Medical Device Software Development: Risks vs Potentials

Medical devices are the cornerstone of modern care delivery, with over 2 million types available worldwide.
As healthcare innovation moves forward, medical device software development initiatives have become integral to the healthcare innovations. However, while they yield impressive outcomes in healthcare delivery, there is a range of risks and bottlenecks that need to be considered. Let’s explore them in this article.
Medical Device Software Engineering Trends in 2024
As we navigate through 2024, the field of medical device software engineering is experiencing various transformative shifts. Let’s review these trends in medical devices in more detail.
Trend 1. Shifting From Hardware to Software
In 2024, the medical device industry shifted from hardware-centric to software-driven innovations due to regulatory advantages, cost-effectiveness, and streamlined care delivery. This transition is making healthcare solutions more dynamic, cost-effective, and patient-focused.
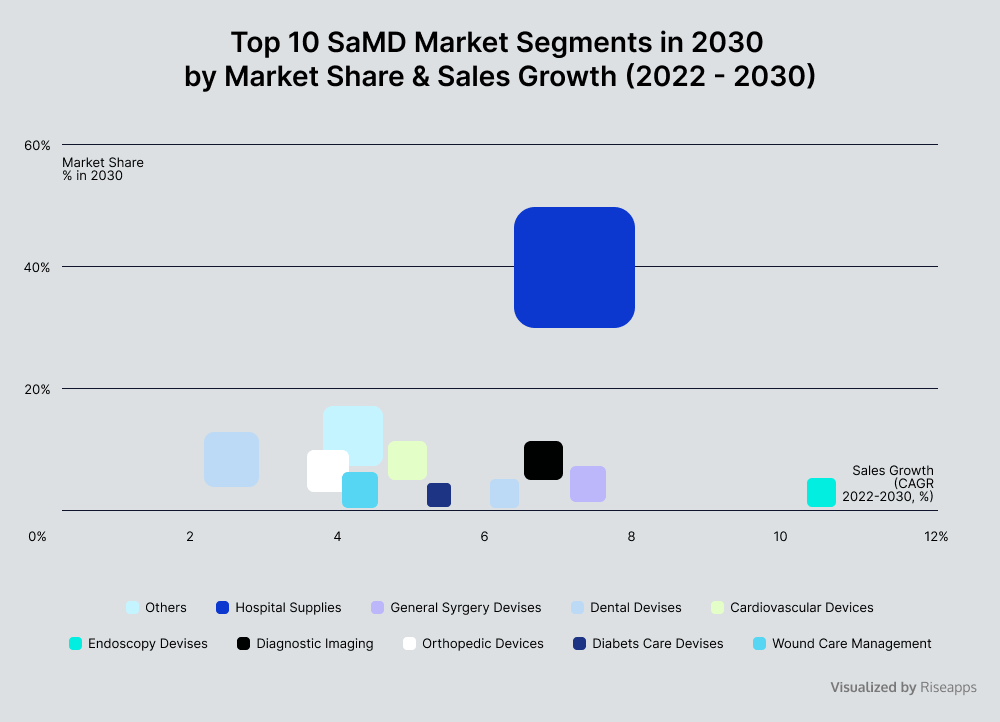
Trend 2. AI-Powered Medical Devices
With Artificial Intelligence (AI) being at the forefront of innovation in 2024, the market for FDA-approved AI-driven medical devices has grown 10 times since 2020 and is expected to grow further.
As the potential of AI-powered medical devices expands, they offer promising opportunities to enhance patient care through advanced technologies and data-driven insights. For example:
- AI-powered solution for sleep tracking and health insights monitors vital signs and provides personalized recommendations for improved sleep and overall health (Oura Ring);
- AI-based cardiac imaging is able to create personalized 3D models of coronary arteries to assist its precise diagnosis and treatment (HeartFlow);
- AI-driven symptom checker provides personalized health advice based on symptoms and user inputs (Buoy Health).

Trend 3. Upgrading Security Measures
Enhanced security is on the researchers’ agenda in 2024. In particular, the Vanderbilt Department of Computer Science has secured a $2 million contract to find solutions for enhancing software security for medical devices.
With that in mind, we can anticipate cutting-edge data protection technologies coming to the market soon.
Medical Device Software Development: Definition & Types
Medical device software development encompasses a vast field of creating software solutions that support or directly operate medical devices.
To help ensure that the level of regulatory control is commensurate with the risk posed by the device, medical device software is segmented into classes:
- Class I devices pose a low risk and have minimal regulatory requirements;
- Class II devices present moderate risk and require additional controls and testing;
- Class III devices are high-risk and subject to the most stringent regulatory requirements.
These various software systems are crucial components in modern healthcare, ensuring the functionality, reliability, and regulatory compliance of medical equipment. Let’s explore their major types, capabilities, and impact.
Embedded Medical Software
Embedded software solutions are specialized computing systems designed to perform specific tasks within larger systems or devices. They typically have dedicated hardware and software tailored for reliability, and efficiency, and often operate in real time, providing the most integrated and essential part of the healthcare device, especially electrical and electronic parts.
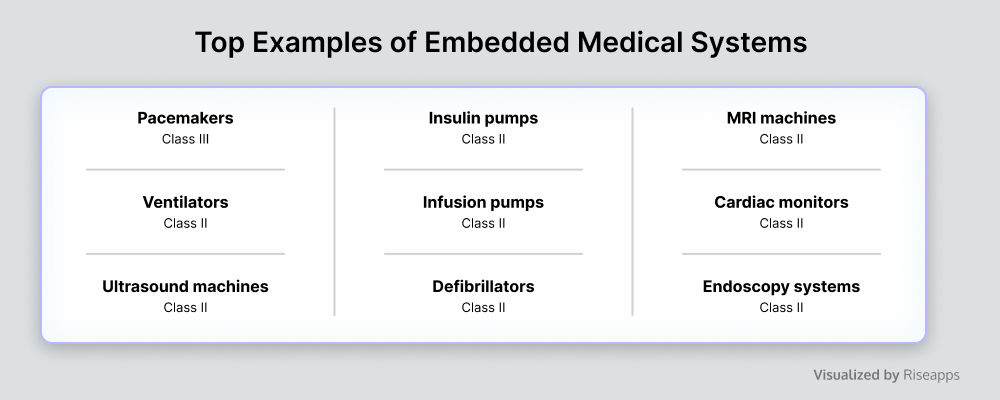
Embedded systems play a crucial role in meeting specific operational, functional, and regulatory requirements across diverse domains of the healthcare industry, enhancing reliability, efficiency, and functionality in complex environments.
Key Differentiators:
- Real-time operation
- High reliability
- Low power consumption
- High data security
Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
IoMT (Internet of Medical Things) refers to interconnected medical devices and applications that exchange health-related data over multiple healthcare networks, facilitating remote monitoring and healthcare management.
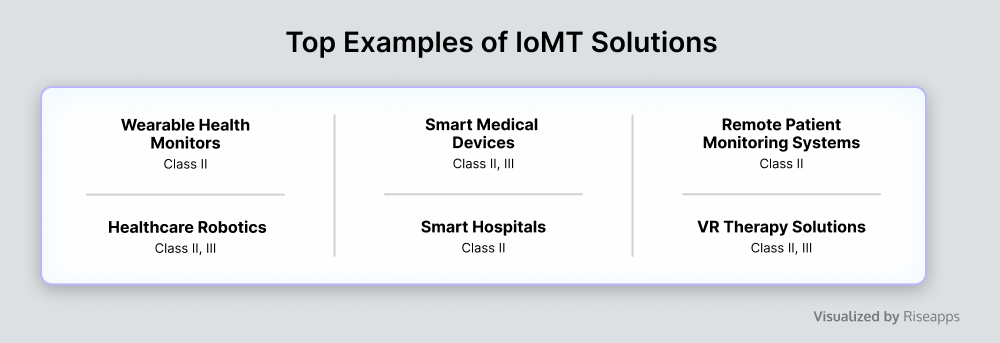
Unlike embedded systems, IoMT solutions are focused on networked connectivity and data exchange across multiple devices, whereas embedded solutions are dedicated to specific tasks within individual devices or systems without extensive network interaction.
