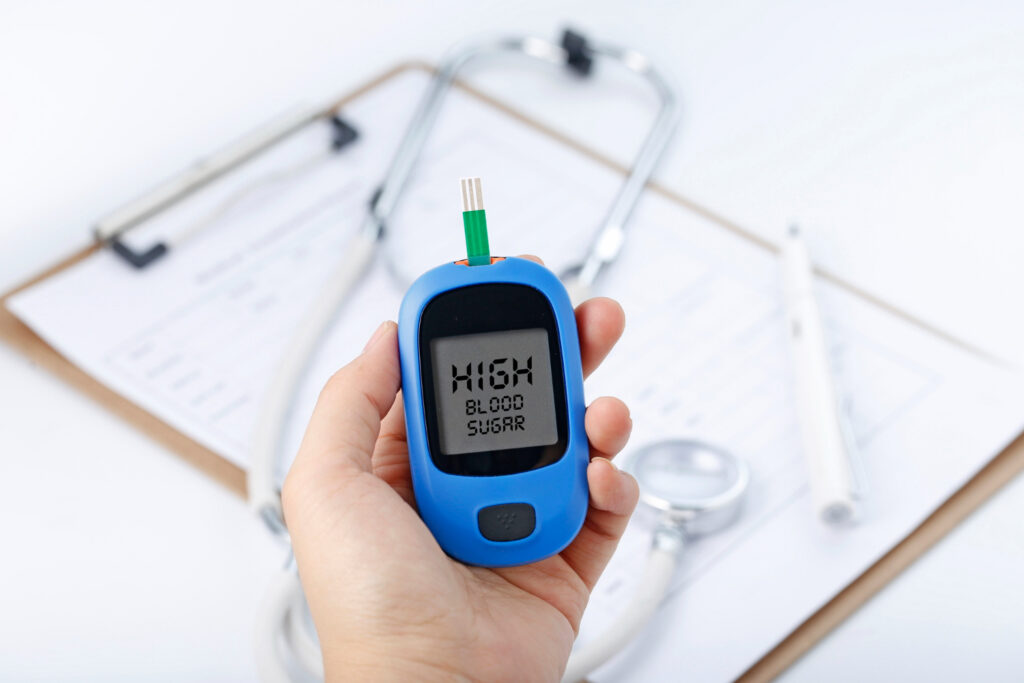
According to ZS’s 2024 Future of Health report, which surveyed 9,500 healthcare consumers and 1,359 healthcare providers across six countries, more than 50% of respondents in the US, UK, and China believe connected health solutions can help prevent illness and improve long-term health outcomes through proactive monitoring of personal health data.
Real-world solutions like InteliWound, an AI-powered wound management platform developed by Riseapps, are already proving this value—helping clinicians reduce treatment time, enhance decision-making, and optimize workflows. Similarly, RxPhoto, a HIPAA-compliant medical imaging platform, is transforming documentation in dermatology, aesthetics, and plastic surgery. Automated, structured patient photo management improves treatment tracking and reduces the administrative workload for physicians.
In this article, you’ll discover how to create a connected medical device platform that delivers quality healthcare services without barriers.
Connected medical devices and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) market in numbers
Below are relevant statistics that showcase the current state of the IoMT and connected medical devices market.
Market growth in figures:
- In 2023, connected medical devices accounted for 54% of total remote RPM revenues. The number of remotely monitored patients is expected to reach 126.1 million by 2027 compared to only 56.8 million in 2021 (Berg Insight).
- The global revenue of medical devices is forecasted to reach a whopping $539.11 billion in 2025 (Statista).
Key market trends driving growth:
- Increased demand for real-time remote monitoring devices and software solutions due to aging populations and rising chronic disease cases. The global population aged 60 years and older is expected to double from 1 billion in 2020 to 2.1 billion by 2050 (World Health Organization). Approximately 95% of adults aged 60 and older have at least one chronic condition, with 79% having two or more (National Council on Aging).
- AI and big data integration enable early diagnosis, predictive healthcare, and automated alerts. In 2024, the AI-based network-connected medical devices market reached $22.3 billion, up from $15.42 billion in 2023 (Market Research). As one example, GE Healthcare Technologies, Inc. introduced the SIGNA Champion, which uses AI to enhance the precision and efficiency of MRI scans.