Adopting IoMT offers improved patient care outcomes, operational efficiency gains, enhanced remote accessibility to healthcare services, valuable data-driven insights, and scalable, flexible solutions to meet future healthcare needs.
Key Differentiators:
- Interoperability
- Remote monitoring
- Real-time alerts
- Data-driven insights
Software as a Medical Device
Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) performs medical functions on general-purpose computing platforms, involving a network of medical devices and applications connected to healthcare IT systems.
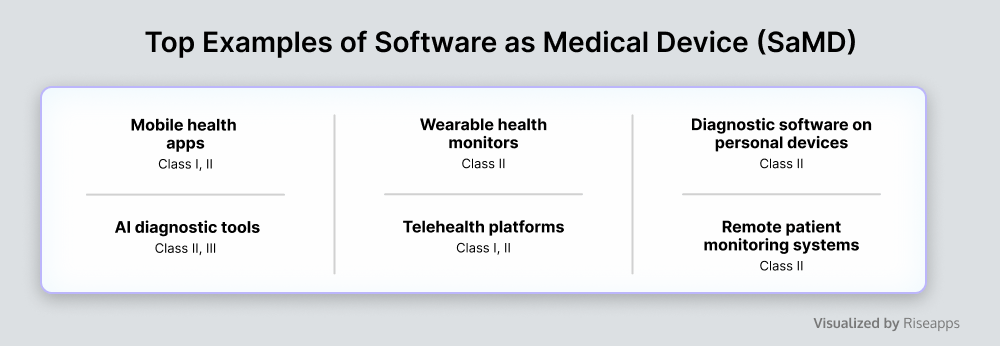
SaMD enhances patient outcomes through real-time monitoring and data analysis, enabling early diagnosis and personalized treatment. By streamlining clinical workflows and minimizing manual data entry and errors, it also improves operational efficiency and reduces costs.
Key Differentiators:
- Data analysis
- Connectivity
- Remote monitoring
- User-friendly interfaces
- Interoperability with other systems
Supportive Software for Medical Devices
This software supports the operation of medical devices, providing additional features for improved patient engagement, optimized device management and maintenance, accelerated workflows, enhanced security measures, and other enhancements.
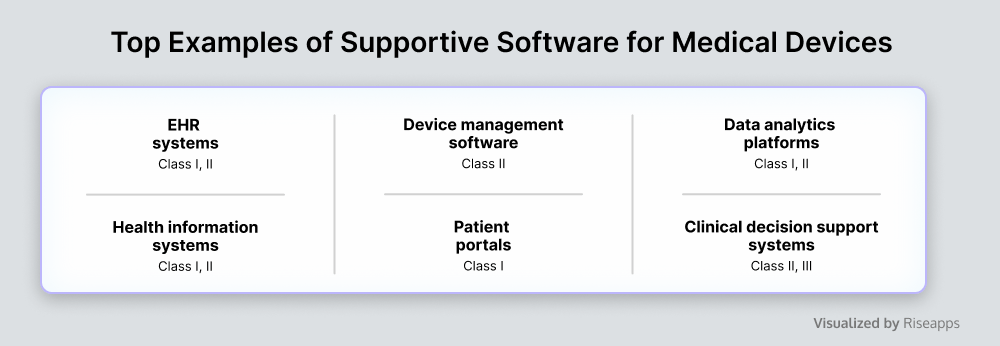
While not essential for medical device operability, such solutions improve overall usability and efficiency. For example, emulators testing software helps validate medical device functionalities by simulating diverse patient scenarios, while clinical decision support systems leverage data-driven insights.
Key Differentiators:
- Seamless data integration
- Convenient UI/UX
- Robust data management capabilities
- Enhanced security measures
- Scalability
Must-Have Features To Achieve Top-Notch Software Design for Medical Devices
The right feature set for medical device software is a game-changer. While functionality varies across different types of medical software devices, some essential features are indispensable. Let’s review them.
Real-Time Monitoring and Data Collection
Real-time monitoring and data collection module is the foundation of any medical device software.
Imagine this: with real-time insights, clinicians can make informed decisions swiftly, respond to emergencies promptly, and adjust treatments as needed. This can significantly boost operational efficiency and healthcare outcomes.
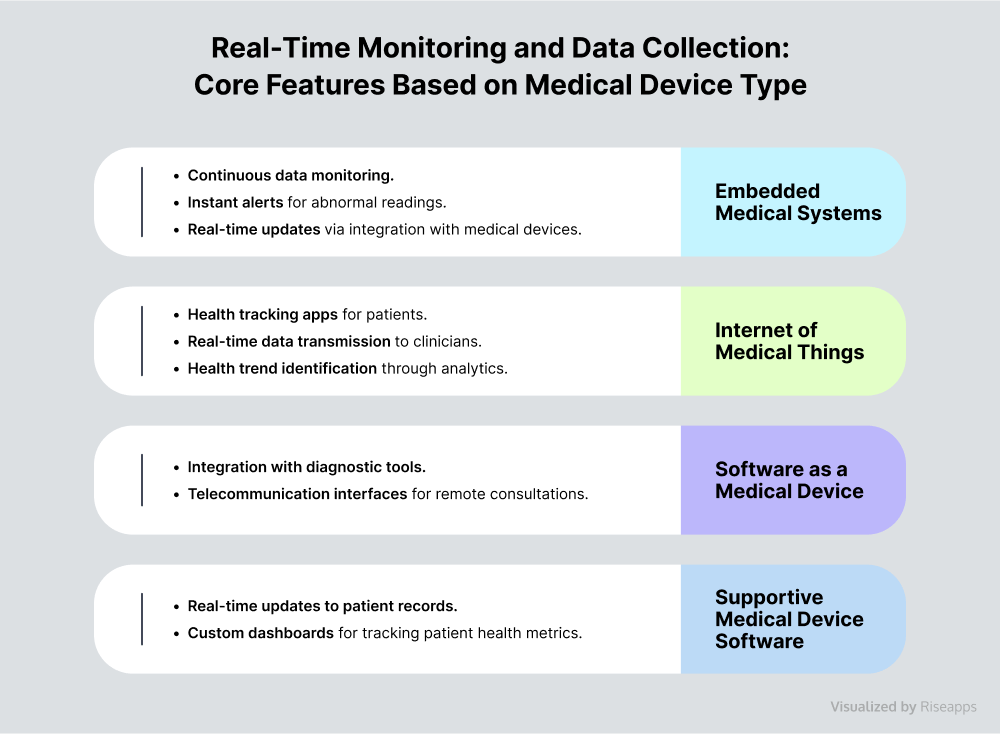
Example:
The monitoring module for the world-class patient care tool, Carehalo, developed by Riseapps.
This functionality allows health practitioners to collect, store, and manage various patient monitoring data, such as blood pressure, temperature, and others. Sophisticated data collection and analysis algorithms assist physicians in delivering efficient and timely chronic disease management care.
Remote Accessibility and Control
Remote accessibility and control capabilities are a must-have for any medical device software.
Be it monitoring the patient’s chronic condition like diabetes or managing critical situations such as cardiac arrhythmias, remote control capabilities in medical device software play a crucial role in allowing immediate intervention. This, in turn, improves operational efficiency and reduces the need for frequent in-person visits and hospital admissions.
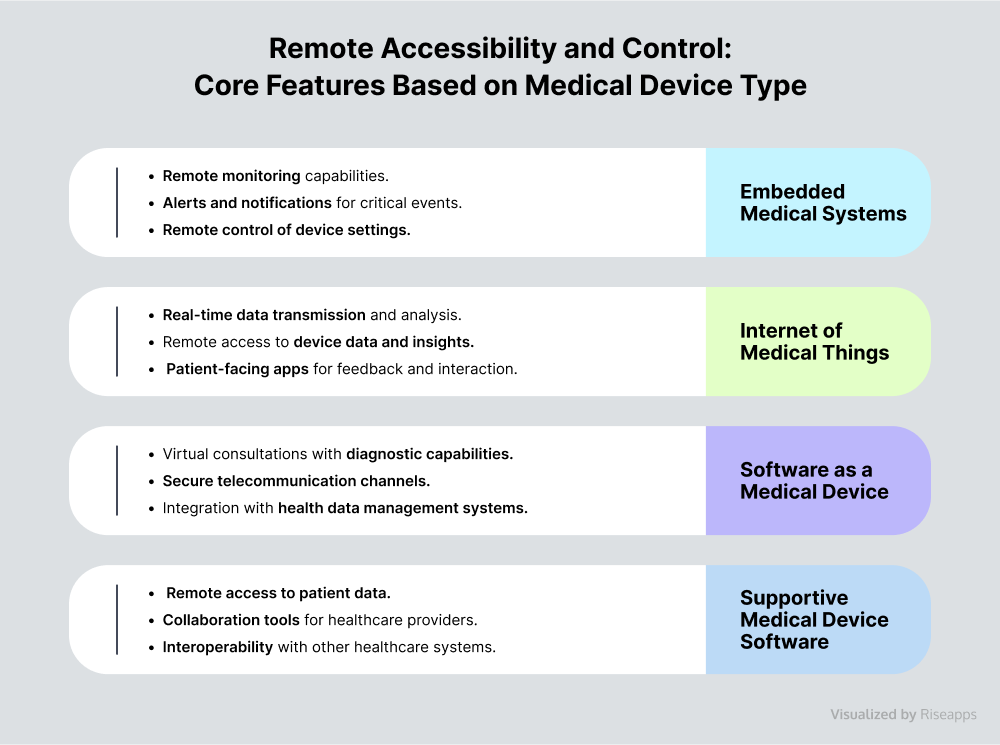
Example:
Remote control for fitness or physical therapy sessions with Fit20.
Riseapps developed an app that reads real-time sensor data from fitness machines and displays the progress. Coaches manage sessions via an iPad app, receiving processed and visualized data to aid client workouts and physical therapy sessions.
Automated Alerts and Notifications
Alerts and notifications are another handy feature of medical device software. Real-time monitoring of patient vital signs and immediate abnormal event notifications enable medical specialists to intervene promptly during medical emergencies, which can be life-saving. Additionally, they facilitate proactive health management by enabling early detection of potential issues.
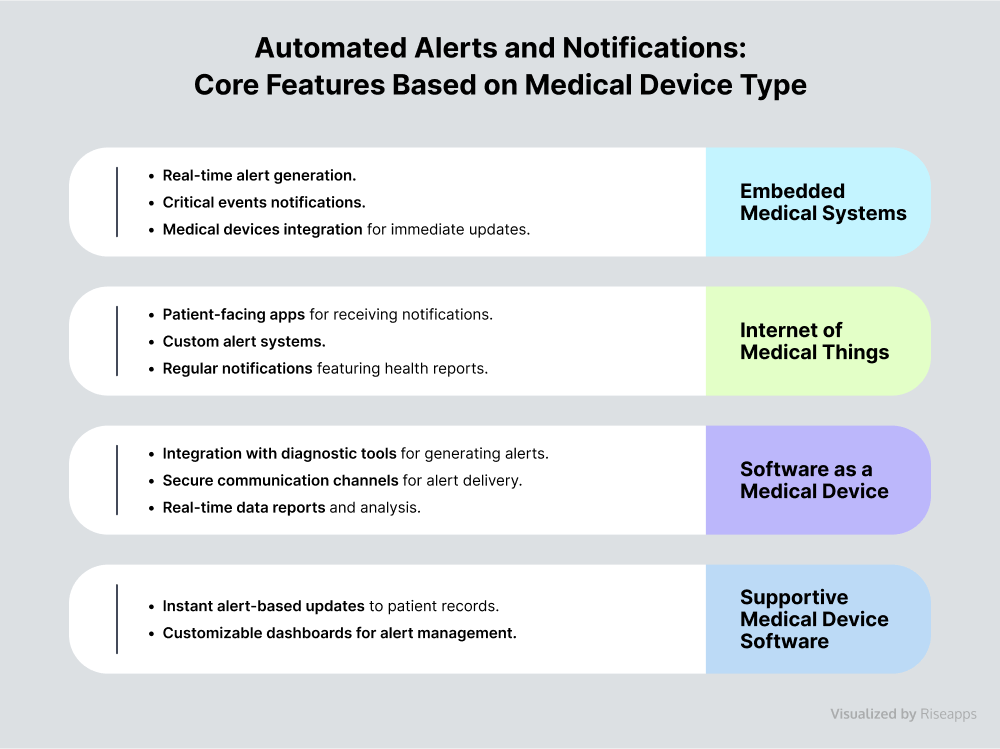
Example:
Daily check-up workflows within a brain health assessment and coaching platform, Amen Clinics.
Riseapps helped the client leverage custom reminders and notifications on interactive mental health check-ins. Thanks to them, Amen Clinics patients are more consistent in marking and tracking daily progress right in the app. Based on the progress data, therapists can adapt coaching plans accordingly.

Clinical Decision Support Tools
Integrating clinical decision support tools as a part of medical device software functionality is an efficient way of leveraging technology to empower clinicians with actionable insights.
Real-time data analysis, proactive alerts, and evidence-based decision-making tools — clinical decision support features encompass these capabilities and many others.
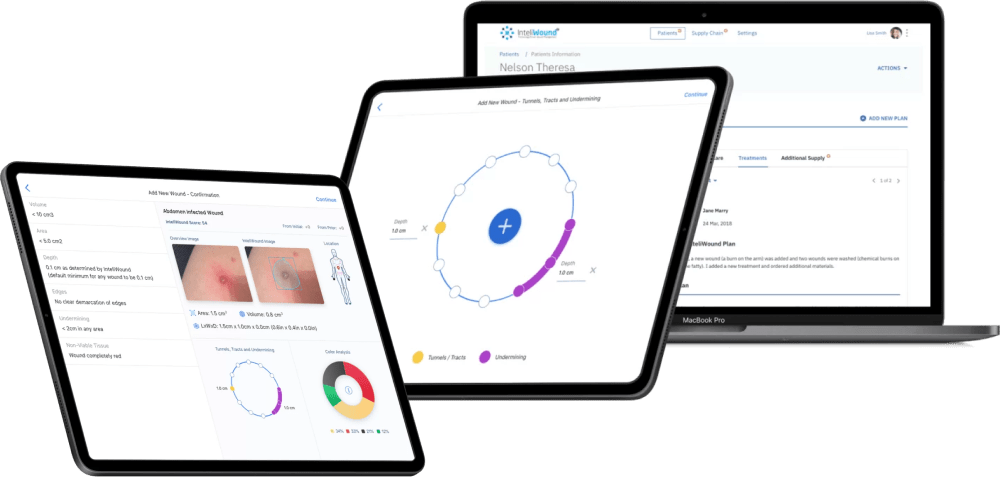
Example:
Value-based treatment suggestions for the wound care delivery tool.