- Regulatory support for telehealth and RPM reimbursement, expanding access to digital health solutions. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) have expanded reimbursement for RPM services, which are essential for managing chronic conditions.
- 5G technology, making connected healthcare more efficient and accessible worldwide by increasing telehealth adoption, enhancing surgical robotics, and improving emergency response systems. 5G can allow healthcare providers globally to save approximately $90 billion by 2030 (5G’s Healthcare Impact by STL Partners).
Key market segments and leading players
Certain connected medical devices examples are having faster adoption, particularly in the realm of chronic disease management:
Implantable cardiac rhythm management (CRM). With such connected medical devices industry leaders as Medtronic, Abbott, Boston Scientific, and BIOTRONIK, this segment has delivered connective CRM devices for over 20 years. In a pivotal trial for Boston Scientific’s modular cardiac rhythm management system, 97.5% of patients were free from leadless pacemaker-related major complications. The system allowed the termination of 61.3% of arrhythmia episodes (MedTech Dive).
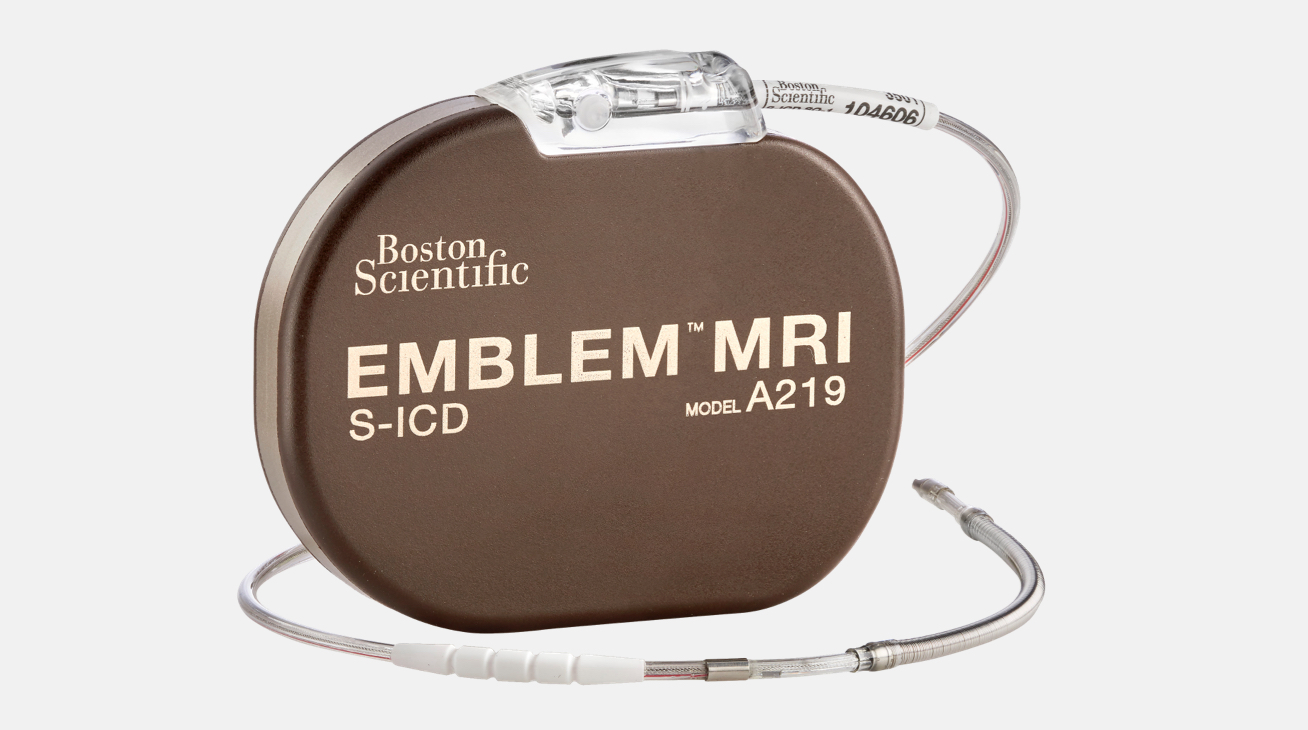
Image source: Boston Scientific
Remote ECG monitoring and wearables. Companies like AliveCor, iRhythm Technologies, and InfoBionic are top performers in this medical device category, offering AI-powered cardiac monitoring solutions. InfoBionic can potentially improve care for over 300 million patients through Epic-connected health systems (BusinessWire). Using AliveCor smart medical devices can save up to $169.34 per patient by reducing the need for serial 12-lead ECGs (National Library of Medicine).