Based on the camera-based technology to scan and analyze wounds, the InteliWound platform designed by Riseapps employs a custom algorithm with a set of treatment instructions, allowing nurses and physicians to follow the provided guidelines or offer their own wound care suggestions.
Patient Engagement Features
Patient engagement features in medical device software empower patients with interactive tools, personalized health education, and remote monitoring capabilities. These functionalities enhance patient involvement, improve adherence to treatment plans, and support better health outcomes through continuous engagement and access to personalized care.
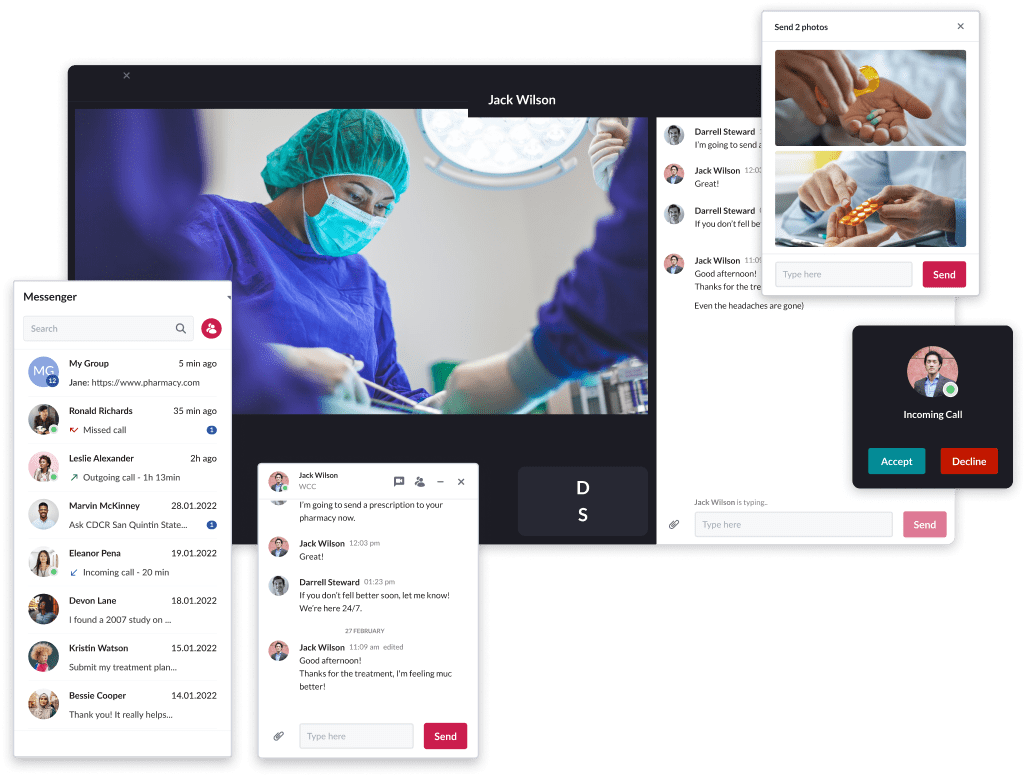
Example:
Patient-centered EHR platform for the accredited provider of Durable Medical Equipment, Prosthetics, Orthotics, and Supplies.
Riseapps designed a feature-rich mobile application with an easy-to-use appointment scheduling interface, support for real-time video calls, peer-to-peer and group-based chatting options, customizable notifications, visualized patient information stats, an interactive map of facilities, and other useful tools.
Mobile Compatibility
Mobile devices can powerfully enhance medical device software. With mobile-first functionalities embedded within medical device software, patients and doctors can easily use their smartphones and tablets to access real-time health insights, streamline engagement, and improve overall care delivery.
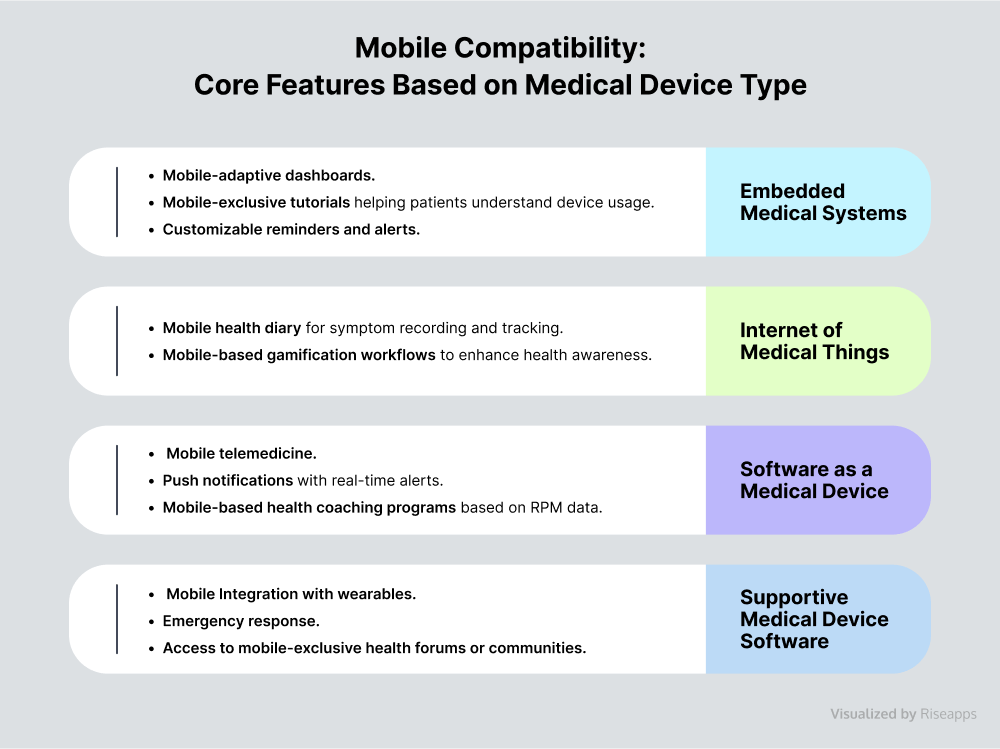
Example:
Fully-featured medical device app development for AI telemedicine platform.
Riseapps developed a HIPAA-compliant cross-platform solution for Black Doctor 24/7 that encompasses intuitive mobile UI/UX design, built-in telemedicine features, and an AI-powered virtual assistant for health self-assessments and symptom checking.
Integration with Cloud Services
Integrating cloud services into medical device software significantly enhances data accessibility, scalability, secure storage, and real-time data sharing.
Dedicated medical devices like portable ultrasound machines, remote monitoring systems, IoMT devices, and health apps can all benefit from devices cloud development and integration.
Example:
Cloud data management and storage for a virtual health clinic.
Riseapps ensured all records collected through the Kego app are stored in designated cloud storage, while providing fast and secure data transfer between the apps and the database. The data is meticulously categorized for easy tracking and management, while patients and doctors can access their appointment history, medical charts, and payment records at any time.
Requirements for Software Development: Medical Devices and SaMD
Developing software for medical devices involves strict adherence to a multitude of industry requirements, spanning from stringent security protocols to rigorous regulatory compliance standards and beyond. Let’s review these medical device software project essentials in more detail.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Medical device software development must adhere to stringent regulatory standards varying by region. Non committing to industry regulations can cause disciplinary measures such as delaying the certification of a product or even a criminal case.