Image source: AliveCor
Glucose monitoring and diabetes management. Such medical device manufacturers as Abbott, Dexcom, Tandem Diabetes Care, and Insulet prevail in the fast-growing market of connected insulin pumps and CGMs. Real-world data from Abbott’s FreeStyle Libre system for glucose monitoring showed a 38% reduction in time spent in hypoglycemia (<70 mg/dL) when glucose monitoring frequency increased (Abbott).

Image source: Dexcom
Medication compliance monitoring. Solutions from Compliance Meds Technologies, MedMinder, MedReady, and Hero help improve medication adherence via smart pill dispensers. A study conducted by MedMinder revealed that without reminders, medication adherence rates were in the range of 50-60% and increased dramatically to 90-100% after activating reminders.

Image source: MedMinder
5 business benefits of building a connected medical devices environment
Adopting connected medical devices and IoMT infrastructure delivers significant advantages for healthcare providers, patients, and medical technology companies.
Enhanced patient outcomes and personalized care
- Real-time remote health monitoring detects potential medical issues before they escalate, reducing hospital readmissions.
- AI-driven analytics personalize treatment plans, ensuring better disease management and medication adherence.
- Chronic disease patients (e.g., diabetes, cardiac issues, respiratory disorders) benefit from continuous, at-home monitoring.
Real-life example: Observa Care, an ambitious initiative in Australia that aims to provide over 7 million people living in distant and rural areas with due care. The company uses wearable devices connected via nbn network-connected medical devices to monitor patients’ health metrics in real time to assist medical professionals in patient engagement, treatment, and triage. With the help of Observa Care, patients can recover at home, reducing hospital stays, and alleviating the burden of travel from rural regions. In 2023, Observa Care was honored as the overall winner in the Innovate with nbn Grants Program, highlighting their commitment to bridging the healthcare gap in regional and rural Australia.
Operational efficiency and cost reduction for healthcare providers
- Automated data collection and AI-powered triage systems allow doctors to focus on high-priority cases.
- Smart hospital solutions (connected infusion pumps, asset tracking, and automated inventory systems) improve clinical workflows and reduce waste.
Real-life example: TeleTracking’s cloud-based software assists hospitals in managing bed allocations and patient flow. For instance, Maidstone and Tunbridge Wells Trust implemented this system, resulting in significant improvements in patient flow and reduced wait times (from 1000 patients waiting 52 weeks for treatment to 0 patients within 15 months).
Increased accessibility and inclusion in healthcare
- IoMT expands access to healthcare in rural areas, enabling virtual consultations and remote diagnostics.
- Connected wearables and telemedicine integrations help elderly patients and individuals with mobility issues receive continuous care.
- Multilingual voice-assisted AI supports non-native speakers and people with disabilities, ensuring inclusive connected healthcare solutions.
Real-life example: CardMedic, an app developed to facilitate communication between healthcare workers and patients, uses scripts to bridge communication gaps. Such a tool is particularly beneficial for patients with language barriers or disabilities, ensuring they receive accurate and timely information about their care. The platform hosts over 1,200 scripts covering a wide range of medical scenarios, facilitating clear communication in diverse clinical settings. CardMedic is now used in 25 hospitals in the UK (The Oxford Trust).
Stronger data-driven decision-making and research advancements
- Big data analytics and AI-powered medical insights improve clinical research and drug development.
- Aggregated patient data helps predict disease outbreaks, enabling faster public health responses.
Real-life example: GE Healthcare has invested in cloud-connected medical devices platform development to collect, store, and process data from diverse medical devices, enabling the sharing of medical images across diverse specialists. The company has installed over 4 million medical devices worldwide, contributing to a vast amount of healthcare data generation. With the help of enhanced connectivity, GE Healthcare reduces workflow processing time and supports collaborative decision-making, leading to improved patient outcomes.
New revenue streams for MedTech and healthcare enterprises
- Subscription-based RPM modules integrated into existing solutions create recurrent and stable revenue streams for healthcare providers.
- Medical device manufacturers monetize APIs and software integrations, allowing seamless connectivity with a variety of healthcare systems such as electronic health record (EHR) systems, healthcare information exchange (HIE) systems, and laboratory information systems (LISs) ensure interoperability and quick access to holistic patient information.
- Pharmaceutical companies use real-world patient data for clinical trials and conduct studies on drug effectiveness.
Real-life example: Teladoc Health has introduced subscription models for their telemedicine and remote patient monitoring services. Thanks to subscription-based service delivery, Teladoc Health ensures a steady revenue stream while offering patients continuous care and support. By 2023, Teladoc Health reached a milestone of 50 million virtual visits, underscoring the widespread adoption and trust in their telehealth services.
Real-world success in medical IoT development
Delayed or incomplete patient information leads to reactive rather than proactive care which can be threatening for patients and increase hospital readmissions. Remote patient monitoring via connected medical devices integrated with key healthcare systems can provide physicians with real-time patient data and an opportunity to act quickly. Riseapps helped create an RPM web app for the CareHalo chronic disease management platform. It consolidates real-time patient data which can be used to predict and prevent high-risk medical conditions.
Customer request
A US-based healthcare company sought to enhance their chronic disease management platform, CareHalo, by integrating a HIPAA-compliant RPM module. This module needed to securely collect, store, and manage sensitive patient data, ensuring an efficient workflow for healthcare providers.

Solution
Riseapps developed a web-based RPM application featuring distinct roles for medical assistants and providers. The application offers an intuitive user interface, enabling seamless data collection and management. Advanced monitoring algorithms prioritize patient care based on urgency, and strict adherence to HIPAA guidelines ensures the confidentiality and integrity of electronically protected health information (e-PHI).
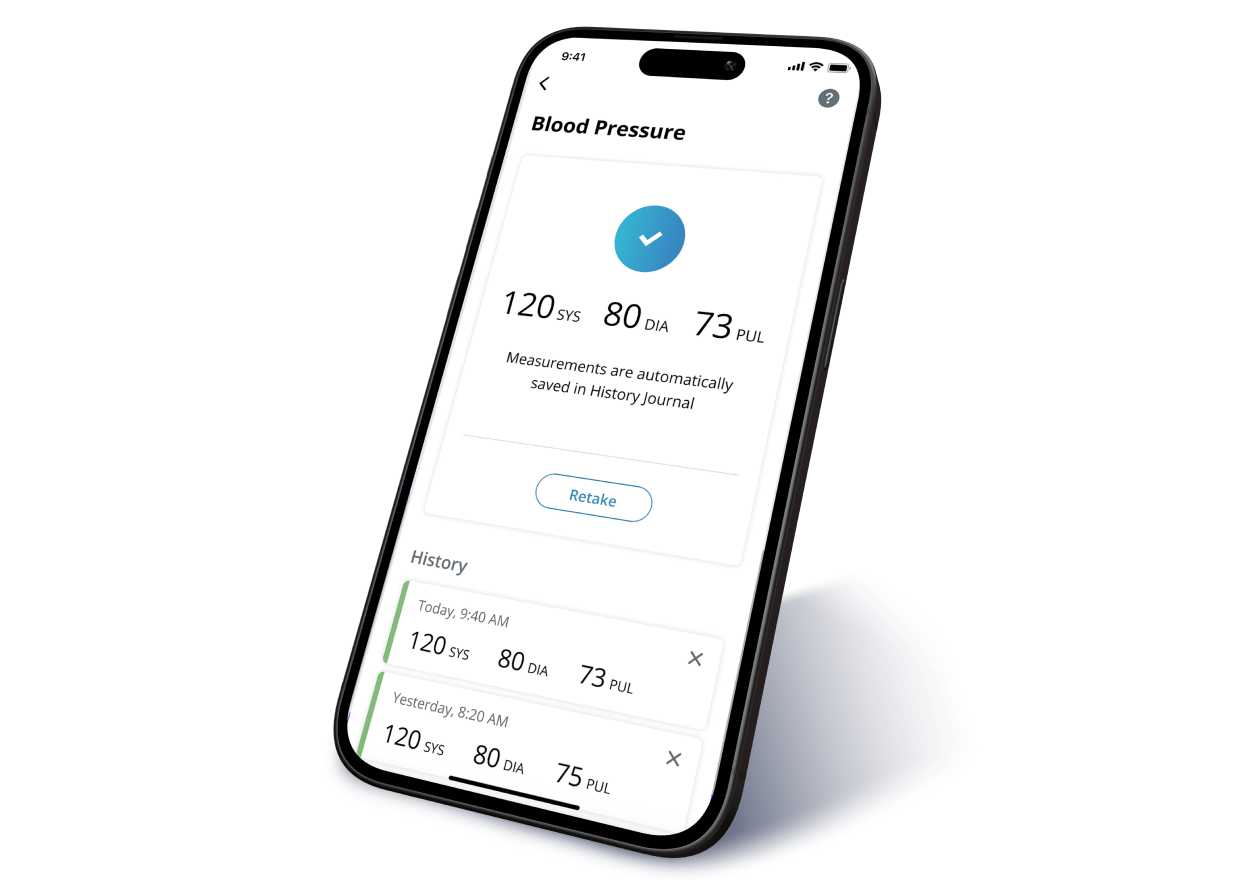
Results
The implementation of the RPM module has empowered healthcare practitioners to proactively monitor patient health, facilitating early intervention and reducing the need for in-person visits. This advancement not only enhances patient outcomes but also contributes to operational efficiency and profitability for the healthcare provider.