Major action steps include:
- Identify medical device regulation requirements for your specific case.
- Implement compliance strategies for market approval.
- Engage regulatory experts for guidance on complex issues.
Agile Change Management
Agile methodology adapts to change in a timely manner, aligning with the principles of IEC 63004, and facilitates proactive management of software requirements changes, ensuring traceability and control.
In addition, it not only enhances Return on Investment (ROI) but also provides the accelerated delivery of safer and more effective medical device software development solutions.
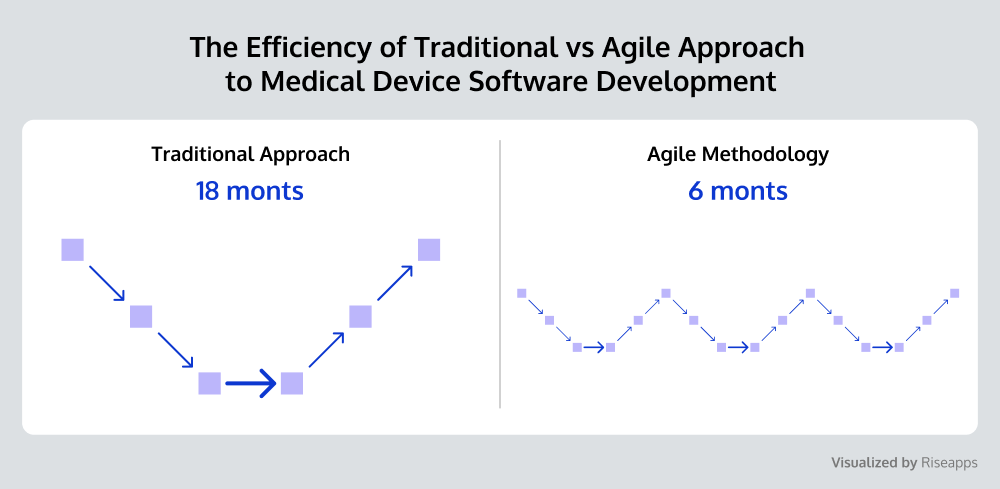
Major action steps include:
- Adopt iterative software development cycles for flexibility.
- Prioritize regulatory compliance in each sprint.
- Foster cross-functional team communication and alignment.
- Leverage the recommendations and guidelines outlined in TIR 44.
Security and Privacy
The protection of patients’ sensitive information from breaches or unauthorized disclosure is necessary to keep patients’ trust and comply with the law in the case of wrongful termination.
Therefore, developers must take a proactive approach in deploying strategies to effectively support sensitive medical data traffic and protect data integrity and confidentiality.
Major action steps include:
- Implement strong encryption (e.g., AES) and access controls.
- Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments.
- Stay updated with evolving Data Protection Act updates and other privacy laws.
Reliability and Accuracy
Since medical device software plays a critical role in diagnosis, patient monitoring, and treatment delivery, it must be exceptionally reliable and accurate. To ensure these high standards, developers must undertake rigorous testing and validation processes.
Major action steps include:
- Conduct thorough unit, integration, and acceptance testing.
- Establish robust quality assurance processes (ISO 13485).
- Validate software performance in diverse clinical settings.
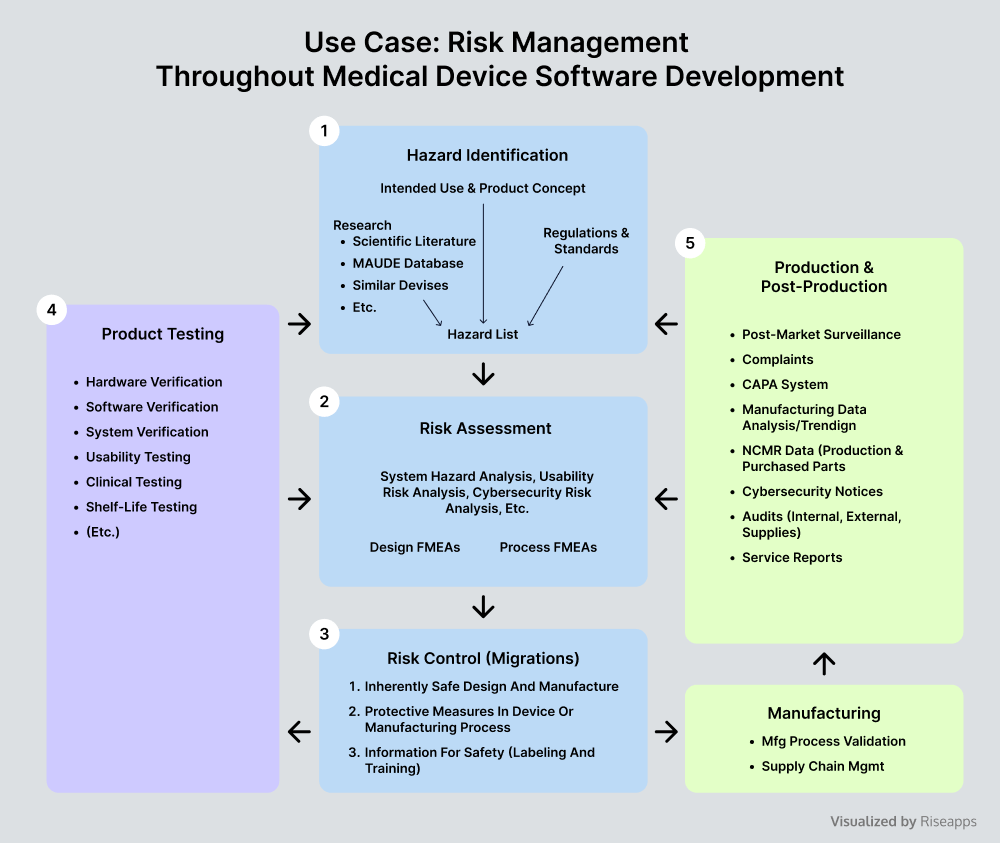
Risk Assessment
Thorough risk assessments in medical device software development involve identifying hazards and assessing their potential impact in clinical settings. Thanks to such software safety classification and risk prioritization, software developers are able to implement targeted mitigation strategies, including design controls, rigorous process validation, comprehensive documentation, and others.
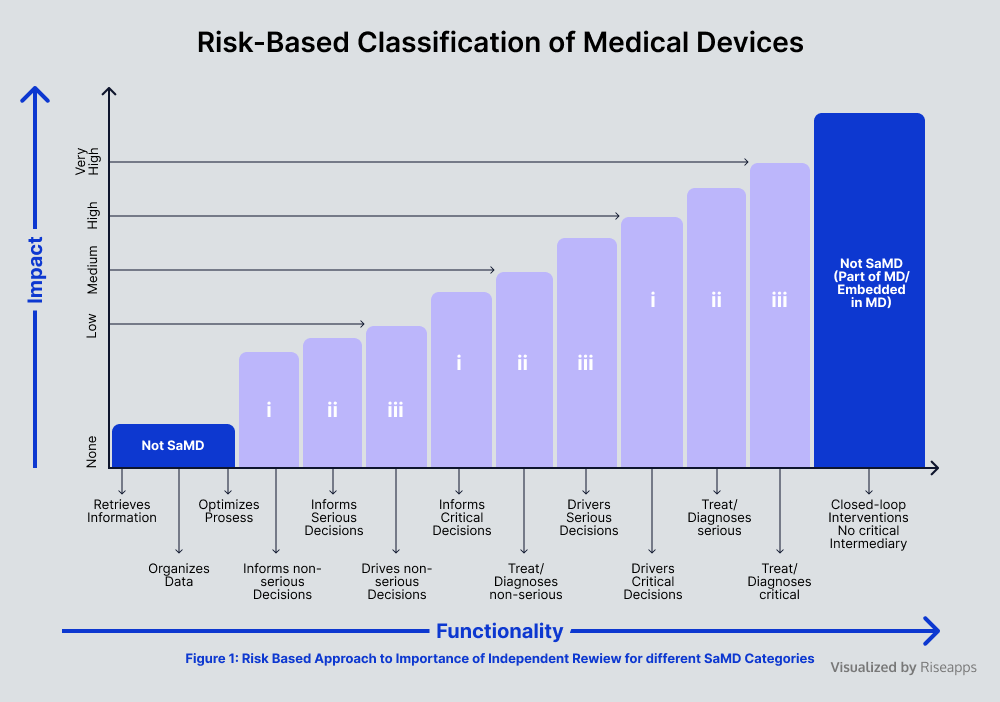
Major action steps include:
- Identify and prioritize risks based on severity.
- Implement targeted mitigation strategies based on software safety classification.
- Monitor risks associated with medical devices throughout the software life cycle.
Risk Management
By integrating a software risk management process and best practices into every phase of software development, medical device software developers ensure that software meets stringent software safety standards and compliance, including ISO 14971 for health risks management, ISO 64304 and IEC 1385 for quality system implementation, and IEC 62914, to name a few.
Major action steps include:
- Consider various hazards, from medical software failure to data breaches.
- Ensure efficient problem resolution process and mitigation strategies.
- Communicate risks clearly to stakeholders.
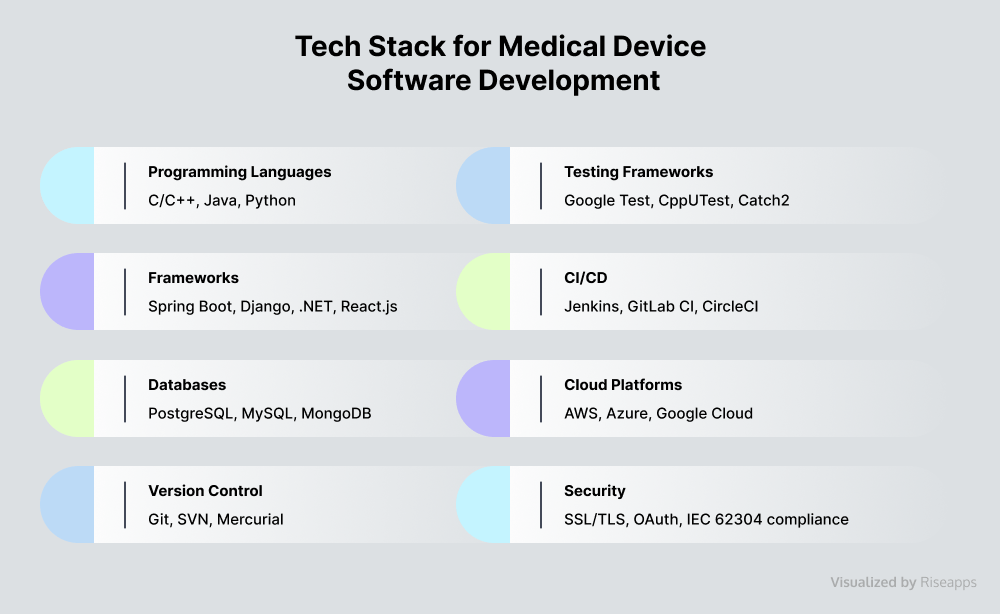
Well-Suited Tech Stack
Choosing the right tech stack involves balancing technical capabilities with a range of project-specific and industry requirements.
Major action steps include:
- Select embedded coding languages prioritizing interoperability, safety, and compliance.
- Ensure scalability and seamless integration capabilities.
- Verify security measures and regulatory compliance.
Interoperability
Medical device software cannot be isolated from other healthcare software systems.
To facilitate real-time data exchange, enhance care coordination, and support comprehensive patient management, such solutions require integration with multiple systems. See the landscape of important integrations in the table below.
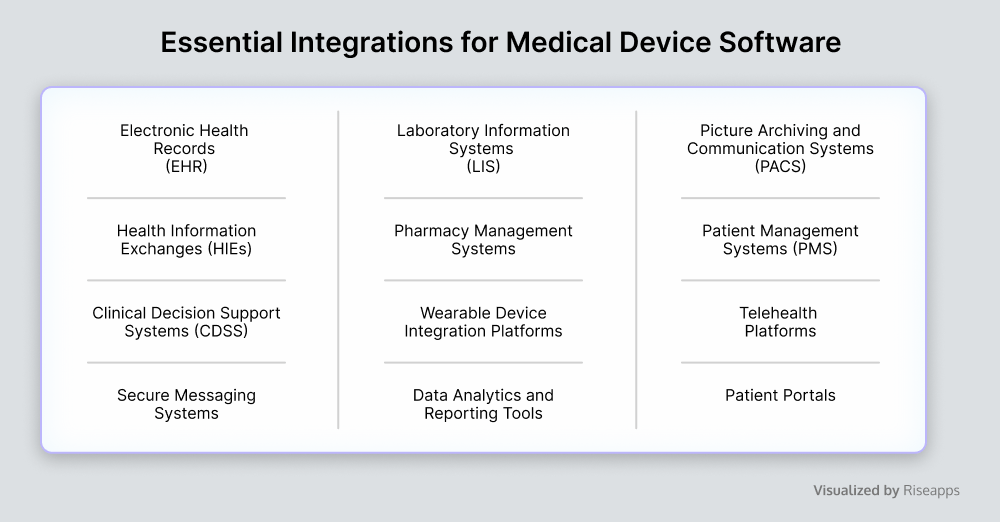
Interactions between medical devices and systems necessitate strict adherence to standards for accurate information exchange. Medical devices often communicate using different protocols and data formats such as HL7, DICOM, and MDCC. If not addressed properly, this leads to unsupported software systems and compatibility issues.
Major action steps include:
- Standardize communication protocols.
- Conduct rigorous interoperability testing across systems.
- Adhere to regulatory guidelines to ensure patient safety.
Medical Device Software Development Process: From Specification to Support
The development of medical device software is a complex, multi-phase process. Ensure its success by following a thorough software development path.
Define Your Specifications
In the initial phase, software requirements are meticulously defined by gathering detailed input from stakeholders including healthcare professionals, regulatory bodies, and patients.
In addition, a thorough user needs analysis is conducted to understand clinical and operational requirements. Relevant regulatory standards, such as FDA guidelines, ISO 13485, and others, should also be identified at this stage.
Design Your Blueprint
This medical device software development stage includes designing the overall system architecture, encompassing hardware interfaces, data flow, and security measures.
Detailed designs are developed for each software component, specifying algorithms, data structures, and interaction flows for intuitive user interfaces. Throughout this phase, rigorous risk management practices are applied, too.
Develop the Device Software
The implementation stage includes writing clean, efficient code that adheres to industry best practices and regulatory standards.
To develop early-stage versions of the software, prototyping is used, allowing for the key functionality testing and gathering feedback from stakeholders. Various software modules are also integrated during this phase for efficient data exchange and control.
Verify and Validate
This step is essential for identifying and correcting any issues or discrepancies early in the software development lifecycle.