Discover below the key components of a resilient IoMT architecture and core principles of achieving smooth connectivity.
Components of the IoMT architecture
A well-structured architecture of connected medical devices consists of several interconnected layers that enable real-time health monitoring, predictive analytics, and seamless data exchange between patients, healthcare providers, cloud, and on-premises healthcare systems. The core components include medical devices, cloud infrastructure, AI-driven analytics, and web and mobile interfaces for medical providers and patients.
Medical devices layer
This layer includes wearable health monitoring devices, implantable devices, and smart medication adherence tools that collect and transmit real-time patient data. With the help of these devices, clinicians can provide patients with efficient chronic disease management, post-surgical recovery, and proactive patient monitoring and treatment.
Wearable health monitors
Smartwatches, ECG patches, and glucose monitors continuously track heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and glucose levels and provide real-time alerts to patients and healthcare providers, enabling early intervention and better disease management. For example, a highly integrated smartwatch designed for non-invasive glucose monitoring demonstrated 84.34% clinical accuracy in blood glucose measurements during real-life testing on 23 volunteers (National Library of Medicine).
Implantable medical devices
Pacemakers, insulin pumps, and neurostimulators are surgically implanted devices that offer continuous, real-time therapeutic support. Connected pacemakers can adjust heart rhythms remotely, while smart insulin pumps automatically deliver insulin based on a patient’s glucose levels.
Smart pill dispensers and medication adherence devices
Automated pill dispensers help patients adhere to prescribed treatment regimens. Devices such as MedMinder and Hero Health send reminders and alerts to prevent missed doses and reduce medication non-adherence risks. For instance, a study reported a high mean medication adherence rate of 98% among users of such devices (Springer).
Cloud computing infrastructure
Cloud service providers offer secure storage, real-time data processing, and seamless accessibility for healthcare providers. Scalability and security of connected medical devices are essential requirements when designing an architecture to handle massive volumes of medical data.
Data ingestion in the cloud via secure gateways
- Medical device data is securely transmitted through gateways that filter and encrypt health information before sending it to cloud servers.
- These gateways ensure real-time synchronization between connected medical devices in the cloud, hospital networks, and remote healthcare providers.
Cloud storage and processing
- Cloud storage systems, including data lakes and data warehouses, store structured and unstructured health data securely.
- HIPAA-compliant cloud platforms such as AWS HealthLake, Microsoft Azure Health Data Services, and Google Cloud Healthcare API ensure data privacy and regulatory compliance.
Security and monitoring
- End-to-end encryption (AES-256) secures patient data from cyber threats.
- Role-based, data-centric, and context-centric access control and identity management solutions ensure that only authorized medical personnel can access sensitive health information.
Data analytics and machine learning module
The analytics and AI layer in healthcare enables real-time health insights, predictive diagnostics, and personalized patient care.
Data analytics layer for health insights
- The IoMT analytics layer aggregates real-time health data from multiple medical devices, transforming raw data into actionable insights.
- Data visualization tools generate comprehensive health reports for doctors, hospitals, and patients.