Code reviews, static analysis, and unit testing are performed to ensure the software conforms to the design specifications and coding standards. The software should also be tested in real-world scenarios to confirm that it meets user needs, operates safely, and performs effectively within its intended environment.
Secure Regulatory Approval
At this phase, comprehensive documentation should be prepared, including technical files, design history files, and risk management reports. Submitting this documentation to regulatory bodies, such as the FDA or EMA, initiates the review and approval process. Meanwhile, compliance testing is performed to validate that the software meets essential regulatory requirements.
Deploy Your Software
Once regulatory approval is obtained, the software is prepared for deployment in healthcare settings.
This includes ensuring proper software installation and configuration on medical devices and healthcare systems, migrating data from legacy systems to the new software, and ensuring a smooth transition and minimal disruption to operations supported with user training sessions.
Ensure Ongoing Support
The project does not end with the software deployment. Regular maintenance activities and incident management activities are conducted to address issues, enhance performance, and ensure ongoing compliance with evolving regulatory standards.
Risks To Avoid During the Medical Device Software Development Process
Conflicting Requirements
Conflicting requirements from different stakeholders, such as healthcare providers, regulatory agencies, medical device manufacturers, and patients, can create significant prioritization challenges in medical device software development.
💡 How to avoid: Analyze and prioritize requirements based on their importance, feasibility, and impact on the project.
Insufficient Documentation
In this highly regulated field, precise and clear documentation is critical. Without a comprehensive Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) outlining all software components, libraries, and dependencies, project risks and challenges multiply significantly.
💡 How to avoid: Establish clear documentation standards and document all requirements clearly and unambiguously in the SRS document.
Requirements Validation
Lack of stakeholder availability or engagement during validation can result in unvalidated requirements. This oversight could lead to undetected defects or usability issues that pose risks to patient health, necessitating costly and time-consuming rework.
💡 How to avoid: Set up validation protocols and clearly define stakeholder roles and responsibilities early in the project.
Poor UI/UX Design
Inefficient UI design can impede healthcare professionals’ ability to navigate critical features swiftly, impacting workflow efficiency and potentially delaying timely patient care.
💡 How to avoid: Implement user-centered design practices and conduct usability testing with real users.
Integration Issues
Improperly integrated health tech solutions may hinder the software’s ability to communicate effectively with medical devices, affecting the real-time monitoring of patient conditions or the accurate delivery of therapeutic interventions.
💡 How to avoid: Use standardized protocols and conduct thorough integration testing to ensure compatibility.
Neglecting Compliance Testing
Failure to adequately test for regulatory compliance can result in non-compliance issues, along with potential rejections and fines from regulatory bodies.
💡 How to avoid: Involve regulatory experts in the testing phase and conduct thorough compliance testing based on relevant standards and guidelines.
Software Obsolescence
In the rapidly evolving medical device software development, outdated software may lack essential operational efficiency or fail to meet evolving regulatory standards, potentially resulting in vulnerabilities that compromise patient data privacy or expose systems to cyber threats.
💡 How to avoid: Establish a proactive software maintenance plan that includes regular updates and ongoing monitoring of technological advancements.
Tailored Delivery Process: Medical Device Software Development Services
To mitigate risks and optimize the efficiency of medical device software, it’s beneficial to consider a tailored project delivery from a robust healthcare software development partner. Such a partner can navigate various development service options and help identify the best fit for your business.
As a seasoned expert and a leading provider of medical device software development services, Riseapps has a proven track record of delivering custom medical device software while working with startups, SMEs, and enterprise-level vendors, including Fortune 500 companies. Find out how you can benefit from this expertise.
Project Discovery

The Project Discovery service by Riseapps is designed for those healthcare organizations who aim to conceptualize their project idea, align all stakeholders, ensure regulatory compliance, and create a comprehensive plan that guides the custom medical device software development process.
Through analysis and feasibility studies, we conduct comprehensive research, planning, and analysis to define the project scope, requirements, and objectives, along with establishing a clear project roadmap that meets regulatory guidelines and client expectations.
AI R&D and Prototyping
Depending on specific business needs, AI can profoundly impact medical devices and health tech ecosystems overall. At Riseapps, our focus is on exploring AI algorithms and conducting prototyping to enhance the capabilities of custom medical device software with the latest advancements in medical technology.
Proof of Concept for Medical Device Software
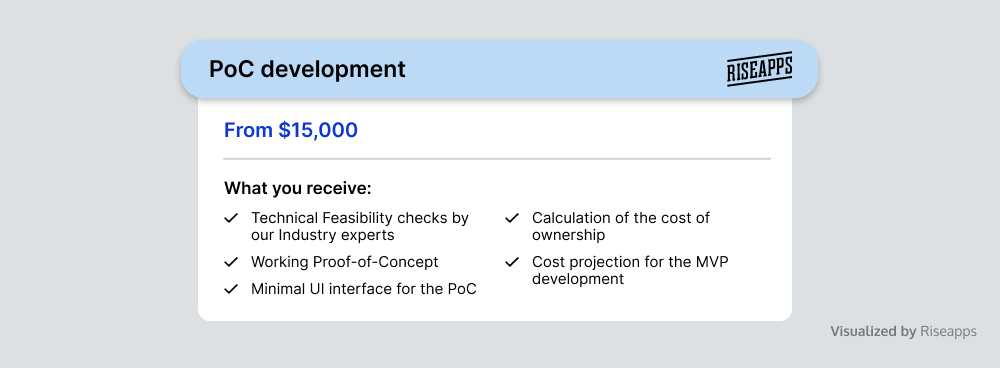
Riseapps’ Proof of Concept service is crucial for those who seek to validate the feasibility and potential of medical device software before committing to full-scale software development.
At this stage, we develop and test a working prototype, gather stakeholder feedback, and identify potential risks associated with the software release. By validating the concept, refining requirements, and addressing potential challenges early on, we ensure that the subsequent software development phases are built on a solid, well-tested base.
MVP Development

A custom MVP medical device software development allows for early validation of concepts, minimizes development risks, and accelerates time to market. Rigorous testing, regulatory compliance checks, and user feedback are essential elements here.
Fully-Fledged SaMD Solution

For healthcare providers who aim to deploy a mature, fully-fledged Software as a Medical Device solution, Riseapps offers to bring in a team of experts who will refine the MVP version or a legacy system, perfecting it based on user insights, market trends, and regulatory standards.
The focus here is on adding extensive features that not only expand the software’s capabilities but also solidify its position as a reliable, innovative solution in the competitive landscape of medical device software development. As a result, you get a robust, highly secure, and fully functional medical device software solution ready for large-scale deployment.
Real-Life Cases: Software Development for Medical Devices
Next-Level Diagnostic Imaging
A solution provider for medical aesthetics and med spas approached Riseapps to revitalize the cutting-edge medical imagery solution, RxPhoto.
Major Challenge: The need to improve operability, enhance robustness, and create a roadmap for the solution improvement.
In order to enhance the existing app-based diagnostic imaging process, Riseaaps identified a range of improvement areas, from minor bug fixes to restructuring the app’s architecture and migration to a more robust programming language.
As a result of 2 years of cooperation and continuous improvement, RxPhoto has become a top-notch tool that helps clinicians increase their consultation conversion rates and maintain high client retention.
3D Wound Scanning Solution
InteliWound, a US-based health tech company, collaborated with Riseapps to create a SaMD solution — a comprehensive wound management platform with integrated 3D wound scanning capabilities.
Major Challenge: The high cost and complexity of traditional wound care delivery methods, which are further compounded by clinical personnel shortages, inadequate oversight, and complex healthcare regulations.