- AI-powered dashboards help identify trends in patient vitals, allowing healthcare professionals to intervene before health conditions worsen.
Machine learning models for predictive healthcare services
- Predictive analytics suggest treatment adjustments, helping doctors make data-driven medical decisions faster.
- Machine learning assists in diagnosing conditions like sepsis, stroke risk, and cardiac irregularities, reducing treatment delays and improving patient survival rates.
Consumption layer
The final layer of the IoMT architecture includes interface-powered digital solutions for providers, caregivers, and patients to interact with real-time health data.
Web interfaces for healthcare providers and medical staff
- Web applications with comprehensive dashboards allow clinicians to remotely monitor patients and access real-time health updates.
- Alerts and recommendations functionality help prioritize urgent cases, reducing the burden on hospital staff.
Mobile and web-based patient health apps
- Patients can use mobile health apps to track their health metrics, receive medication reminders, and book appointments with clinicians via telehealth platforms.
- Apps like Dexcom Clarity, Apple Health, and MySugr integrate with medical devices, helping patients manage chronic conditions more effectively. Users of Dexcom Clarity experienced up to a 15% increase in time spent within their target glucose range (70-180 mg/dL) compared to non-users.
IoT communication technologies powering connected medical devices
Seamless connectivity is the backbone of the IoMT ecosystems, enabling real-time data transfer, remote monitoring, and AI-driven analytics. Modern connected medical devices rely on multiple wireless communication protocols, including Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Wi-Fi, 5G, LPWAN, Zigbee, and RFID to ensure secure and efficient health data exchange.
Bluetooth low energy (BLE): Short-range connectivity for wearable devices
BLE is a widely used low-power, short-range communication technology designed for wearable health monitors, fitness trackers, and implantable medical devices. BLE enables continuous data collection and transmission without draining battery life, making it an ideal solution for always-on healthcare devices.
Why BLE is essential for connected healthcare devices:
- Optimized for low-energy operation – Reduces power consumption, extending battery life for smartwatches, ECG patches, and glucose monitors.
- Reliable short-range connectivity – Provides stable, low-latency data exchange between wearable devices and mobile apps or cloud platforms.
- Seamless integration with mobile health ecosystems – BLE-enabled medical devices sync effortlessly with smartphones, tablets, and hospital systems for real-time monitoring.
Example: The Dexcom G6 Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM) uses BLE to send real-time glucose readings to mobile apps, allowing diabetes patients to track their blood sugar levels without frequent finger pricks.
Wi-Fi: High-bandwidth connectivity for telemedicine and cloud-based healthcare
Wi-Fi remains a key enabler of high-bandwidth, real-time healthcare applications, including video consultations, cloud data synchronization, and in-hospital connectivity. Unlike BLE, which is optimized for low-energy, localized communication, Wi-Fi supports larger data transfers, making it ideal for connected imaging devices, digital health records, and telehealth platforms.
How Wi-Fi powers IoMT in healthcare:
- Enables real-time telemedicine and remote consultations – High-speed internet allows patients to connect with doctors via video calls, improving access to healthcare.
- Supports large data transfers – Essential for MRI, CT scans, and medical imaging, ensuring quick upload and retrieval of large diagnostic files.
- Secure in-hospital networking – Wi-Fi powers smart hospital systems, from patient tracking and medication management to connected medical equipment.
Example: Teladoc Health, a global leader in telemedicine, uses Wi-Fi-powered video conferencing to connect patients with specialists remotely, reducing unnecessary hospital visits and improving access to healthcare in rural areas.
5G: The game-changer for remote patient monitoring and AI-driven healthcare
5G in healthcare offers ultra-fast, low-latency, and high-bandwidth connectivity. 5G networks eliminate communication delays, enabling real-time AI-driven diagnostics, advanced telemedicine, and remote robotic-assisted surgeries.
How 5G is transforming the connected medical devices security market:
Ultra-low latency for real-time medical interventions
Unlike Wi-Fi and 4G, which suffer from latency issues, 5G’s response time is under 1 millisecond—crucial for applications like AI-powered diagnostics and robotic surgeries. Surgeons can remotely control robotic-assisted surgical systems, such as the Da Vinci surgical robot, in near real-time, making complex procedures possible from remote locations.
Scalability for mass adoption of IoMT devices
5G networks can handle up to 1 million connected devices per square kilometer, supporting the massive IoMT expansion in hospitals, home healthcare, and smart ambulances. Large hospitals with thousands of connected infusion pumps, ventilators, and monitoring systems benefit from stable, congestion-free network performance.
AI-enhanced RPM
5G allows continuous health data streaming from wearable sensors, smart implants, and hospital-based devices, improving the efficiency of AI-powered patient monitoring systems. AI-powered remote ECG monitoring systems, such as those developed by AliveCor, can analyze cardiac irregularities in real time, preventing strokes and heart attacks before they occur.
Advanced mobile health services and edge computing
5G enhances mobile health apps, allowing doctors to access patient vitals, medical images, and treatment histories instantly, even in ambulances and rural clinics. Edge computing over 5G networks enables real-time medical AI processing at the device level, reducing the need for centralized cloud processing and speeding up diagnostics.
Example: In a groundbreaking procedure, a surgeon in Hangzhou, China, successfully performed a remote gallbladder removal on a patient situated over 4,500 kilometers away in Xinjiang. Utilizing 5G-powered robotic technology, the operation was completed seamlessly, demonstrating the potential of 5G to bridge the gap between urban medical centers and patients in remote regions.
LPWAN (LoRa, NB-IoT)
Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWAN), such as LoRa (Long Range) and Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT), provide long-range, low-power communication. These technologies are essential for rural healthcare applications, enabling continuous health monitoring without excessive power consumption. NB-IoT is widely used in pacemakers, smart inhalers, and connected glucose monitors to send patient data over long distances with minimal energy use.
Zigbee and RFID for Smart Hospitals
Zigbee-based networks are used in hospital automation, connecting medical devices, HVAC systems, and patient monitoring tools. RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags track hospital equipment, staff movement, and patient location, improving resource utilization and safety.
How to achieve seamless connectivity between medical devices and healthcare infrastructure
Interoperability is a major challenge in connected healthcare. Successful integration depends on:
- Standardized protocols. FHIR and HL7 frameworks ensure compatibility across healthcare ecosystems.
- Automated device management. Over-the-air (OTA) updates keep medical devices secure and functional.
- Cloud-based synchronization. Reduces data fragmentation and improves real-time diagnostics.
With a clear understanding of how to develop, integrate, and optimize medical device solutions, let’s consider possible applications of such solutions in different healthcare settings.
Use cases for adopting connected medical devices
Below are some of the most impactful use cases driving the adoption of connected medical devices in modern healthcare.
Remote patient monitoring and chronic disease management
Chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disorders, and respiratory diseases require continuous monitoring to prevent complications and improve long-term outcomes. Connected medical devices allow patients to get continuous vital sign measurements from home, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits and enabling early detection of deteriorating health conditions.
How it works:
- Wearable ECG patches and connected blood pressure monitors transmit real-time vitals to healthcare providers for improved medical services.
- Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) track blood sugar levels, sending alerts for abnormal fluctuations.
- AI-powered predictive analytics detect health risks early, allowing doctors to intervene before emergencies occur.
Real-world example: According to a study by Arizona cardiology practice, RPM reduced hospital readmissions for heart patients by 50%, freeing up hospital resources.
Treatment and medication adherence
Non-adherence to prescribed medication regimens costs healthcare systems billions annually and leads to avoidable hospitalizations and worsening conditions. Connected medication adherence devices ensure that patients take the right dose at the right time, improving compliance and treatment effectiveness.
How it works:
- Smart pill dispensers provide audible reminders and automated dispensing.
- AI-powered apps send personalized alerts based on patient habits and medication schedules.
- Caregivers and doctors receive real-time adherence reports, allowing intervention when necessary.
Real-world example: Hero Health’s smart pill dispenser helped improve medication adherence by over 95% for chronic disease patients in the US.
Point-of-care diagnostics
Traditional diagnostic tests require patients to visit hospitals or labs, often delaying treatment. Point-of-care diagnostic devices allow for on-the-spot disease detection, reducing waiting times and improving treatment outcomes.
How it works:
- Portable blood testing devices analyze biomarkers, infections, and chronic disease indicators within minutes.
- AI-enhanced imaging devices provide instant skin cancer or retinal disease detection in remote areas.
- Connected stethoscopes and smart otoscopes enable virtual consultations, helping doctors diagnose illnesses remotely.