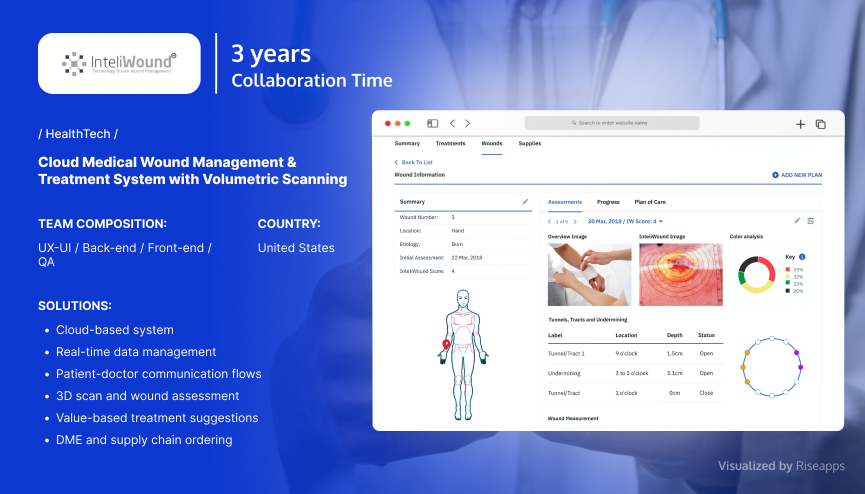
To accelerate and optimize wound care delivery practices, Riseapps created a HIPAA-compliant technical solution that provides a volumetric measurement of wounds via advanced camera technology within seconds.
As a result, the solution enabled thousands of patients to access efficient wound care, with the client reporting immediate financial returns, improved outcomes, and accelerated operational workflows.
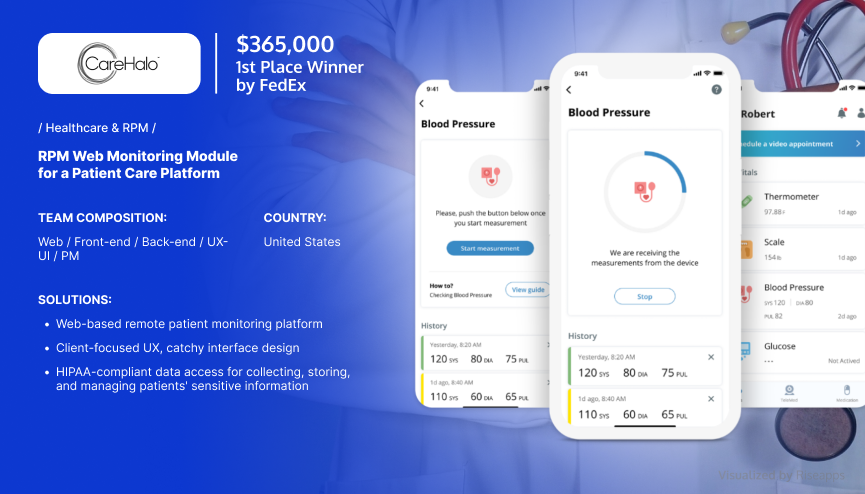
Remote Patient Monitoring Tool
CareHalo, a leading SaaS healthcare software solutions provider, sought a reliable partner to create a fully-fledged remote patient monitoring tool.
Major Challenge: Develop comprehensive, multifunctional software with steady workflows that enable doctors and nurses to manage multiple cases.
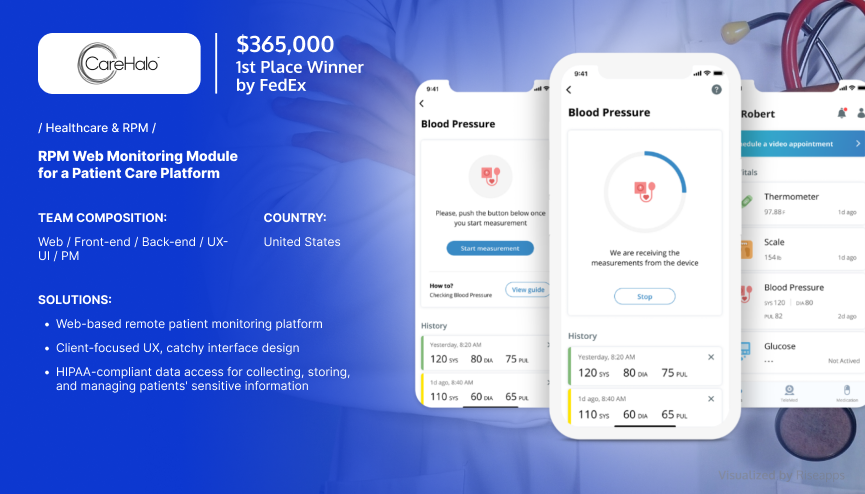
Having tackled the client’s existing issues, Riseapps led a medical device app development project, building a complex web app for a chronic disease management platform. The solution allows health practitioners to collect, store, and manage various patients’ monitoring data, including blood, pressure, temperature, and many other vital signs.
As a result, the data collected and managed within the app was used to predict and prevent events that would otherwise require medical intervention. This enabled CareHalo to optimize care delivery while cutting costs and increasing profits.
FAQ
What is medical device software development?
The medical device software development process involves designing, creating, testing, and maintaining software specifically intended for use in a medical device. This process ensures that the software meets stringent safety, efficacy, and regulatory standards to support various medical operations, such as diagnostics, monitoring, treatment, or data management.
What is medical software development?
Medical software development refers to the process of creating software applications used in the healthcare industry to support various medical functions, such as diagnostics, treatment planning, patient management, and medical research.
What is the difference between software as a medical device and medical device software?
Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) refers to standalone software intended to perform without being part of a hardware device, such as a diagnostic app on a smartphone. Medical device software, on the other hand, includes any software that is part of a medical device's functionality, whether embedded within the medical equipment or working in conjunction with it.
What is an example of software as a medical device?
An example of software as a medical device (SaMD) is a mobile app that uses algorithms to analyze data from a wearable heart monitor to detect irregular heart rhythms and alert patients or medical professionals in real-time. This software operates independently of any specific hardware medical device.
What are the 5 phases of medical device development?
Medical device development encompasses the following five stages:
- Step 1 – Concept and Feasibility: this involves defining the medical device concept, assessing feasibility, and conducting initial research on functionality and market potential.
- Step 2 – Design and Software Development: the creation of detailed designs and prototypes, refining the software, and ensuring all components work together.
- Step 3 – Verification and Validation: extensive testing to verify design specifications and validate the medical device's effectiveness and patient safety.
- Step 4 – Regulatory Approval: compiling necessary documentation to seek healthcare solutions approval from authorities like the FDA or EMA.
- Step 5 – Production: collaborate with medical device manufacturers to bring custom medical systems and equipment to market.
- Step 6 – Post-Market Surveillance: perform ongoing surveillance of healthcare devices and other medical systems.
What are the different types of medical device software?
Different types of medical device software include embedded medical systems, Software as a Medical Device (SaMD), health information systems (HIS), diagnostic health software, therapeutic software and mobile apps, and other medical devices. Each of these healthcare devices serves unique functions such as managing medical device operations, providing diagnostic support, and facilitating treatment.
Is QMS necessary for SaMD?
Healthcare regulatory frameworks often mandate developing medical device software under a licensed Quality Management System (QMS). A certified QMS is crucial for evaluating liability, incident identification, and ensuring product reliability and safety throughout medical device app development stages. Without QMS certification of integrated health tech solutions, selling medical equipment or software products will not be possible.
Contact Us