Real-world examples:
- Abbott’s ID NOW™ rapid COVID-19 test delivered PCR-equivalent results in under 13 minutes, expediting the pandemic response.
- Handheld ultrasound scanners like Butterfly iQ allow paramedics and rural clinics to perform real-time diagnostics without large, expensive equipment.
Elderly care and fall prevention
Falls among older adults account for over 3 million emergency visits per year. AI-powered fall detection and senior monitoring systems significantly reduce response times, enabling faster medical intervention.
How it works:
- Wearable fall detection sensors (like Apple Watch and Vayyar Home) automatically alert caregivers if a fall occurs.
- AI-driven motion analysis identifies mobility risks, allowing preventive interventions.
- Connected home monitoring systems track daily activities and behavioral changes, detecting early signs of dementia or declining health.
Real-world examples:
- Apple Watch’s fall detection feature has helped emergency responders reach fallen seniors in minutes, saving lives. For example, in January 2025, the feature was credited with aiding the rescue of stranded skiers who suffered a 1,000-foot fall in Washington State. The automatic SOS alert provided critical information to rescuers, leading to a swift and effective response (NY Post).
- Vayyar Home’s contactless monitoring system alerts caregivers about unusual inactivity, potential falls, or wandering behavior in seniors with dementia.
Connected ambulances
Emergency response depends on speed, accuracy, and real-time data exchange. 5G-powered connected ambulances enhance pre-hospital care, ensuring patients receive life-saving interventions even before reaching the hospital.
How it works:
- IoT-enabled ambulances connect to ER teams, sharing real-time patient vitals for faster diagnosis.
- 5G networks allow high-speed, AI-driven diagnostics while en route to the hospital.
- Portable defibrillators, ECG monitors, and oxygen sensors provide continuous monitoring during transport.
Real-world example: London’s Air Ambulance Charity is considering using AI insights to improve pre-hospital care, in particular, for trauma risk prediction.
Why choose Riseapps for developing a connected medical device solution
Building a secure, interoperable, and scalable connected medical device ecosystem requires deep technical expertise, regulatory compliance knowledge, and a user-centric approach. At Riseapps, we specialize in full-cycle IoMT development, helping MedTech companies and healthcare providers create compliant and high-performance connected medical solutions.
Proven expertise in medical IoT and digital healthcare
- End-to-End IoMT Development. From device firmware and cloud integration to AI-powered analytics and cybersecurity, we build seamless healthcare software solutions.
- FDA, HIPAA, and MDR compliance. Our development process follows strict regulatory requirements, ensuring data security and legal compliance.
- Integration with EHRs and hospital systems. We implement FHIR and HL7 standards to enable real-time data exchange with existing healthcare platforms.
Cutting-edge technologies for connected medical devices
- AI and machine learning for smart healthcare. We integrate predictive analytics, AI-powered diagnostics, and personalized treatment recommendations into IoMT platforms.
- Edge computing and 5G-enabled devices. Our solutions leverage low-latency connectivity for real-time health monitoring, enhancing device performance, and improving patient outcomes.
- Cybersecurity and data protection. End-to-end encryption and AI-driven anomaly detection secure patient data from cyber threats.
Scalable and future-proof healthcare solutions
- Cloud-cased infrastructure. We build scalable, multi-device IoMT systems, ensuring long-term adaptability as new medical devices emerge.
- Remote device management and OTA updates. Our solutions support continuous software updates, ensuring regulatory compliance and security enhancements.
- Customizable IoMT platforms. We design flexible, interoperable solutions tailored to your specific medical device requirements.
FAQ
What are the main challenges in developing a connected medical device ecosystem?
Key challenges include ensuring seamless and uninterrupted interoperability between healthcare systems and medical devices, cybersecurity risks, regulatory compliance (HIPAA, MDR, FDA, GDPR), real-time data synchronization, and scalability.
How do connected medical devices improve patient outcomes?
Connected medical devices enable real-time remote patient monitoring (RPM), AI-driven diagnostics, personalized treatment recommendations, and early disease detection, reducing hospital visits and improving chronic disease management.
How can businesses generate revenue from connected medical devices?
MedTech companies and healthcare enterprises monetize IoMT through subscription-based RPM services, data-driven healthcare insights, SaaS platforms for hospitals, and API integrations with third-party healthcare providers.
Contact Us








